Nucleotide sugar transporters (NSTs) are multimembrane-spanning proteins in the plane of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) or Golgi membrane and are crucial for the synthesis of glycoconjugates (Fig. 1) 2,5). Glycosylation is performed by various types of glycosyltransferase in the lumens of the ER and the Golgi apparatus. All glycosyltransferases require high-energy donor sugars activated by the addition of a nucleoside mono- or diphosphate (CMP, UDP or GDP), which are referred to as nucleotide sugars. Nucleotide sugars are synthesized in the cytosol (or in the nucleus in the case of CMP-sialic acid). The translocation of nucleotide sugars from the cytosol into the lumen of each compartment is mediated by NSTs. NSTs transport nucleotide sugars by coupling with the antiport of nucleoside monophosphate (NMP), which is produced as the result of a glycosyltransferase reaction and a subsequent luminal nucleoside diphosphatase (NDPase) reaction. Recently, some NSTs have been reported to transport nucleotide sugars by coupling with the antiport of another nucleotide sugar or nucleoside diphosphate (Muaraoka et al., 2007). Indeed, NSTs are likely to be key components in the synthesis of glycoconjugates.
The nucleotide sulfate, 3'-phosphoadenosine 5'-phosphosulfate (PAPS), is a universal sulfuryl donor for sulfation. Sulfate is transferred from PAPS to a defined position on the sugar residue or proteins by sulfotransferases. In a similar fashion to nucleotide sugars, PAPS is synthesized in the cytosol by a PAPS synthetase and is translocated from the cytosol into the Golgi lumen through a PAPS transporter (PAPST) 1,3). Thus PAPS transporters belong to the nucleotide sugar transporter family (Fig.2).
Since the original cloning of NST, which was reported in 1996, many other NSTs have been cloned and their transport activities identified (Table 1). The Hugo Nomenclature committee categorizes NSTs and PAPSTs as solute carrier transporters that do not perform active transport using energy derived from ATP. This group of transporters comprise the SLC35 (solute carrier 35) family of proteins (Table 1). The SLC35 family is divided into five sub-groups, A~F. In addition to these NSTs, many GDP-Man transporters have been identified in plants and fungi (Fig. 2).
Ten human NST genes, including PAPS transporters, have now been cloned and their protein activities identified (Table1, Fig.2). Among them, four NSTs have multi-substrate specificities2). Four other NSTs transport single specific nucleotide sugars, and a further two transport PAPS1,3). The inactivation of the GDP-Fuc transporter (SLC35C1) and the CMP-Sia transporter (SLC35A1) causes congenital disorders of glycosylation (CGD)-IIc/ leukocyte adhesion deficiency type II and CGDIIf, a new type of CGD-II, respectively (Table1). In model organisms, such as C. elegans, Drosophila, Leishmania, and yeast, mutations of NST genes have been identified and used for the functional analysis of NSTs, which will help to clarify the physiological functions of sugar chains. |
| Category | Nucleotide sugar transporters |
| Protocol Name | Cloning and expression of nucleotide sugar or PAPS transporter genes |
Authors
 |
Nishihara, Shoko
Laboratory of Cell Biology, Department of Bioinformatics, Graduate School of Engineering, Soka University
|
| KeyWords |
|
Reagents
 |
| ● |
GATEWAY™ Cloning System (Invitrogen/Life Technologies, Carlsbad, CA) |
|
| Methods |
|
1. |
Cloning and expression of nucleotide sugar or PAPS transporter genes |
| 1) |
A TBLASN search of the database was performed using the amino acid sequence corresponding to the open reading frame (ORF) of the NST or PAPST gene that was expected to have the desired activity in order to obtain the cDNA sequence encoding a full-length ORF. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 2) |
The DNA fragment corresponding to the full-length ORF was amplified by a two-step PCR procedure.
In the first round of PCR, the SNT or PAPST cDNA was amplified from the appropriate cDNA library using the forward primer 5’-AAAAAGCAGGCT-(gene-specific sequence)-3’, and the reverse primer 5’-AGAAAGCTGGGT-(gene-specific sequence)-3’. In the second PCR step, the product from the first reaction was used as the template, and was amplified with the forward primer 5’-GGGGACAAGTTTGTACAAAAAAGCAGGCT-3’, and the reverse primer 5’-GGGGACCACTTTGTACAAGAAAGCTGGGT-3’. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 3) |
The amplified fragment was inserted into the pDONR™201 vector (Invitrogen/Life Technologies) by recombination to create an entry clone for use during the subsequent subcloning steps. |
Comment 1
|

|
| 4) |
The insert was transferred between the attR1 and attR2 sites of the yeast expression vector YEp352GAP-II-HA* to generate YEp352GAP-II-NST (or PAPST)-HA for assaying the NST or PAPST activity**. |
Comment 1
|

|
| 5) |
The insert was transferred between the attR1 and attR2 sites of the appropriate mammalian expression vectors* to generate the expression vector encoding HA epitope tagged or c-Myc tagged NST or PAPST for assaying NST or PAPST activity. The tags were also used to identify intracellular localization by immuno-staining using anti-HA antibody or anti-cMyc antibody**. |
Comment 1
|
|
|
| Notes | Nucleotide sugar transporters (NSTs) and PAPS transporters (PAPSTs) generally share a high level of sequence homology. Indeed, partially conserved NST and PAPST activity is observed between homologous NSTs and PAPSTs (Fig. 2). Therefore, TBLASTN search was used for gene identification.1,2,3) |
| Figure & Legends |
Figure & Legends 
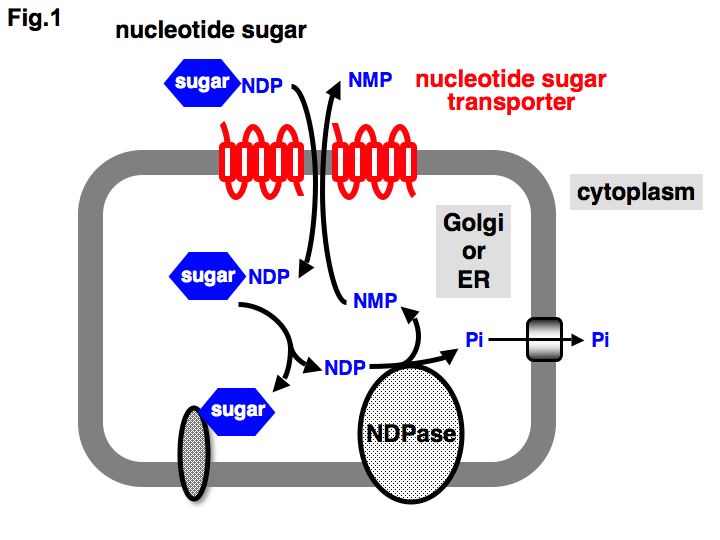
Fig. 1. Schematic representation of nucleotide sugar transporters (NSTs) and glycosylation pathways.
NSTs transport nucleotide sugars from the cytosol into the lumen of the ER/Golgi compartment by coupling with the antiport of nucleoside monophosphate (NMP), which is produced as the result of a glycosyltransferase reaction and a subsequent luminal nucleoside diphosphatase (NDPase) reaction. Some NSTs transport nucleotide sugars by coupling with the antiport of another nucleotide sugar or nucleoside diphosphate4).

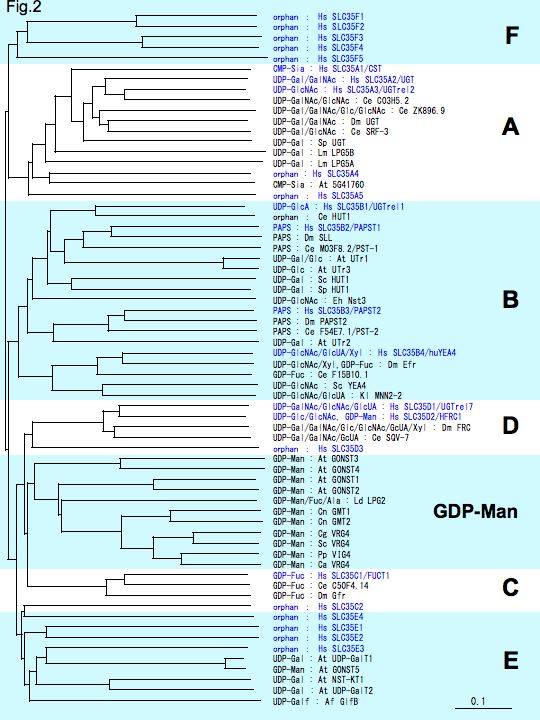
Fig. 2. Phylogenetic tree of nucleotide sugar transporters (NSTs) and PAPS transporters (PAPSTs).
Sugar nucleotide transporters (NSTs) and PAPS transporters (PAPSTs) with known substrates were used to generate the phylogenetic tree by ClustalX 2.0.10. [substrate: species, name of transporters].
At : Arabidopsis thaliana, Af : Aspergillus fumigatus, Ca : Candida albicans, Ce : Caenorhabditis elegans, Cg : Candida glabrata, Cn : Cryptococcus neoformans, Dm : Drosophila melanogaster, Eh : Entamoeba histolytica, Hs : Homo sapiens, Kl : Kluyveromyces lactis, Ld : Leishmania donovani, Lm : Leishmania major, Pp : Pichia pastoris, Sc : Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Sp : Saccharomyces pombe.

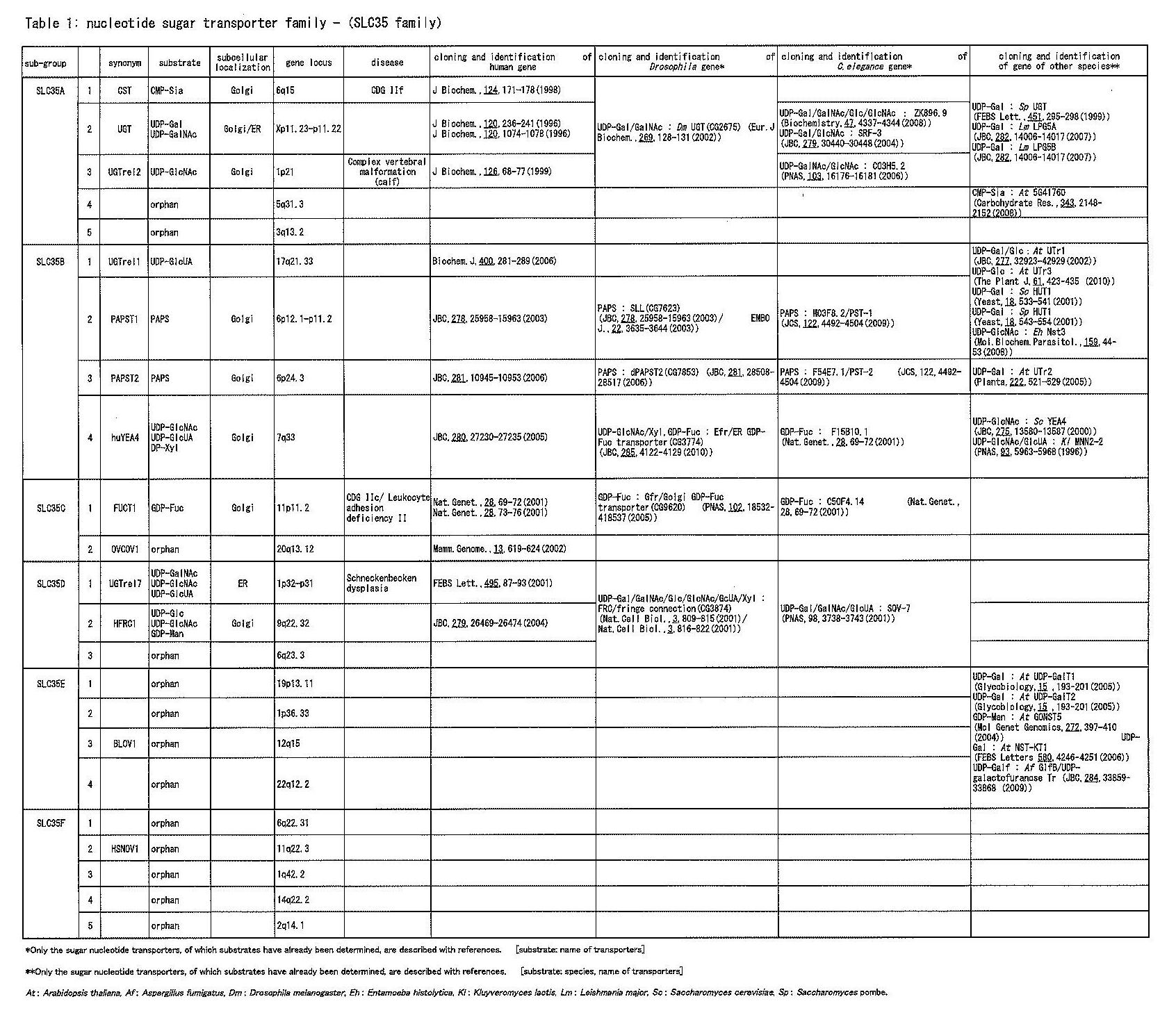
Table 1. Nucleotide sugar transporter family - (SLC35 family)
|
| Copyrights |
 Attribution-Non-Commercial Share Alike Attribution-Non-Commercial Share Alike
This work is released underCreative Commons licenses
|
| Date of registration:2013-12-27 18:10:31 |
- Kamiyama, S., Suda, T., Ueda, R., Suzuki, M., Okubo, R., Kikuchi, N., Chiba, Y., Goto, S., Toyoda, H., Saigo, K., Watanabe, M., Narimatsu, H., Jigami, Y., and Nishihara, S. (2003) Molecular cloning and identification of 3'-phosphoadenosine 5'-phosphosulfate transporter. J Biol Chem. 278, 25958-25963 [PMID : 12716889]
- Suda, T., Kamiyama, S., Suzuki, M., Kikuchi, N., Nakayama, K., Narimatsu, H., Jigami, Y., Aoki, T., and Nishihara, S. (2004) Molecular cloning and characterization of a human multisubstrate specific nucleotide-sugar transporter homologous to Drosophila fringe connection. J Biol Chem. 279, 26469-26474 [PMID : 15082721]
- Kamiyama, S., Sasaki, N., Goda, E., Ui-Tei, K., Saigo, K., Narimatsu, H., Jigami, Y., Kannagi, R., Irimura, T., and Nishihara, S. (2006) Molecular cloning and characterization of a novel 3'-phosphoadenosine 5'-phosphosulfate transporter, PAPST2. J Biol Chem. 281, 10945-10953 [PMID : 16492677]
- Muraoka, M., Miki, T., Ishida, N., Hara, T., and Kawakita, M. (2007) Variety of nucleotide sugar transporters with respect to the interaction with nucleoside mono- and diphosphates. J Biol Chem. 282, 24615-24622 [PMID : 17599910]
- Nishihara, S. (2008) Nucleotide sugar transporter genes and their functional analysis. Experimental Glycoscience - Glycobiology, edited by Naoyuki Taniguchi et al., Springer, Part1, Section III, 103-107.
|
This work is licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-Non-Commercial Share Alike. Please include the following citation
How to Cite this Work in an article:
Nishihara, Shoko,
(2013). GlycoPOD https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD.
Web.26,4,2024 .
How to Cite this Work in Website:
Nishihara, Shoko,
(2013).
Cloning and expression of nucleotide sugar or PAPS transporter genes.
Retrieved 26,4,2024 ,
from https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD/protocolShow.action?nodeId=t94.
html source
Nishihara, Shoko,
(2013).
<b>Cloning and expression of nucleotide sugar or PAPS transporter genes</b>.
Retrieved 4 26,2024 ,
from <a href="https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD/protocolShow.action?nodeId=t94" target="_blank">https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD/protocolShow.action?nodeId=t94</a>.
Including references that appeared in the References tab in your work is
much appreciated.
For those who wish to reuse the figures/tables, please contact JCGGDB
management office (jcggdb-ml@aist.go.jp).
|
|