High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), thin-layer chromatography (TLC) and capillary electrophoresis have been used for the separation and detection of oligosaccharides released from glycosphingolipids (GSLs). Since intact oligosaccharides exhibit no effective absorption in the UV-Vis region, chemical derivatization of oligosaccharides with 2-aminopyridine (AP), 2-aminobenzamide (AB), 2-aminobenzoic acid (AA), or 4-aminobenzoic ethyl ester (4-ABEE) is frequently used to confer fluorescence or UV-absorption to oligosaccharides for detection1). However, chemical derivatization is somewhat time-consuming and requires purification which may lead to a loss of samples. In this section, the enzymatic derivatization of glycolipid-derived oligosaccharides using a specific enzyme is described.
6-Gala series GSLs possessing R-Gal (α/β)1-6Galβ1-1’Cer have been found in some mollusks, pathogenic parasites and fungi, but their physiological functions and metabolic pathways are not fully understood. In this section, we describe a new method to detect 6-gala series GSLs utilizing the specificity of a novel enzyme, EGALC, which is capable of hydrolyzing 6-gala series GSLs to produce intact oligosaccharides and ceramides2). EGALC catalyzes not only hydrolysis but also transglycosylation reaction3). In the latter reaction, EGALC transfers oligosaccharides from the GSLs to acceptors such as fluorescent 1-alkanols. Utilizing the transglycosylation reaction of EGALC, a specific, easy, fast, sensitive and reproducible method of detecting 6-gala series GSLs was developed using NBD-pentanol as an acceptor4). The fluorescent products (NBD-pentanol-conjugated 6-gala oligosaccharides) were separated and detected by TLC or HPLC with a fluorescent detector. Moreover, not only GSLs but also glycoglycerolipids having the R-Gal(α/β)1-6Galβ1-1’diacylglycerol structure such as digalactosyldiacylglycerol (DGDG) can be detected by this method. This method was successfully applied to the detection of 6-gala series GSLs in a fungus (Rhizopus oryzae) and parasite (Taenia crassiceps). The method would be useful for the study of glycolipids which share the R-Gal (α/β)1-6Gal structure5). |
| Category | Glycolipids and related compounds |
| Protocol Name | Fluorescent labeling of 6-gala (neogala) series glycosphingolipids by EGALC |
Authors
 |
Ishibashi, Yohei
*
Department of Bioscience and Biotechnology, Graduate School of Bioresource and Bioenvironmental Sciences, Kyushu University
Ito, Makoto
Department of Bioscience and Biotechnology, Graduate School of Bioresource and Bioenvironmental Sciences, Kyushu University
*To whom correspondence should be addressed.
|
| KeyWords |
|
Reagents
 |
| ● |
Total lipids are prepared by the method described in the section "Extraction of glycolipids" |
| ● |
5-Amino-1-pentanol (Tokyo Chemical Industry Co., Ltd., Tokyo, Japan) |
| ● |
4-Fluoro-7nitoro-2,1,3-benzoxadiazole (NBD-F) (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO) |
| ● |
Pre-coated Silica gel 60 TLC plates (Merck Millipore, Billerica, MA) |
| ● |
0.5 M Sodium acetate buffer, pH 5.5 |
| ● |
HPLC grade acetonitrile (Kanto Chemical Co., Ltd.) |
| ● |
Chloroform (Nacalai Tesque, Inc., Kyoto, Japan) |
| ● |
Methanol (Nacalai Tesque, Inc.) |
| ● |
|
|
Instruments
 |
| ● |
Sep-Pak silica cartridge (Waters Corporation, Milford, MA) |
| ● |
HPLC with fluorescent detector |
| ● |
Asahipak NH2P 50-4E, 4.6 × 250 mm (Showa Denko K. K., Tokyo, Japan) |
| ● |
AE-6935B Visirays (Atto Corp., Tokyo, Japan) |
| ● |
Shimadzu CS-9300 TLC chromatoscanner with the fluorescent detector (Shimadzu Corp., Kyoto, Japan) |
| ● |
|
| ● |
|
|
| Methods |
|
1. |
Preparation of NBD-pentanol |
| 1) |
Mix 25 μmol of NBD-F and 25 μmol of 5-amino-1-pentanol. Incubate at 60°C for 1 min. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 2) |
Dry the mixture with a speed vac concentrator, dissolve in 2 mL of chloroform, and apply to a Sep-Pak silica cartridge equilibrated with chloroform. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 3) |
Elute NBD-pentanol from the cartridge with chloroform/methanol (9/1, v/v). Dry the eluent with a speed vac concentrator, and dissolve it in ethanol. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 4) |
Check the quality and quantity of purified NBD-pentanol by TLC with AE-6935B Visirays and with ninhydrin reagent to detect unreacted 5-amino-1-pentanol. |
Comment 0
|
|
|
|
2. |
Transglycosylation reaction |
| 1) |
Prepare 10 μL of a reaction mixture containing an appropriate amount of total lipid (>400 ng), 20 nmol of NBD-pentanol, and 10 μU of EGALC in 50 mM sodium acetate buffer, pH 5.5, and incubate at 37°C for 2 h. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 2) |
Add 80 μL of chloroform/methanol (2/1, v/v) and 10 μL of water. After vortexing for a few seconds, centrifuge at max speed for 3 min. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 3) |
Collect the upper phase containing NBD-pentanol-conjugated oligosaccharides, add chloroform/methanol/water (86/14/1, v/v/v), and centrifuge at max speed for 3 min. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 4) |
Collect the upper phase, and dry it with a speed vac concentrator. TLC or HPLC is available to detect the transglycosylation products. |
Comment 0
|
|
|
|
3. |
TLC analysis of transglycosylation products |
| 1) |
Dissolve a dried sample in 10 μL of methanol, and apply it to a TLC plate. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 2) |
Develop the TLC plate with chloroform/methanol/0.02% CaCl2 (5/4/1, v/v/v) for 30 min. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 3) |
Visualize transglycosylation products by AE-6935B Visirays or UV transiluminator. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 4) |
Quantify products with a Shimadzu CS-9300 TLC chromatoscanner with the fluorescent detector (excitation 475 nm). |
Comment 0
|
|
|
|
4. |
HPLC analysis of transglycosylation products |
| 1) |
Set excitation and emission wavelengths of the fluorescent detector to 470 and 530 nm, respectively. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 2) |
Dissolve a dried sample in 120 μL of acetonitrile/water (9/1, v/v), and centrifuge at max speed for 5 min. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 3) |
Apply 100 μL of the supernatant to Asahipak NH2P 50-4E equilibrated with solvent A (acetonitrile/water (9/1, v/v)). HPLC gradient conditions; 0% solvent B (acetonitrile/water (1/1, v/v)) to 100% B in 25 min at a flow rate of 1.0 mL/min. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 4) |
Before performing the next run, equilibrate the column with 100% solvent A for 10 min. |
Comment 0
|
|
|
| Notes | This method using EGALC can be applied to glycolipids having the R-Gal(α/β)1-6Galβ1-1ceramide/diacylglycerol structure but not other GSLs such as ganglio-series, globo-series, and lacto-series GSLs.
An excess amount of NBD-pentanol in the reaction could be removed by Folch's partition, by which NBD-pentanol and fluorescent oligosaccharides were moved to organic and aqueous phases, respectively. Then, the aqueous phase was withdrawn and used for further analysis.
The limit of detection (LOD) of TLC was approximately 1.5 pmol (S/N=3) while that of HPLC was 50 fmol (S/N=5). The detection of the labeled oligosaccharides was linear from 4 pmol to 60 pmol for TLC, and from 250 fmol to 60 pmol for HPLC. |
| Figure & Legends |
Figure & Legends 
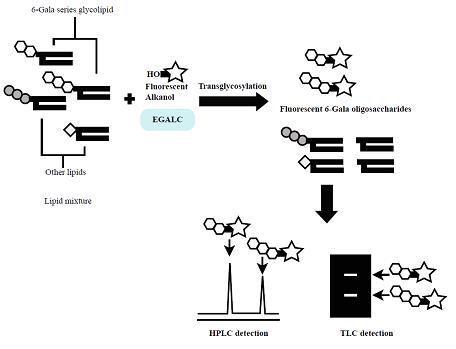
Fig. 1. The scheme of transglycosylation-based fluorescent labeling of 6-gala series GSLs by EGALC.
This figure was originally published in Glycobiology. 19(7):797–807. 2009 "Transglycosylation-based fluorescent labeling of 6-gala series glycolipids by endogalactosylceramidase" Ishibashi Y. Ito M. et al. Oxford University Press.

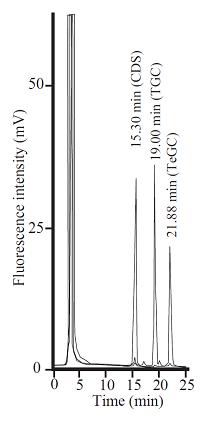
Fig. 2. Separation of NBD-pentanol-conjugated oligosaccharides generated from CDS (Ceramide disaccharide), TGC (Trigalactosylceramide) and TeGC (Tetragalactosylceramide) on an amino column (NH2P 50-4E).
This figure was originally published in Glycobiology. 19(7):797–807. 2009 "Transglycosylation-based fluorescent labeling of 6-gala series glycolipids by endogalactosylceramidase" Ishibashi Y. Ito M. et al. Oxford University Press.
|
| Copyrights |
 Attribution-Non-Commercial Share Alike Attribution-Non-Commercial Share Alike
This work is released underCreative Commons licenses
|
| Date of registration:2016-01-13 16:45:00 |
- Pabst., M., Kolarich, D., Poltl, G., Dalik T., Lubec, G., Hofinger, A., and Altmann, F. (2009) Comparison of fluorescent labels for oligosaccharides and introduction of a new postlabeling purification method. Analytical Biochemistry 384, 263–273 [PMID : 18940176]
- Ishibashi, Y., Nakasone, T., Kiyohara, M., Horibata, Y., Sakaguchi, K., Hijikata, A., Ichinose, S., Omori, A., Yasui, Y. Imamura, A., Ishida, H., Kiso, M., Okino, N., and Ito, M. (2007) A novel endoglycoceramidase hydrolyzes oligogalactosylceramides to produce galactooligosaccharides and ceramides. Journal of Biological Chemistry 282, 11386–11396 [PMID : 17244618]
- Ishibashi, Y., Kiyohara, M., Okino, N., and Ito, M. (2007) Synthesis of fluorescent glycosphingolipids and neoglycoconjugates which contain 6-gala oligosaccharides using the transglycosylation reaction of a novel endoglycoceramidase (EGALC). Journal of Biochemistry 142, 239–246 [PMID : 17567653]
- Ishibashi, Y., Nagamatsu, Y., Meyer, S., Imamura, A., Ishida, H., Kiso, M., Okino. N., Geyer, R., and Ito, M. (2009) Transglycosylation-based fluorescent labeling of 6-gala series glycolipids by endogalactosylceramidase. Glycobiology 19, 797–807 [PMID : 19389917]
- Ishibashi, Y., Nagamatsu, Y., Miyamoto, T., Matsunaga, N., Okino, N., Yamaguchi, K., and Ito, M. (2014) A novel ether-linked phytol-containing digalactosylglycerolipid in the marine green alga, Ulva pertusa. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 452, 873–880. [PMID : 25157808]
|
This work is licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-Non-Commercial Share Alike. Please include the following citation
How to Cite this Work in an article:
Ishibashi, Yohei,
Ito, Makoto,
(2016). GlycoPOD https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD.
Web.7,4,2025 .
How to Cite this Work in Website:
Ishibashi, Yohei,
Ito, Makoto,
(2016).
Fluorescent labeling of 6-gala (neogala) series glycosphingolipids by EGALC.
Retrieved 7,4,2025 ,
from https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD/protocolShow.action?nodeId=t78.
html source
Ishibashi, Yohei,
Ito, Makoto,
(2016).
<b>Fluorescent labeling of 6-gala (neogala) series glycosphingolipids by EGALC</b>.
Retrieved 4 7,2025 ,
from <a href="https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD/protocolShow.action?nodeId=t78" target="_blank">https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD/protocolShow.action?nodeId=t78</a>.
Including references that appeared in the References tab in your work is
much appreciated.
For those who wish to reuse the figures/tables, please contact JCGGDB
management office (jcggdb-ml@aist.go.jp).
|
|