This section explains the recommended protocol for glycan profiling experiments using lectin microarrays. The core procedure, which is common to all kinds of samples, is the following; protein quantification, Cy-3 labeling of glycoproteins, removal of excess free-Cy3 using gel filtration, and ending with the application of Cy-3 labeled glycoproteins onto a lectin microarray. |
| Category | Sugar binding proteins |
| Protocol Name | |
Authors
 |
Hirabayashi, Jun
*
Biotechnology Research Institute for Drug Discovery, Department of Life Science and Biotechnology, National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST)
Yamada, Masao
Glycan Profiling System Division/Executive Director, GP Biosciences Ltd.
*To whom correspondence should be addressed.
|
| KeyWords |
|
Reagents
 |
| ● |
PBS: 0.01M Phosphate-Buffered Saline, pH 7.2–7.4 |
| ● |
PBS-T: PBS containing 1% (v/v) Triton X-100 |
| ● |
TBS: 25 mM Tris, 140 mM NaCl, 3 mM KCl, pH7.5 |
| ● |
Micro BCATM Protein Assay Reagent Kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., Waltham, MA, Cat #23235) |
| ● |
Cy3 Mono-Reactive dye pack 1mg × 5 (GE Healthcare, Little Chalfont, UK, Cat #PA23001) |
| ● |
|
| ● |
ZebaTM Desalt Spin Columns, 0.5 mL (25 columns) (Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc. Cat #89882) |
| ● |
Probing Solution (GP Biosciences Ltd., Sapporo, Japan) |
| ● |
Kimtex Quarterfold (Kimbery-Clark Corporation, Irving, TX, Cat #33560) |
|
Instruments
 |
| ● |
Centrifuge (Allegra® X-15R: Beckman Coulter, Inc., Brea, CA) |
| ● |
Centrifuge (MX-301: Tomy Seiko Co., Ltd., Tokyo, Japan) |
| ● |
Sonicator (Tabletop Ultrasonic Cleaner, Model 1510: Branson Ultrasonics Corporation, Danbury, CT) |
| ● |
Spin-filters (5 kDa cut-off) (Merck Millipore, Billerica, MA, Cat No.UFC900596 24pk) |
| ● |
Rotator (Rotary Mixer NRC20D, tapping function Cat No.A-1.5: Nissin Corp., Tokyo, Japan) |
| ● |
96-well Microplate Reader (SpectraMax M5: Molecular Devices, Sunnyvale, CA) |
| ● |
LecChipsTM (GP Biosciences Ltd.) |
| ● |
GlycoStationTM Reader (GP Biosciences Ltd.) |
| ● |
Array-Pro Analyzer Ver.4.5 (Media Cybernetics Inc., Bethesda, MD) |
| ● |
GlycoStationTM Tools (GP Bioscieces Ltd.) |
| ● |
GlycoStationTM Tools Pro Suite (GP Biosciences Ltd.) |
| ● |
Centrifuge desiccator and Vacuum unit (UT-1000, Cat #CVE-200D: Tokyo Rikakikai Co. Ltd. (EYELA), Tokyo, Japan) |
|
| Methods |
|
1. |
Quantification of proteins |
| 1) |
Prepare 1.5 mL micro-centrifuge tubes labeled as BSA in a tube rack and add 240 μL PBS to one of the BSA tubes. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 2) |
Add 10 μL of 2 μg/mL BSA solution to the BSA tube for preparing 80 μg/mL BSA solution, and mix it. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 3) |
Place the tube of BSA 80 μg/mL and a tube of the glycoprotein sample prepared from protocols 13.1.1 to 13.1.3 (above). |
Comment 0
|

|
| 4) |
Prepare in a 96 well-microplate a serial dilution series of BSA solution starting from a concentration of 80 μg/mL (well volume, 100 μL), by diluting it by a ratio of 1/2, down to 1/128 of the initial concentration. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 5) |
Prepare the same dilution series in the microplate for the glycoprotein sample. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 6) |
Mix Micro BCA Reagent A (MA) 2.5 mL, Micro BCA Reagent B (MB) 2.4 mL and Micro BCA Reagent C (MC) 100 μL in a 15 mL tube (hereinafter WR means a Working Reagent prepared in this way). |
Comment 0
|

|
| 7) |
Add 100 μL WR to all the wells of the microplate. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 8) |
Seal all wells with a plate seal. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 11) |
Measure the absorbance at 562 nm in a microplate reader. |
Comment 0
|
|
|
|
2. |
Cy3 fluorescence labeling |
| 1) |
Dilute samples to 50 μg/mL by adding PBS based on the result of the Micro BCA Protein Assay. In the case of whole cell lysates, use PBS-T in place of PBS. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 2) |
Add 20 μL of each diluted sample into a tube containing Cy3 amount which is used for labeling of 100 μg proteins. |
Comment 1
|

|
| 3) |
Thoroughly mix each sample using a pipette. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 4) |
Centrifuge to spin down any fluids on the tube sidewall. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 5) |
Place the tubes in a container shielded from the light and incubate for 1 h at 25°C. |
Comment 0
|
|
|
|
3. |
Gel filtration to remove excess free-Cy3 |
| 2) |
Remove the column’s bottom plugs and loosen caps (do not remove the caps). |
Comment 0
|

|
| 3) |
Place the column in a 2.0 mL micro-centrifuge tube. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 4) |
Centrifuge at 1,500 × g for 1 min to remove storage solution. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 5) |
Mark on the side of the column at where the compacted resin is slanted upward. Place the column in the micro-centrifuge with the mark facing outward in all the subsequent centrifugation steps. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 6) |
Add 300 μg for 1 min to remove buffer. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 7) |
Repeat Step 4–6 twice (3 times in total), discarding buffer from the collection tube. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 8) |
Place the column in a new collection tube, remove the cap and apply all of the sample (20 μL) to the top of the compact resin bed. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 9) |
Apply 25 μL of TBS to the top of the gel bed after the sample has fully absorbed. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 10) |
Centrifuge at 1,500 × g for 2 min to collect the sample. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 11) |
Discard desalting columns after use. |
Comment 0
|
|
|
|
4. |
Apply the sample to lectin microarray |
| 1) |
Measure each volume of the Cy3-labeled samples with a micro-pipette. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 2) |
Prepare a total volume of 1 mL by adding GP Biosciences’s probing solution. The protein concentration becomes 1 μg/mL as 1 μg protein is eluted. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 3) |
Serial dilute each sample eluate to 500 ng/mL, 250 ng/mL, 125 ng/mL, 62.5 ng/mL, 31.25 ng/mL, 15.625 ng/mL using probing solution. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 4) |
Take out the LecChips (stored at −20°C) and place in an incubation box. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 5) |
Apply 100 μL Probing Solution with an 8 channel multi-pipette to well of the LecChips. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 6) |
Throw away Probing Solution and place a LecChip face down on a paper (e.g., Kimtex Quarterfold) to blot Probing Solution from the wells. |
Comment 1
|

|
| 7) |
Before drying up the wells, apply 100 μL Probing Solution to the wells. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 8) |
Repeat the above step 6 and step 7 (Probing Solution washing 3 times in total). |
Comment 0
|

|
| 9) |
Throw away Probing Solution and apply 100 μL of these samples to each well of the LecChips with a pipette. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 10) |
Incubate the LecChips in an incubation box at 25°C for at least 16 h with shaking at a low speed. |
Comment 0
|
|
|
|
5. |
Data acquisition and analysis |
| 1) |
Scan the LecChips with a GlycoStationTM Reader following the recommended reader settings and conditions. In order to detect very weak signals while avoiding saturation of strong signals, it is recommended that you take additional scans while adjusting the gain and the exposure time around the recommended condition. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 2) |
Data is analyzed with Array-ProTM Analyzer Ver.4.5. The net intensity for each lectin spot is calculated by subtracting the background from the signal intensity. The digitized data is displayed differentially with GlycoStationTM Tools. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 3) |
The latest GlycoStationTM Tools Pro Suite covers the function of Array-ProTM Analyzer Ver.4.5. |
Comment 0
|
|
|
| Figure & Legends |
Figure & Legends 
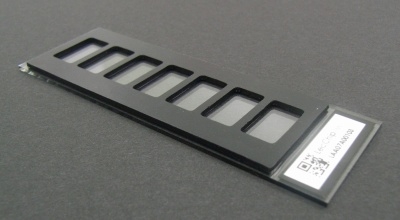
Fig.1. LecChipTM
The LecChipTM Ver.1.0 contains 45 lectins. The 45 lectins were selected from a number of candidates taking into consideration each lectin’s specificity to glycan structures and stability. The characteristics of lectins as a recognizer of glycans are classified into several categories, for instance, fucose recognizer (PSA etc.), sialic acid (MAL etc.), lactose (ECA etc.), asialo (PHA-E etc.), poly-lactosamin (LEL etc.), mannose (ConA etc.), O-glycan (Jacalin etc.) , and others. LecChipTM Ver.1.0 has 7 wells (the volume of which is 100 μL) on a slide glass and 45 lectins in each well. |
| Copyrights |
 Attribution-Non-Commercial Share Alike Attribution-Non-Commercial Share Alike
This work is released underCreative Commons licenses
|
| Date of registration:2014-09-11 16:39:22 |
- Kuno, A., Uchiyama, N., Koseki-Kuno, S., Ebe, Y., Takashima, S., Yamada, M., and Hirabayashi, J. (2005) Evanescent-field fluorescence-assisted lectin microarray: a new strategy for glycan profiling. Nature Methods 2, 851–856 [PMID : 16278656]
- Ebe, Y., Kuno, A., Uchiyama, N., Koseki-Kuno, S., Yamada, M., Sato, T., Narimatsu, H., and Hirabayashi, J. (2006) Application of lectin microarray to crude samples: differential glycan profiling of Lec mutants. J. Biochem. 139, 323–327 [PMID : 16567396]
- Tateno, H., Uchiyama, N., Kuno, A., Togayachi, A., Sato, T., Narimatsu, H., and Hirabayashi, J. (2007) A novel strategy for mammalian cell surface glycome profiling using lectin microarray. Glycobiology 17, 1138–1146 [PMID : 17693441]
|
This work is licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-Non-Commercial Share Alike. Please include the following citation
How to Cite this Work in an article:
Hirabayashi, Jun,
Yamada, Masao,
(2014). GlycoPOD https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD.
Web.1,5,2024 .
How to Cite this Work in Website:
Hirabayashi, Jun,
Yamada, Masao,
(2014).
Lectin Microarray.
Retrieved 1,5,2024 ,
from https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD/protocolShow.action?nodeId=t45.
html source
Hirabayashi, Jun,
Yamada, Masao,
(2014).
<b>Lectin Microarray</b>.
Retrieved 5 1,2024 ,
from <a href="https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD/protocolShow.action?nodeId=t45" target="_blank">https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD/protocolShow.action?nodeId=t45</a>.
Including references that appeared in the References tab in your work is
much appreciated.
For those who wish to reuse the figures/tables, please contact JCGGDB
management office (jcggdb-ml@aist.go.jp).
|
|