Epidermal growth factor (EGF) domains are posttranslationally modified with unique O-linked glycans. Here we describe methods to detect enzyme activity mediating the modification of O-GlcNAc and O-fucose glycans of EGF domains.
In vitro O-GlcNAc transferase assay
To detect O-GlcNAc transferase activity toward EGF domains, membrane fraction proteins were prepared from Drosophila S2 cells and used as an enzyme source.
|
| Category | Glycosyltransferases & related proteins |
| Protocol Name | Enzyme assay of O-fucose, fringe, and O-GlcNAc transferases modifying epidermal growth factor domains ~In vitro O-GlcNAc transferase assay |
Authors
 |
Okajima, Tetsuya
*
Department of Biochemistry II, Nagoya University Graduate School of Medicine
Furukawa, Koichi
Department of Biochemistry II, Nagoya University Graduate School of Medicine
*To whom correspondence should be addressed.
|
| KeyWords |
|
Reagents
 |
| ● |
UDP-[3H]GlcNAc (60 Ci mmol-1; American Radiolabeled Chemicals, Inc., St. Louis, MO) |
| ● |
EGF20-V5His produced in K. lactis |
| ● |
glycosylation buffer (25 mM HEPES-NaOH (pH 7.0), 1 mM MnCl2, 1 mg/mL bovine serum albumin) |
|
Instruments
 |
| ● |
nitrogen cavitation apparatus (Parr Instrument Co., Moline, IL) |
| ● |
Discovery DSC-18 SPE tubes (50 mg; Supelco/Sigma-Aldrich, Bellefote, PA) |
|
| Methods |
|
1. |
Preparation of membrane fraction proteins |
| 1) |
S2 cells were pelleted, washed with PBS, and resuspended in 1 mL of ice-cold PBS containing 1 mM phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride (PMSF). |
Comment 0
|

|
| 2) |
The cell suspension was then placed in a nitrogen cavitation apparatus, and exposed to N2 at 400 psi for 30 min. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 3) |
After release of the pressure, which disrupts the cells, the sample was centrifuged in a ST-720M rotor (Kubota) at 3,000 rpm (1,500 × g) for 5 min to remove nuclei and remaining whole cells. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 4) |
The supernatant was collected, and centrifuged in a TLS-55 (Beckman) at 40,000 rpm (100,000 × g) for 1 h at 4°C. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 5) |
The pellet was resuspended in ice-cold 50 mM HEPES-NaOH (pH 7.0), and stored at -80°C in small aliquots until used for O-GlcNAc transferase assay. |
Comment 0
|
|
|
|
2. |
O-GlcNAc transferase assay |
| 1) |
Before the reaction, UDP-[3H]GlcNAc was dried under vacuum (Speed-Vac) and resuspended in water. |
Comment 1
|

|
| 2) |
For the assay, 1.6 μM UDP-[3H]GlcNAc (60 Ci mmol-1), 2 μg of EGF20-V5His, and 0.2 μg of membrane fraction proteins were mixed in the glycosylation buffer. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 3) |
After incubation for 2 h at 25°C, the reaction was stopped by addition of 1 mL of ice-cold 50 mM EDTA. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 4) |
Discovery DSC-18 SPE tubes were conditioned by loading 1 mL of 80% acetonitrile, 0.052% TFA, and then equilibrated with 1 mL of H2O. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 5) |
The sample was loaded to the tube and washed with 5 mL of H2O, and the labeled substrates were then eluted with 2 mL of 80% acetonitrile, 0.052% TFA. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 6) |
Radioactivity in the eluate was measured using a liquid scintillation counter. |
Comment 0
|
|
|
| Figure & Legends |
Figure & Legends

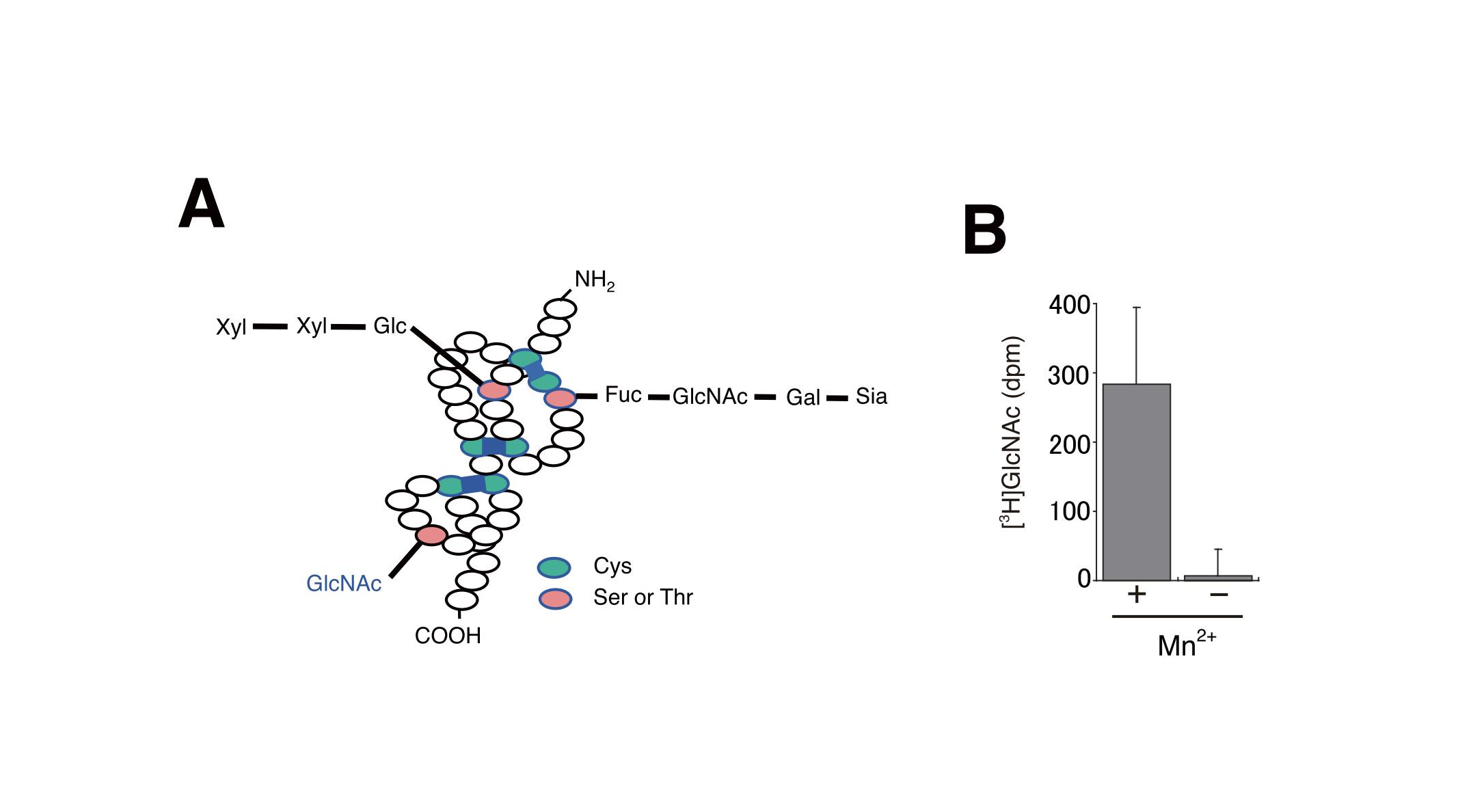
Fig. 1. Detection of O-GlcNAc transferase activity using membrane fraction proteins.
(A) The structure of O-glycans on the EGF domains.
Reprinted from Methods Enzymol., 480, Sakaidani Y, Furukawa K, Okajima T., O-GlcNAc modification of the extracellular domain of Notch receptors, 355-73, 2010, doi:10.1016/S0076-6879(10)80016-3.
(B) In vitro glycosylation assays. O-GlcNAc transferase activity was measured using S2 cell membrane fraction proteins, recombinant EGF20 and UDP-[3H]GlcNAc in the presence or absence of Mn2+. The experimental values have been adjusted by subtracting the background value obtained without acceptor substrates. Bar, S.D. (n = 3).
This figure was originally published in J Biol Chem. Matsuura A. Okajima T. et al. "O-linked N-acetylglucosamine is present on the extracellular domain of notch receptors" 2008, 283(51):35486-95. © the American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology.
|
| Copyrights |
Copyright 2010. Elsevier, for Fig.1(A) in Figure & Legends
Copyright 2010. Ritsumeikan University, JCGGDB & AIST. for the rest of the contents
|
| Date of registration:2013-12-25 10:02:15 |
- Matsuura, A., Ito, M., Sakaidani, Y., Kondo, T., Murakami, K., Furukawa, K., Nadano, D., Matsuda, T., and Okajima, T. (2008) O-linked GlcNAc is present on the extracellular domain of Notch receptors. J Biol Chem. 283, 35486-35495 [PMID : 18948267]
- Sakaidani, Y., Furukawa, K., and Okajima, T. (2010) O-GlcNAc modification of extracellular domains of Notch receptors. Methods Enzymol. 480, 355-73 [PMID : 20816217]
|
|
For those who wish to reuse the work, please contact JCGGDB management office (jcggdb-ml@aist.go.jp).
|
|