Mannan-binding protein (MBP), also called mannose-binding protein (MBP) or mannan-binding lectin (MBL), is a Ca2+-dependent (C-type) mammalian lectin specific for mannose, N-acetylglucosamine and fucose. MBP activates complement through the lectin pathway, and is an important serum component associated with innate immunity (Kawasaki T. 1999). MBP also binds to human colorectal carcinoma cells.
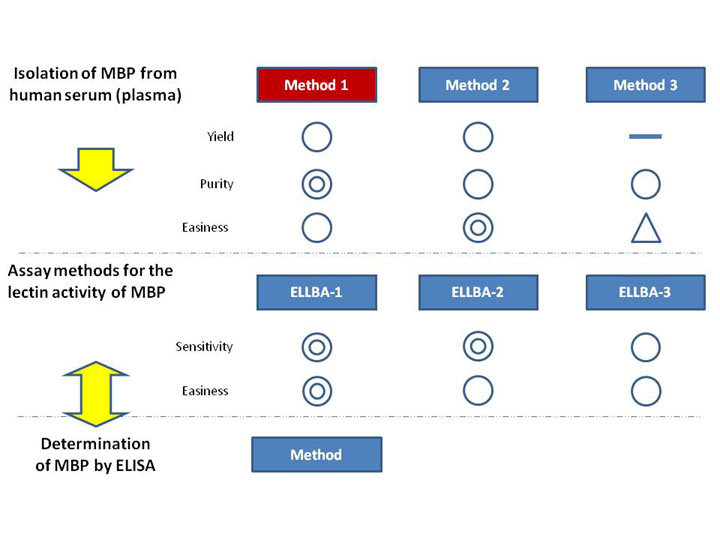
This chart shows the relation between a family of mannan-binding protein (MBP)-associated protocols.
- The methods for the isolation of MBP
Isolation of mannan-binding protein from human serum (plasma) ~Method 1
Isolation of mannan-binding protein from human serum (plasma) ~Method 2
Isolation of mannan-binding protein from human serum (plasma) ~Method 3
- The methods for the estimation of the lectin activity of the purified MBP
Assay method for the lectin activity of mannan-binding protein ~ELLBA-1*
Assay method for the lectin activity of mannan-binding protein ~ELLBA-2
Assay method for the lectin activity of mannan-binding protein ~ELLBA-3
*PV-Man used in ELLBA-1 is not commercially available at present.
- The method for MBP protein determination
Determination of mannan-binding protein by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assaying (ELISA)
This method can be used for the estimation of the MBP content not only in the purified samples
but also in the crude samples like human serum or plasma.
Characteristics of each method were evaluated in a 3-point scale (see below).
|
| Category | Sugar binding proteins |
| Protocol Name | Isolation of mannan-binding protein from human serum (plasma) ~Method 1 |
Authors
 |
Kawasaki, Nobuko
Research Center for Glycobiotechnology, Ritsumeikan University
|
| KeyWords |
|
Reagents
 |
| ● |
Pooled human plasma from healthy donors |
| ● |
|
| ● |
Mannan-agarose (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO) |
| ● |
Heparin-agarose (AF–Heparin HC- 650M: Tosoh Corp., Tokyo, Japan) |
| ● |
Loading buffer for mannan-agarose affinity column chromatography: 10 mM imidazole-HCl buffer, pH 7.8, 1 M NaCl, 20 mM CaCl2 *1 |
| ● |
Elution buffer for mannan-agarose affinity column chromatography: 10 mM imidazole-HCl buffer, pH 7.8, 1 M NaCl, 5 mM EDTA *2 |
| ● |
Loading buffer for heparin-agarose affinity column chromatography: 20 mM phosphate buffer, pH 7.0, 1 mM EDTA *3 |
| ● |
Washing buffer for heparin-agarose affinity column chromatography: 20 mM phosphate buffer, pH 7.0, 0.1 M NaCl, 1 mM EDTA *4 |
| ● |
Elution buffer for heparin-agarose affinity column chromatography: 20 mM phosphate buffer, pH 7.0, 0.2 M NaCl, 1 mM EDTA *5 |
| ● |
10% and 4% polyacrylamide gels, for SDS-PAGE under reducing and non-reducing conditions, respectively, or a 5–20% gradient polyacrylamide gel (Laemmli method) |
|
Instruments
 |
| ● |
|
| ● |
Columns for open column chromatography |
| ● |
Ultrafiltration membrane filter (cut-off, 10 kDa) equipped with a centrifugal unit |
| ● |
0.22 μm membrane filter (Merck Millipore, Billerica, MA) |
|
| Methods |
|
1. |
Isolation of mannan-binding protein from human serum (plasma) ~Method 1 |
| 1) |
Prepare 1 L pooled human plasma (starting material). |
Comment 0
|

|
| 2) |
Adjust the pH of the plasma to 7.2 by adding 2 M sodium acetate at 4°C. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 3) |
Add 99.5% ethanol to the plasma to a final concentration of 8 vol % and mix them at −3 ~ −2°C. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 4) |
Centrifuge the mixture at 10,000 × g for 30 min at 0°C and discard the precipitate. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 5) |
Add 10 M acetic acid to the supernatant (approx. 1.1 L) to adjust the pH to 6.8, and 99% ethanol to a final concentration of 21 vol %, and mix them at −6°C. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 6) |
Filter the mixture with a filter press (or with a Nutsche and filter paper or membrane filter, or a glass filter, G3) and separate the residue (Cohn’s alcohol fractionation of plasma proteins, Fr.II + Fr.III) (Cohn EJ. et al. 1946) from the supernatant. The residue can be kept as a frozen cake (ca. 50g) at −80°C. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 7) |
Suspend the residue (the thawed cake) in distilled water, 10 times the weight of the cake, at 0–5°C and adjust the pH of the suspension to 5.25 with 0.5 M hydrochloric acid. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 8) |
Extract the MBP-containing fraction derived of the suspension by vigorous stirring for 1 h at 4°C. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 9) |
Centrifuge the mixture at 10,000 × g for 30 min at 4°C and discard the precipitate. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 10) |
Adjust the pH of the supernatant to 7.0 with 1 M NaOH or 1M HCl. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 11) |
Add NaCl and polyethylene glycol 4000, to final concentrations of 0.15 M and 4 w/v %, respectively, and stir the suspension vigorously at 4°C for 40 h. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 12) |
Centrifuge the suspension at 10,000 × g for 30 min at 4°C and discard the precipitated residue. |
Comment 1
|

|
| 13) |
To the clear supernatant (ca. 460 mL), add NaCl, 1 M CaCl2, and 1 M imidazole buffer (pH 7.8) to final concentrations of 1 M, 20 mM, and 10 mM, respectively, and filter the solution through a 0.22 μm membrane filter. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 14) |
Apply the filtrate to a mannan-agarose column (gel volume: 10 mL), which has been washed with 7 column volumes of mannan-column elution buffer (reagent *2) and then equilibrated with mannan-column loading buffer (reagent *1). Perform affinity column chromatography at 4°C at a flow rate of 50–60mL/h. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 15) |
Wash the column with approx. 7 column volumes of the mannan-column loading buffer (reagent *1) until the absorbance at 280 nm (A280) becomes lower than 0.05. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 16) |
Elute the bound components with mannan-column elution buffer (reagent *2) with A280 nm monitoring. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 17) |
Concentrate the pooled eluate fraction and change the buffer to heparin column-loading buffer by centrifugation in 10 kDa cut-off Amicon Ultra, or briefly dialyze the concentrated fraction against heparin-column loading buffer (reagent *3). |
Comment 1
|

|
| 18) |
Apply the mannan affinity-purified protein dissolved in the heparin column loading buffer to a heparin-agarose column (gel volume: 10 mL), wash the column with 50 mL each of heparin column loading buffer (reagent *3) and heparin column washing buffer (reagent *4), and then elute the bound proteins with heparin column elution buffer (reagent *5). |
Comment 0
|

|
| 19) |
Concentrate the eluate with a centrifugal filter device and store as purified MBP. The yield of the purified MBP with this method is 0.7–1 mg/L of serum. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 20) |
Add NaCl to a final concentration of 0.5–1.0 M to the eluate from the heparin column to keep the MBP stable. |
Comment 1
|
|
|
| Initial amount | |
| Produced amount | |
| Discussion | The purified MBP preparation gives a single band corresponding to 31 kDa (subunit size) under reducing conditions and some more than 100 kDa bands (3–6 oligomers of the structural unit) (3 × subunits), the whole molecular mass being approximately 300–600 kDa, under non-reducing conditions on SDS-PAGE (see Fig. 1C, lane 3). The lectin and complement activating activities of the purified MBP are assayed as described in "Assay method for the lectin activity of mannan-binding protein ~ELLBA-1,2,3" and the reference (Kawasaki N. et al. 2008), respectively. |
| Figure & Legends |
Figure & Legends 
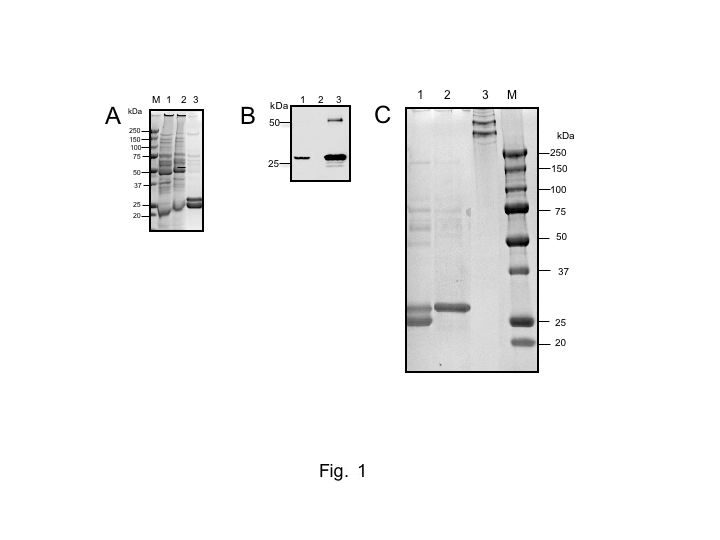
Fig. 1. SDS-PAGE and Western blotting of MBP-containing fractions in the purification steps for human serum MBP with Method 1
A, SDS-PAGE of samples before and after mannan column chromatography. Lane 1, before application to a mannan column; lane 2, pass-through fraction from the mannan column; lane 3, eluate from the mannan column. B, Western blotting of samples before and after mannan column chromatography. MBP was detected with the 1st antibody, mouse anti-human MBP monoclonal antibody (1 μg/mL: HYB 131-01), and 2nd antibody (HRP- conjugated goat anti-mouse IgG, 1:2000 dilution, Zymed-Invitrogen). The protein bands were visualized with a chemiluminescent substrate kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., Waltham, MA). Lanes 1~3, as in A. C, SDS-PAGE of samples before and after heparin column chromatography. Lane 1, eluate from the mannan column; lanes 2 and 3: eluate from the heparin column. Lanes 1 and 2, under reducing conditions; lane 3, under non-reducing conditions. In A and C, lane M shows molecular size markers. The proteins were detected by colloidal Coomassie brilliant blue G-250 staining. SDS-PAGE was performed on a 12.5% acrylamide gel in A-C. |
| Copyrights |
 Attribution-Non-Commercial Share Alike Attribution-Non-Commercial Share Alike
This work is released underCreative Commons licenses
|
| Date of registration:2015-02-25 13:33:58 |
- Kawasaki, T. (1999) Structure and biology of mannan-binding protein, MBP, an important component of innate immunity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1473, 186–195 [PMID : 10580138]
- Cohn, E.J., Strong, L.E., Hughes, W.L., Mulford, D.J., Ashworth, J.N., Melin, M., and Taylor, H.L. (1946) Preparation and properties of serum and plasma proteins. IV. A system for the separation into fractions of the protein and lipoprotein components of biological tissues and fluids. J Am Chem Soc. 68, 459–475 [PMID : unknown]
- Kawasaki, N, Ma, B.Y., and Kawasaki, T. (2008) Roles of serum lectins in host defense. Experimental Glycoscience, Glycobiology. Taniguchi N. et al (eds): pp.162–166, Springer Japan
- Nakamura, N., Nonaka, M., Ma, B.Y., Matsumoto, S., Kawasaki, N., Asano, S., and Kawasaki, T. (2009) Characterization of the interaction between serum mannan-binding protein and nucleic acid ligands. J Leukoc Biol. 86, 737–748 [PMID : 19465640]
|
This work is licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-Non-Commercial Share Alike. Please include the following citation
How to Cite this Work in an article:
Kawasaki, Nobuko,
(2015). GlycoPOD https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD.
Web.30,4,2024 .
How to Cite this Work in Website:
Kawasaki, Nobuko,
(2015).
Isolation of mannan-binding protein from human serum (plasma) ~Method 1.
Retrieved 30,4,2024 ,
from https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD/protocolShow.action?nodeId=t46.
html source
Kawasaki, Nobuko,
(2015).
<b>Isolation of mannan-binding protein from human serum (plasma) ~Method 1</b>.
Retrieved 4 30,2024 ,
from <a href="https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD/protocolShow.action?nodeId=t46" target="_blank">https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD/protocolShow.action?nodeId=t46</a>.
Including references that appeared in the References tab in your work is
much appreciated.
For those who wish to reuse the figures/tables, please contact JCGGDB
management office (jcggdb-ml@aist.go.jp).
|
|