Pulmonary surfactant proteins A and D (SP-A and SP-D) belong to the collectin subgroup of the C-type lectin superfamily, along with mannan-binding proteins. SP-A and SP-D are mainly synthesized in alveolar type II cells and secreted into alveolar spaces. The structure of pulmonary collectins is characterized by four domains that consist of an N-terminus involved in interchain disulfide bonding, a collagen-like domain, a coiled coil neck domain, and a carbohydrate recognition domain. SP-A forms a bouquet-like structure consisting of six trimeric subunits. SP-D exhibits cruciform structure consisting of four trimeric subunits. SP-A and SP-D are now well recognized to be important members that constitute innate immunity in the lung. |
| Category | Sugar binding proteins |
| Protocol Name | Isolation of pulmonary surfactant proteins from bronchoalveolar lavage fluids |
Authors
 |
Ariki, Shigeru
Department of Biochemistry, Sapporo Medical University School of Medicine
Nishitani, Chiaki
Department of Biochemistry, Sapporo Medical University School of Medicine
Kuroki, Yoshio
*
Department of Biochemistry, Sapporo Medical University School of Medicine
*To whom correspondence should be addressed.
|
| KeyWords |
|
Reagents
 |
| ● |
Pooled bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) fluids from rats or pooled fluids of therapeutic bronchoalveolar lavage from individuals with pulmonary alveolar proteinosis |
| ● |
Buffer A (10 mM Tris-HCl buffer, pH 7.4, containing 150 mM NaCl) |
| ● |
Buffer B (10 mM Tris-HCl buffer, pH 7.4) |
| ● |
NaBr solution (1.64 M NaBr in buffer A) |
| ● |
|
| ● |
Buffer C: loading buffer for SP-A isolation (10 mM Tris-HCl buffer, pH 7.4, containing 5 mM CaCl2) |
| ● |
Buffer D: loading buffer for SP-D isolation (10 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.4, containing 150 mM NaCl and 5 mM CaCl2) |
| ● |
Buffer E: elution buffer for SP-A isolation (10 mM Trsi-HCl, pH 7.4, containing 5 mM EDTA) |
| ● |
Buffer F: elution buffer for SP-D isolation (10 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.4, containing 150 mM NaCl and 5 mM EDTA) |
| ● |
Superose 6 10/300 GL (GE Healthcare, Little Chalfont, UK) |
| ● |
Dialysis membrane (MWCO: 14,000)(Viskase Companies, Inc., Darien, IL) |
| ● |
1-butanol (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO) |
|
Instruments
 |
| ● |
|
| ● |
Columns for open column chromatography |
|
| Methods |
|
1. |
Isolation and purification of SP-A from BAL fluids |
| 1) |
Prepare pooled BAL fluids (starting materials) after lavaging by the buffer A. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 2) |
Add 0.5 M CaCl2 into BAL fluids to a final concentration of 5 mM. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 3) |
Centrifuge the pooled BAL fluids at 85,000 × g at 4°C overnight. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 4) |
Separate the supernatant and the precipitate. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 5) |
Suspend and homogenize the precipitate with the NaBr solution. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 6) |
Centrifuge the homogenate at 60,000 × g at 4°C for 4 h. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 7) |
Collect and suspend the pellicle with the buffer A. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 8) |
Centrifuge the suspension at 100,000 × g at 4°C for 1 h. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 9) |
Collect the precipitate, which is the surfactant fraction, and discard the supernatant. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 10) |
Suspend the precipitate with 1–2 mL distilled water. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 11) |
Inject the suspension of the surfactant into the 100 mL of 1-butanol which is strongly being mixed by stir bar, and continues to be mixed at room temperature at least for 1 h (delipidation of the surfactant). |
Comment 0
|

|
| 12) |
Centrifuge the surfactant-butanol mixture at 1,600 × g at room temperature for 30 min. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 13) |
Collect the precipitate (delipidated surfactant) and discard the supernatant. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 14) |
Vapor the residual butanol in the precipitate by gentle stream of nitrogen. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 15) |
Suspend the delipidated surfactant with 3–4 mL of distilled water. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 16) |
Dialize the delipidated surfactant against the buffer B at 4°C for 2–3 days with 3–4 exchanges of the same buffer. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 17) |
Centrifuge the dialysate at 150,000 × g at 4°C for 1 h. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 19) |
Add 0.5 M CaCl2 into the supernatant to a final concentration of 5 mM. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 20) |
Apply the supernatant to a mannose-sepharose column after equilibrating the column with the buffer C (the loading buffer). |
Comment 0
|

|
| 21) |
Wash the column with the buffer C until the absorbance of 280 nm becomes approximately 0. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 22) |
Elute the bound components with the buffer E (elution buffer) with A280-nm monitoring. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 23) |
Apply the eluate to the Superose 6 10/300 GL column which is equilibrated with the buffer B and elute the protein with A280-nm monitoring. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 24) |
Collect the first protein peak which is the purified SP-A. |
Comment 0
|
|
|
|
2. |
Isolation and purification of SP-D from BAL fluids |
| 1) |
Collect the supernatant after centrifuging BAL fluids at 85,000 × g (1(4)). |
Comment 0
|

|
| 2) |
Apply the supernatant to a mannose-sepharose column after equilibrating the column with the buffer D (the loading buffer). |
Comment 0
|

|
| 3) |
Wash the column with the buffer D until the absorbance of 280 nm becomes approximately 0. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 4) |
Elute the bound components with the buffer F (elution buffer) with A280-nm monitoring. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 5) |
Apply the eluate to the Superose 6 10/300 GL column which is equilibrated with the buffer A and elute the protein with A280-nm monitoring. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 6) |
Collect the first protein peak which is the purified SP-D. |
Comment 0
|
|
|
| Figure & Legends |
Figure & Legends 
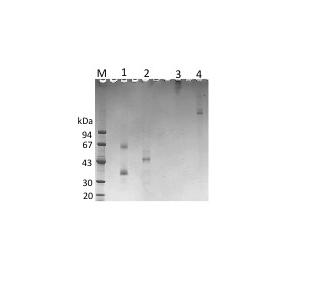
Fig. 1. Electrophoretic profile of purified SP-A and SP-D.
SDS-PAGE was performed under reducing (lanes 1 and 2) and nonreducing (lanes 3 and 4) conditions. Lanes 1 and 3, SP-A; lanes 2 and 4, SP-D. |
| Copyrights |
 Attribution-Non-Commercial Share Alike Attribution-Non-Commercial Share Alike
This work is released underCreative Commons licenses
|
| Date of registration:2014-10-27 14:30:30 |
- Kuroki, Y., and Akino, T. (1991) Pulmonary surfactant protein A (SP-A) specifically binds dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine. J Biol Chem. 266, 3068–3073 [PMID : 1993679]
- Ogasawara, Y., Kuroki, Y., and Akino, T. (1992) Pulmonaru surfactant protein D specifically binds to phosphatidylinositol. J Biol Chem. 267, 21244–21249 [PMID : 1400434]
- Yamazoe, M., Nishitani, C., Takahashi, M., Katoh, T., Ariki, S., Shimizu, T., Mitsuzawa, H., Sawada, K., Voelker, D.R., Takahashi, H., and Kuroki, Y. (2008) Pulmonary surfactant protein D inhibits lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced inflammatory responses by altering LPS binding to its receptor. J Biol Chem. 283, 35878–35888 [PMID : 18990700]
- Sawada, K., Ariki, S., Kojima, T., Saito, A., Yamazoe, M., Nishitani, C., Shimizu, T., Takahashi, M., Mitsuzawa, H., Yokota, S., Sawada, N., Fujii, N., Takahashi, H., and Kuroki, Y. (2010) Pulmonary collectins protect macrophages against pore-forming activity of Legionella pneumophila and suppress its intracellular growth. J Biol Chem. 285, 8434–8443 [PMID : 20056602]
|
This work is licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-Non-Commercial Share Alike. Please include the following citation
How to Cite this Work in an article:
Ariki, Shigeru,
Nishitani, Chiaki,
Kuroki, Yoshio,
(2014). GlycoPOD https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD.
Web.1,5,2024 .
How to Cite this Work in Website:
Ariki, Shigeru,
Nishitani, Chiaki,
Kuroki, Yoshio,
(2014).
Isolation of pulmonary surfactant proteins from bronchoalveolar lavage fluids.
Retrieved 1,5,2024 ,
from https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD/protocolShow.action?nodeId=t142.
html source
Ariki, Shigeru,
Nishitani, Chiaki,
Kuroki, Yoshio,
(2014).
<b>Isolation of pulmonary surfactant proteins from bronchoalveolar lavage fluids</b>.
Retrieved 5 1,2024 ,
from <a href="https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD/protocolShow.action?nodeId=t142" target="_blank">https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD/protocolShow.action?nodeId=t142</a>.
Including references that appeared in the References tab in your work is
much appreciated.
For those who wish to reuse the figures/tables, please contact JCGGDB
management office (jcggdb-ml@aist.go.jp).
|
|