To analyze the composition of glycosphingolipids (GSLs) in samples, thin-layer chromatography (TLC) is usually used. GSLs are visualized with appropriate reagents. |
| Category | Glycolipids and related compounds |
| Protocol Name | Thin-layer chromatography (TLC) of glycolipids |
Authors
 |
Okino, Nozomu
*
Department of Bioscience and Biotechnology, Graduate School of Bioresource and Bioenvironmental Sciences, Kyushu University
Ito, Makoto
Department of Bioscience and Biotechnology, Graduate School of Bioresource and Bioenvironmental Sciences, Kyushu University
*To whom correspondence should be addressed.
|
| KeyWords |
|
Reagents
 |
| ● |
|
| ● |
|
| ● |
CHCl3-MeOH mixture (C/M, volume/volume) |
| ● |
|
| ● |
|
| ● |
|
| ● |
|
| ● |
|
| ● |
|
| ● |
|
|
Instruments
 |
| ● |
TLC plate (Silicagel 60, 20 × 20 cm: Merck Millipore, Billerica, MA) |
| ● |
High performance TLC (HPTLC) plate (Silicagel 60 HPTLC, 10 × 20 cm: Merck Millipore, Billerica, MA) |
| ● |
|
| ● |
Microsyringe (5 μL, Drummond Scientific Company, Broomall, PA) |
| ● |
TLC developing chamber (inside, ~24 cm × ~11 cm × ~21 cm) |
| ● |
|
| ● |
|
| ● |
|
|
| Methods |
|
1. |
Orcinol reagent (for all GSLs) |
| 1) |
Dissolve 200 mg of orcinol in 11.4 mL of H2SO4, and make up to 100 mL with DW. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 2) |
Store the reagent in a refrigerator. |
Comment 0
|
|
|
|
2. |
Resorcinol reagent (for sialic-acid containing GSLs, gangliosides) |
| 1) |
Dissolve 200 mg of resorcinol in 10 mL of DW, then add 80 mL of HCl and 0.25 mL of 0.1M CuSO4. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 3) |
Store the reagent in a refrigerator. |
Comment 0
|
|
|
|
3. |
Purimuline reagent (for all lipids including GSLs, phospholipids, neutral lipids) |
| 1) |
Stock solution: Dissolve 100 mg of purimuline in 100 mL of DW. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 2) |
Dilute 1 mL of the stock solution with 100 mL of acetone-DW (4/1, v/v). |
Comment 0
|

|
| 3) |
Store the reagent in a refrigerator. |
Comment 0
|
|
|
|
4. |
Thin-layer chromatography (TLC) |
| 1) |
Cut the TLC plate as necessary with a glass-cutting pen. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 2) |
Mark lines at the spot with a pencil. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 3) |
Dissolve the lipids in a small amount of CHCl3/MeOH (1/2 or 2/1, v/v). |
Comment 0
|

|
| 4) |
Apply the samples to the TLC plate with a micro-syringe. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 5) |
Develop the TLC plate with an appropriate developing solvent as described below in a TLC chamber.
Solvent systems for analyzing neutral GSL and gangliosides
For neutral GSLs:
CHCl3/MeOH/DW (65/35/8, v/v/v): for all neutral GSLs
CHCl3/MeOH/DW (65/25/4, v/v/v): for non-polar neutral GSLs
CHCl3/MeOH/DW (60/40/10, v/v/v): for polar neutral GSLs
For gangliosides:
CHCl3/MeOH/0.02% CaCl2 (5/4/1, v/v/v) |
Comment 1
|

|
| 6) |
Dry the plate and visualize the GSLs using appropriate staining reagents described below.
Visualization of GSLs with different staining reagents
Orcinol reagent:
Spray the reagent, and heat on a hot plate at 110°C until GSL bands are visible (~ 5 min).
Resolcinol reagent:
Place a clean glass plate on the hot plate at 95°C.
Spray the reagent on the TLC plate.
Put the TLC plate on a clean glass plate attaching the silica surface (sample-loading side) to the clean glass.
Heat at 95°C until GSL bands are visible (~ 10 min).
Purimuline reagent:
Spray the reagent until the TLC plate is wet.
Illuminate the plate with a UV transilluminator (~365 nm). |
Comment 0
|
|
|
| Figure & Legends |
Figure & Legends 
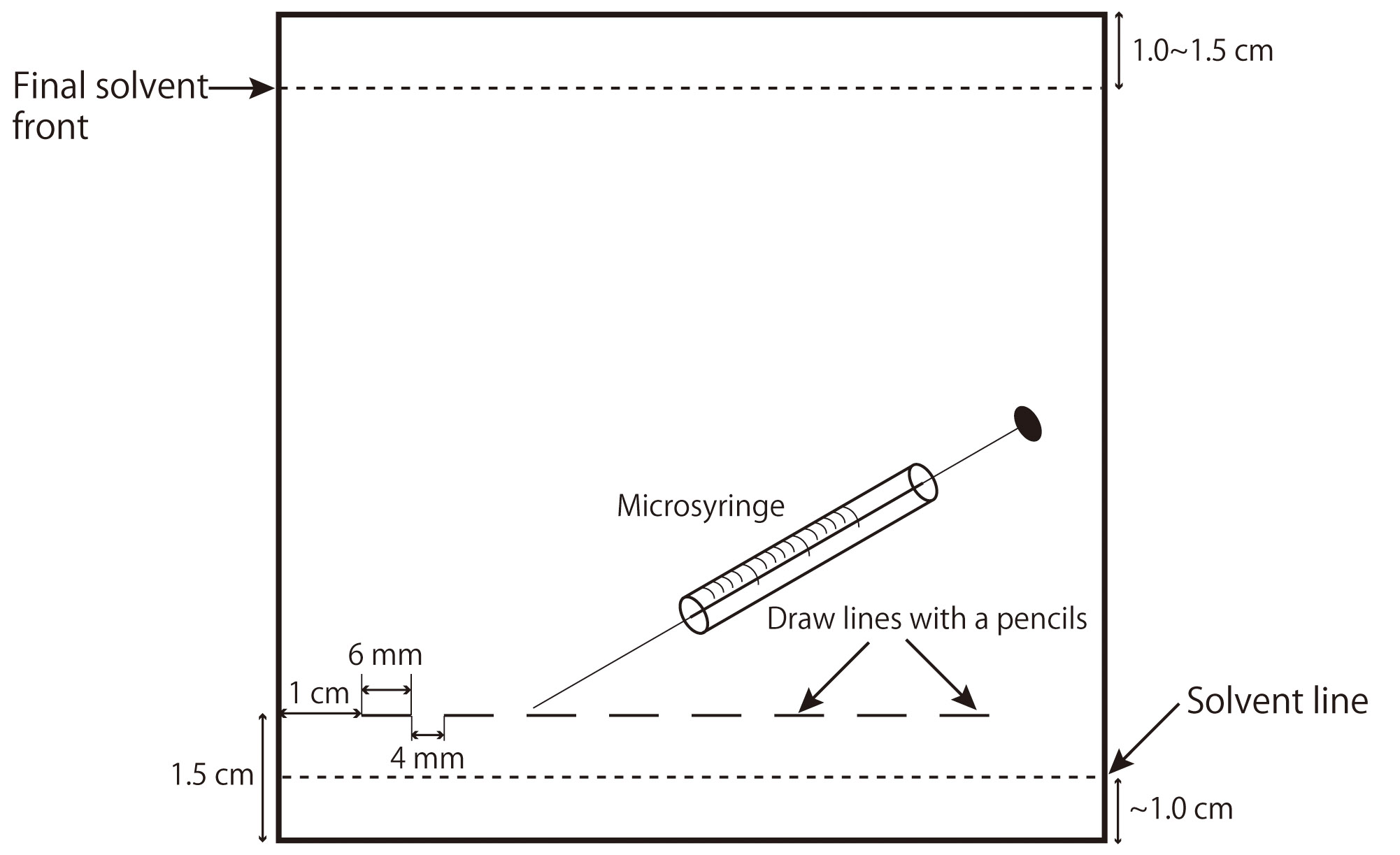
Fig. 1. Spotting of samples on a TLC plate and development with an appropriate solvent

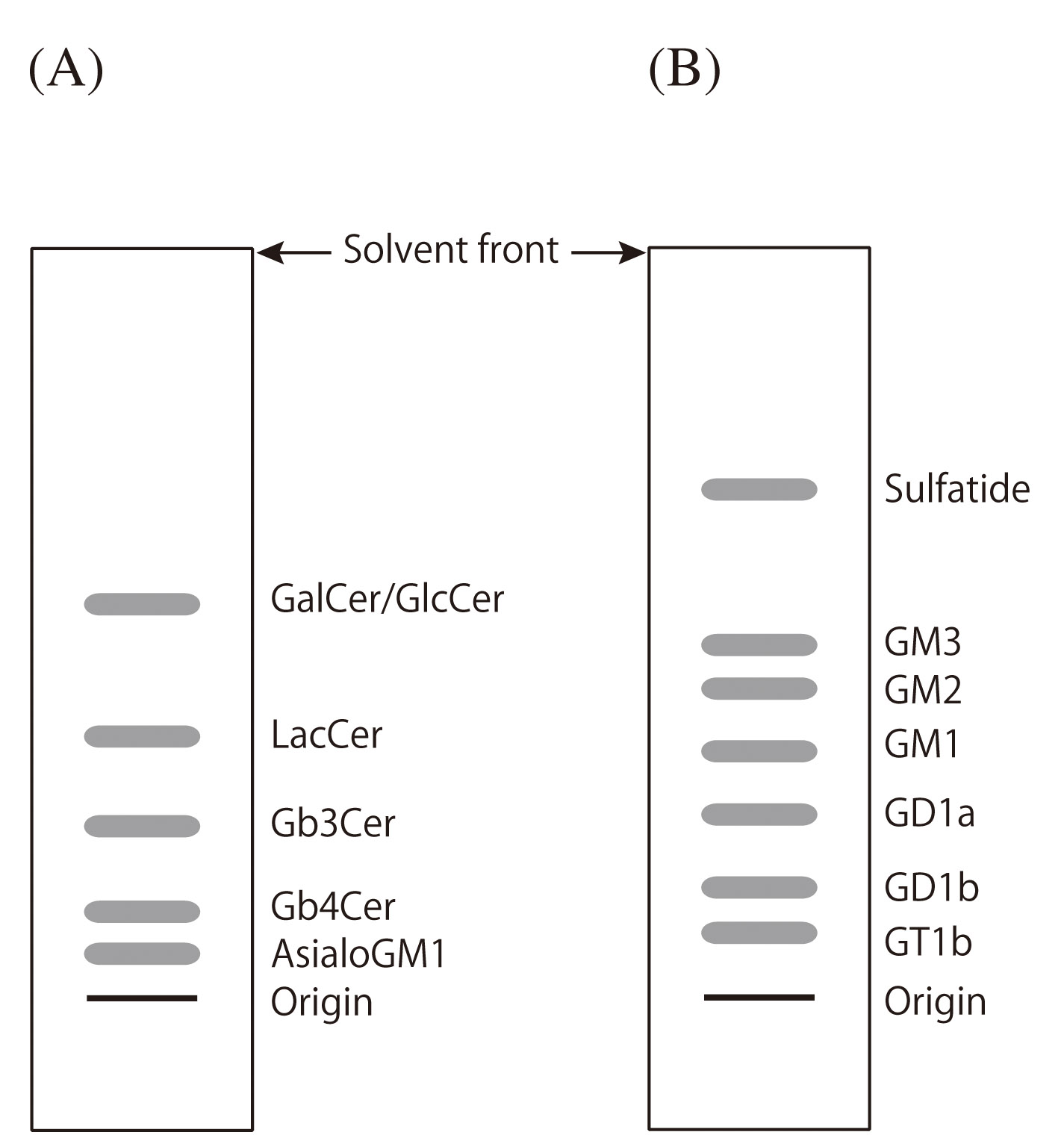
Fig. 2. Illustration showing the separation of GSLs by TLC
(A) neutral GSLs developed with CHCl3/MeOH/DW (60/30/8, v/v/v)
(B) acidic GSLs developed with CHCl3/MeOH/0.02% CaCl2 (5/4/1, v/v/v) |
| Copyrights |
 Attribution-Non-Commercial Share Alike Attribution-Non-Commercial Share Alike
This work is released underCreative Commons licenses
|
| Date of registration:2014-07-31 10:01:29 |
- Macher, B.A., and Klock, J.C. (1980) Isolation and chemical characterization of neutral glycosphingolipids of human neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 255, 2092–2096 [PMID : 7354081]
- Ando, S., Chang, N.C., and Yu, R.K. (1978) High-performance thin-layer chromatography and densitometric determination of brain ganglioside compositions of several species. Anal Biochem. 89, 437–450 [PMID : 103458]
|
This work is licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-Non-Commercial Share Alike. Please include the following citation
How to Cite this Work in an article:
Okino, Nozomu,
Ito, Makoto,
(2014). GlycoPOD https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD.
Web.18,4,2024 .
How to Cite this Work in Website:
Okino, Nozomu,
Ito, Makoto,
(2014).
Thin-layer chromatography (TLC) of glycolipids.
Retrieved 18,4,2024 ,
from https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD/protocolShow.action?nodeId=t2.
html source
Okino, Nozomu,
Ito, Makoto,
(2014).
<b>Thin-layer chromatography (TLC) of glycolipids</b>.
Retrieved 4 18,2024 ,
from <a href="https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD/protocolShow.action?nodeId=t2" target="_blank">https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD/protocolShow.action?nodeId=t2</a>.
Including references that appeared in the References tab in your work is
much appreciated.
For those who wish to reuse the figures/tables, please contact JCGGDB
management office (jcggdb-ml@aist.go.jp).
|
|