Xylosyltransferase (XylT) (EC 2.4.2.26) initiates the biosynthesis of glycosaminoglycan (GAG) chains characteristic of proteoglycans by transfer of xylose (Xyl) from UDP-Xyl to specific serine residues of the core protein (Fig. 1). Thus, it is suggested that XylT is a rate-limitting enzyme in GAG synthesis. XylT-I and XylT-II genes encode XylT in humans*. So far, it has been shown that XylT activities in the serum could be used as a diagnostic marker for systemic sclerosis 1) and reduced XylT activities in seminal plasma might be associated with infertile men 2). In addition, it has been reported that genetic variations in the XylT-I are linked to the formation of abdominal aortic aneurysm, where GAG synthesis is altered 3). In this section, the method for measurement of XylT activities using the synthetic bikunin analogous peptide Q-E-E-E-G-S-G-G-G-Q-K as an acceptor substrate is mentioned. Bikunin, the inhibitory component of the inter-a-trypsin inhibitor, is known to be glycosylated by a chondroitin sulfate chain 4).
* It is suggested that XylT-I and XylT-II are, at least in vitro, functionally identical, because a soluble form of human XT-II expressed in the XylT-deficient pgsA-745 Chinese hamster ovary cell line is indeed capable of catalyzing the transfer of Xyl residue to a variety of peptide substrates. |
| Category | Glycosyltransferases & related proteins |
| Protocol Name | Enzyme assay of xylosyltransferase |
Authors
 |
Koike, Toshiyasu
Department of Biochemistry, Kobe Pharmaceutical University
Nadanaka, Satomi
Department of Biochemistry, Kobe Pharmaceutical University
Kitagawa, Hiroshi
*
Department of Biochemistry, Kobe Pharmaceutical University
*To whom correspondence should be addressed.
|
| KeyWords |
|
Reagents
 |
| ● |
UDP-[14C]Xyl (Perkin Elmer, Waltham, MA) |
| ● |
Synthetic peptide Q-E-E-E-G-S-G-G-G-Q-K (Invitrogen/Life Technologies, Carlsbad, CA)*
* Synthetic peptides derived from APP (amyloid β A4 precursor protein) [T-E-N-E-G-S-G-L-T-N-I-K] and APLP2 (amyloid β A4 precursor-like protein 2) [S-E-N-E-G-S-G-M-A-E-Q-K] are also reported to be good substrates for XylT in vitro 5). |
|
Instruments
 |
| ● |
Superdex peptide HR 10/30 column (GE Healthcare, Little Chalfont, UK) |
| ● |
2300TR liquid scintillation counter (Perkin Elmer) |
|
| Methods |
|
1. |
Enzyme assay of XylT-I using the synthetic bikunin analogous peptide, Q-E-E-E-G-S-G-G-G-Q-K, as an acceptor. |
| 1) |
The reaction mixture for XylT assays (a total volume of 40 μL) contains 10 μL of enzyme preparation (see Comment), 25 mM MES buffer (pH 6.5), 25 mM KF, 5 mM MgCl2, 5 mM MnCl2, 2 mM UDP-[14C]Xyl (3.0 × 105 dpm), and the synthetic peptide Q-E-E-E-G-S-G-G-G-Q-K (10 nmol). |
Comment 1
|

|
| 2) |
The enzyme reaction is performed at 37˚C for 16 h. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 3) |
The 14C-labeled products are separated by gel filtration chromatography on a Superdex peptide column using 0.25 M ammonium bicarbonate containing 7% 1-propanol as the eluent at a flow rate of 0.4 mL/min. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 4) |
The collected fractions (0.4 mL each) are analyzed by liquid scintillation counter (Fig. 2). |
Comment 0
|
|
|
| Figure & Legends |
Figure & Legends

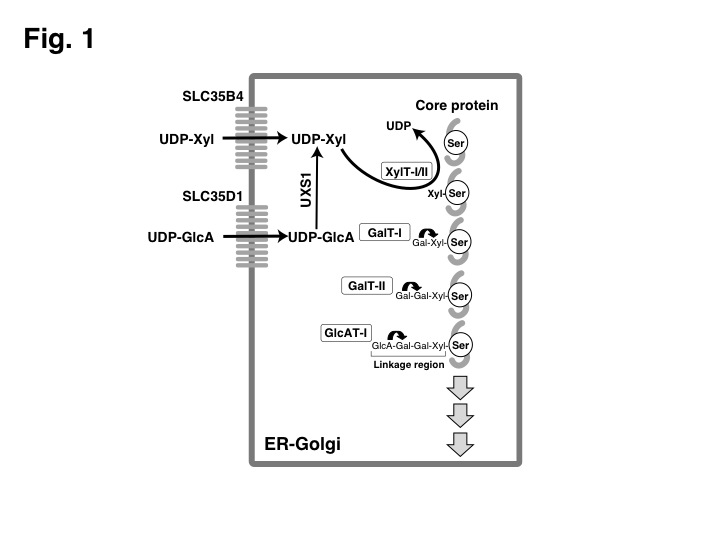
Fig. 1 Representative scheme for the initiation of GAG synthesis by XylT.
In mammals, UDP-Xyl is synthesized within the lumen of the ER/Golgi. XylT requires UDP-Xyl as a donor substrate. The GAG synthesis is initiated by transfer of a Xyl residue to specific serine residues in the core proteins by different XylTs (XylT-I and XylT-II). Next, GalT-I and GalT-II successively transfer two Gal residues. GlcAT-I completes the biosynthesis of the linkage region by transferring a GlcA residue. SLC35D1, Nucleotide sugar transporter to transport UDP-GlcA (ER membrane); SLC35B4, Nucleotide sugar transporter to transport UDP-Xyl (Golgi membrane); UXS1, UDP-Xyl synthase; GalT, galactosyltransferase; GlcAT, glucuronyltransferase.

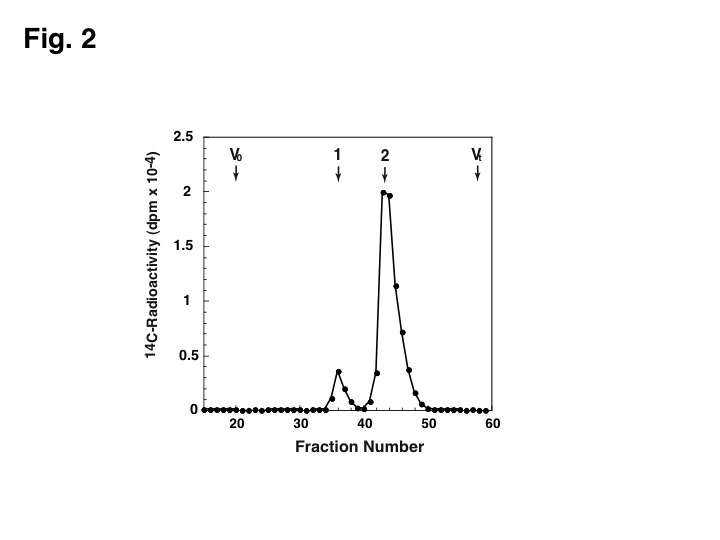
Fig. 2 Gel filtration analysis of XylT-I reaction products.
14C-labelled reaction products were isolated by gel filtration chromatography on a Superdex peptide column using 0.25M ammonium bicarbonate containing 7% 1-propanol as the eluent at a flow rate of 0.4 mL/min. The separated fractions (0.4 mL each) were measured for radioactivities. Peaks: 1, Q-E-E-E-G-S([14C]Xyl)-G-G-G-Q-K ; 2, UDP- [14C]Xyl. |
| Copyrights |
 Attribution-Non-Commercial Share Alike Attribution-Non-Commercial Share Alike
This work is released underCreative Commons licenses
|
| Date of registration:2014-09-11 13:56:31 |
- Gotting, C., Sollberg, S., Kuhn, J., Weilke, C., Huerkamp, C., Brinkmann, T., Krieg, T., and Kleesiek, K. (1999) Serum xylosyltransferase: a new biochemical marker of the sclerotic process in systemic sclerosis. J. Invest. Derm. 112, 919–924 [PMID : 10383739]
- Gotting, C., Kuhn, J., Brinkmann, T., and Kleesiek, K. (2002) Xylosyltransferase activity in seminal plasma of infertile men. Clin. Chim. Acta. 317, 199–202 [PMID : 11814476]
- Gotting, C., Prante, C., Schillinger, M., Exner, M., Domanovits, H., Raith, M., Kuhn, J., and Kleesiek, K. (2008) Xylosyltransferase I variants and their impact on abdominal aortic aneurysms. Clin Chim Acta. 391, 41–5 [PMID : 18294457]
- Brinkmann, T., Weilke, C., and Kleesiek, K. (1997) Recognition of acceptor proteins by UDP-D-xylose proteoglycan core protein b-D-Xylosyltransferase. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 11171–11175 [PMID : 9111016]
- Gotting, C., Kuhn, J., Brinkmann, T., and Kleesiek, K. (1998) Xylosylation of alternatively spliced isoforms of Alzheimer APP by xylosyltransferase. J. Prot. Chem. 17, 295–302 [PMID : 9588955]
|
This work is licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-Non-Commercial Share Alike. Please include the following citation
How to Cite this Work in an article:
Koike, Toshiyasu,
Nadanaka, Satomi,
Kitagawa, Hiroshi,
(2014). GlycoPOD https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD.
Web.26,4,2024 .
How to Cite this Work in Website:
Koike, Toshiyasu,
Nadanaka, Satomi,
Kitagawa, Hiroshi,
(2014).
Enzyme assay of xylosyltransferase.
Retrieved 26,4,2024 ,
from https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD/protocolShow.action?nodeId=t84.
html source
Koike, Toshiyasu,
Nadanaka, Satomi,
Kitagawa, Hiroshi,
(2014).
<b>Enzyme assay of xylosyltransferase</b>.
Retrieved 4 26,2024 ,
from <a href="https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD/protocolShow.action?nodeId=t84" target="_blank">https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD/protocolShow.action?nodeId=t84</a>.
Including references that appeared in the References tab in your work is
much appreciated.
For those who wish to reuse the figures/tables, please contact JCGGDB
management office (jcggdb-ml@aist.go.jp).
|
|