Protein O-mannosyltransferase (the complex of POMT1 and POMT2) and protein O-mannose β1,2-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase 1 (POMGnT1) catalyze the initial and the second step of O-mannosylglycan biosynthesis, respectively (Fig.1). Mutations in POMT1, POMT2 or POMGnT1 genes cause congenital muscular dystrophy with abnormal neuronal migration. |
| Category | Glycosyltransferases & related proteins |
| Protocol Name | Enzyme assay of protein-O-mannosylglycan glycosyltransferases |
Authors
 |
Manya, Hiroshi
Molecular Glycobiology, Tokyo Metropolitan Institute of Gerontology, Tokyo Metropolitan Geriatric Hospital and Institute of Gerontology
Endo, Tamao
*
Molecular Glycobiology, Tokyo Metropolitan Institute of Gerontology, Tokyo Metropolitan Geriatric Hospital and Institute of Gerontology
*To whom correspondence should be addressed.
|
| KeyWords |
|
Reagents
 |
| ● |
Complete EDTA-free, protease inhibitor cocktail (Roche, Basel, Switzerland) |
| ● |
BCA protein assay kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., Waltham, MA) |
| ● |
pGEX-4T-3 (GE Healthcare, Little Chalfont, UK) |
| ● |
Ampicillin sodium salt (Nacalai Tesque Inc., Kyoto, Japan) |
| ● |
LB broth (Life Technologies, Carlsbad, CA) supplemented with 50 μg/mL ampicillin |
| ● |
LB agar plate (1.5 w/v% agar) supplemented with 50 μg/mL ampicillin |
| ● |
Isopropyl-D-thiogalactopyranoside (IPTG) (Life Technologies) |
| ● |
CHAPS (Dojindo Laboratories, Kumamoto, Japan) |
| ● |
n-Octyl-β-D-thioglucoside (Dojindo Laboratories) |
| ● |
Triton X-100 (Nacalai Tesque Inc.) |
| ● |
Mannosylphosphoryldolichol95 [Mannose-6-3H] (Dol-P-[3H]Man, 1.48–2.22 TBq/mmol) (American Radiolabeled Chemicals, Inc., St. Louis, MO) |
| ● |
Aquasol-2 (scintillation cocktail) (Perkin Elmer, Waltham, MA) |
| ● |
UDP-N-acetyl-D-glucosamine (UDP-GlcNAc) (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO) |
| ● |
UDP-GlcNAc [glucosamine-6-3H(N)] (UDP-[3H]GlcNAc, 0.74–1.66 TBq/mmol) (Perkin Elmer) |
| ● |
Benzyl-α-D-mannopyranoside (Benzyl-Man: Sigma-Aldrich) |
| ● |
Trifluoroacetic acid (TFA: Nacalai Tesque Inc.) |
|
Instruments
 |
| ● |
Silicone blade cell scraper (SUMILON: Sumitomo Bakelite, Co., Ltd, Tokyo, Japan) |
| ● |
|
| ● |
Glutathione-Sepharose 4B (GE Healthcare) |
| ● |
Wakopak 5C18-200 column (4.6 × 250 mm: Wako Pure Chemical Industries Ltd., Osaka, Japan) |
| ● |
Potter’s Teflon homogenizer (GTR-1000: EYELA, Tokyo, Japan) |
| ● |
Tip type ultrasonic homogenizer (Astrason: Misonix, Inc. Farmngdale, NY) |
| ● |
Bath type ultrasonic homogenizer (Bioruptor: Cosmo Bio Co., Ltd., Tokyo, Japan) |
| ● |
HPLC (high performance liquid chromatography) system (Gilson, Inc. Middleton, WI) |
|
| Methods |
|
1. |
Preparation of Enzyme Sources from Tissue |
| 1) |
Tissue samples were homogenized with nine volumes (weight/volume) of 10 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.4, 1 mM EDTA, 250 mM sucrose, protease inhibitor cocktail on ice using a potter’s homogenizer. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 2) |
After centrifugation at 900 × g for 10 min, the supernatant was subjected to ultra centrifugation at 100,000 × g for 1 h. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 3) |
The precipitates were used as the microsomal membrane fraction. Protein concentration was determined by BCA assay. |
Comment 1
|
|
|
|
2. |
Preparation of Enzyme Sources from Cultured Cell (in 100 mm culture dish) |
| 1) |
The culture supernatants are removed by aspiration and the cells are rinsed gently with cold-PBS. Then, 5 mL of cold-PBS is added, and the cells scraped into centrifugal tubes and washed with 10 mL of cold-PBS. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 2) |
The cells are collected by centrifugation at 1,000 × g for 10 min at 4ºC. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 3) |
The cell pellet is broken with a tip type sonicator in 500 μL of 10 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.4, 1 mM EDTA, 250 mM sucrose, protease inhibitors cocktail. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 4) |
After centrifugation at 900 × g for 10 min, the supernatant was subjected to ultra centrifugation at 100,000 × g for 1 h. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 5) |
The precipitates were used as the microsomal membrane fraction. Protein concentration was determined by BCA assay. |
Comment 1
|
|
|
|
3. |
Preparation of GST-α-DG (acceptor substrate for POMT assay) |
| 1) |
The expression vector pGEX-GST-α-DG was constructed as follows. The region corresponding to amino acids 313-483 sites of α-DG was amplified from mouse brain total RNA by RT-PCR using the primer set 5’-GGGAATTCCACGCCACACCTACAC-3’ and 5’-GGGTCTAGAACTGGTGGTAGTACGGATTCG-3’, and subcloned it into pGEX-4T-3 to express the peptide as a glutathione-S-transferase (GST)-fusion protein. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 2) |
BL21(DE3) Escherichia coli cells are transformed with pGEX-GST-α-DG. Cultures are prepared by growing single colony overnight in LB broth at 37ºC. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 3) |
The overnight culture is then used to inoculate a fresh 50 mL culture, which is grown at 37ºC to A620 = 0.5. At this point, 1 mM IPTG is added to the culture in order to induce GST-α-DG expression. The induced cells are grown for an additional 4 h, and harvested by centrifugation at 6,000 × g for 15 min at 4ºC. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 4) |
The cell pellet is suspended in 10 mL of PBS, pH 7.4, and broken with a tip type sonicator (Semi-translucent cell suspensions are obtained by 3 sec sonication with 3-sec intervals for 5–10 min.). The cell supernatant is recovered by ultracentrifugation at 100,000 × g for 1 h. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 5) |
Recombinant GST-α-DG proteins are purified from the supernatant with a GSTrap column as follows. Pre-equilibrate the GSTrap column with 10 mL of PBS. Load the supernatant onto the column and wash with PBS at a flow rate 0.2 mL/min. The absorbed recombinant GST-α-DG proteins are eluted with 10 mL of 10 mM reduced glutathione in PBS at a flow rate 1 mL/min. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 6) |
The purified GST-α-DG is dialyzed with 50 mM (NH4)HCO3, pH 7.0. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 7) |
Protein concentration is determined by BCA assay, and the purity of GST-α-DG is checked by SDS-PAGE. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 8) |
The GST-α-DG aliquots are dispensed by 10 μg in microcentrifugal tubes, dried up with a centrifugal evaporator and kept at −80°C. |
Comment 0
|
|
|
|
4. |
|
| 1) |
Dol-P-[3H]Man (1.85 MBq) in chloroform and methanol is transferred into screw-cap centrifugal tube and evaporated with centrifugal evaporator. Add 1 mL of 20 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.0), 0.5% CHAPS and dissolve by sonication with bath type sonicator in ice-cold water. Measure radioactivity and then adjust to 40,000 cpm/μL with 20 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.0), 0.5% CHAPS. Aliquot and store at −80ºC. |
Comment 1
|

|
| 2) |
The POMT reaction buffer (10 mM Tris-HCl, pH 8.0, 2 mM 2-mercaptoethanol, 10 mM EDTA, 0.5% n-octyl-β-D-thioglucoside) is added to the microsomal membrane fraction at a protein concentration of 4 mg/mL. The fraction is suspended by moderate pipetting and solubilized for 30 min on ice with mild stirring occasionally. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 3) |
20 μL of solubilized fraction and 2 μL of Dol-P-[3H]Man solution (prepared in step 4-1) are added to the dried GST-α-DG, vortexed and spun down gently. Immediately, the reaction mixture is incubated at 22ºC for 1 h. The reaction is stopped by adding 200 μL of PBS containing 1% Triton X-100 (1% Triton-PBS). |
Comment 0
|

|
| 4) |
The reaction mixture is centrifuged at 10,000 × g for 10 min. The supernatant is transferred into a screw-cap tube with a packing seal. 400 μL of 1% Triton-PBS and 40 μL of 25% slurry glutathione-Sepharose beads in 1% Triton-PBS are mixed with the supernatant, and rotated with rotary mixer at 4ºC for 1 h. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 5) |
After centrifugation at 1,000 × g for 1 min, the supernatant is removed by aspiration, and the beads are washed 3 times with 20 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.4) containing 0.5% Triton X-100. 2% SDS is added to the beads and boiled at 100ºC for 3 min. The suspension is cooled down to room temperature and mixed with liquid scintillation cocktail. The radioactivity adsorbed to the beads is measured using a liquid scintillation counter (Fig. 2). |
Comment 0
|
|
|
|
5. |
|
| 1) |
10 μL of 1 mM UDP-GlcNAc, 10 μL of UDP-[3H]GlcNAc (100,000 dpm/nmol) and 10 μL of 100 mM Benzyl-Man are mixed in microcentrifugal tube and dried up with a centrifugal evaporator. |
Comment 1
|

|
| 2) |
The POMGnT reaction buffer (140 mM MES-NaOH (pH 7.0), 2% Triton X-100, 5 mM AMP, 200 mM GlcNAc, 10% glycerol, 10 mM MnCl2) is added to the microsomal membrane fraction at a protein concentration of 2 mg/mL. The fraction is suspended with a bath type sonicator on ice and solubilized by moderate pipetting until transparent. After centrifugation at 10,000 × g for 10 min, 20 μL of the supernatant is added to dried substrate (prepared in step 5-1), vortexed gently and incubated at 37ºC for 2 h. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 3) |
The reaction is stopped by boiling at 100ºC for 3 min. Water (180 μL) is added to the reaction mixture and filtered with a centrifugal filter device. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 4) |
The filtrate is analyzed by reversed phase HPLC on the condition as follows. The gradient solvents are aqueous 0.1% TFA (solvent A) and acetonitrile containing 0.1% TFA (solvent B). The mobile phase consists of 1) 100% A for 5 min, 2) a linear gradient to 75% A, 25% B for 20 min, 3) a linear gradient to 100% B for 1 min, and 4) 100% B for 5 min. The peptide separation is monitored by measuring the absorbance at 214 nm and the radioactivity of each fraction (1 mL) is measured by liquid scintillation counting (Fig. 3). |
Comment 0
|
|
|
| Notes | To demonstrate that gene products of POMGnT1, POMT1 and POMT2 have enzymatic activity, the cells transfected with POMGnT1 or POMT1 and POMT2 are used in Figs.2 and 3. |
| Figure & Legends |
Figure & Legends 
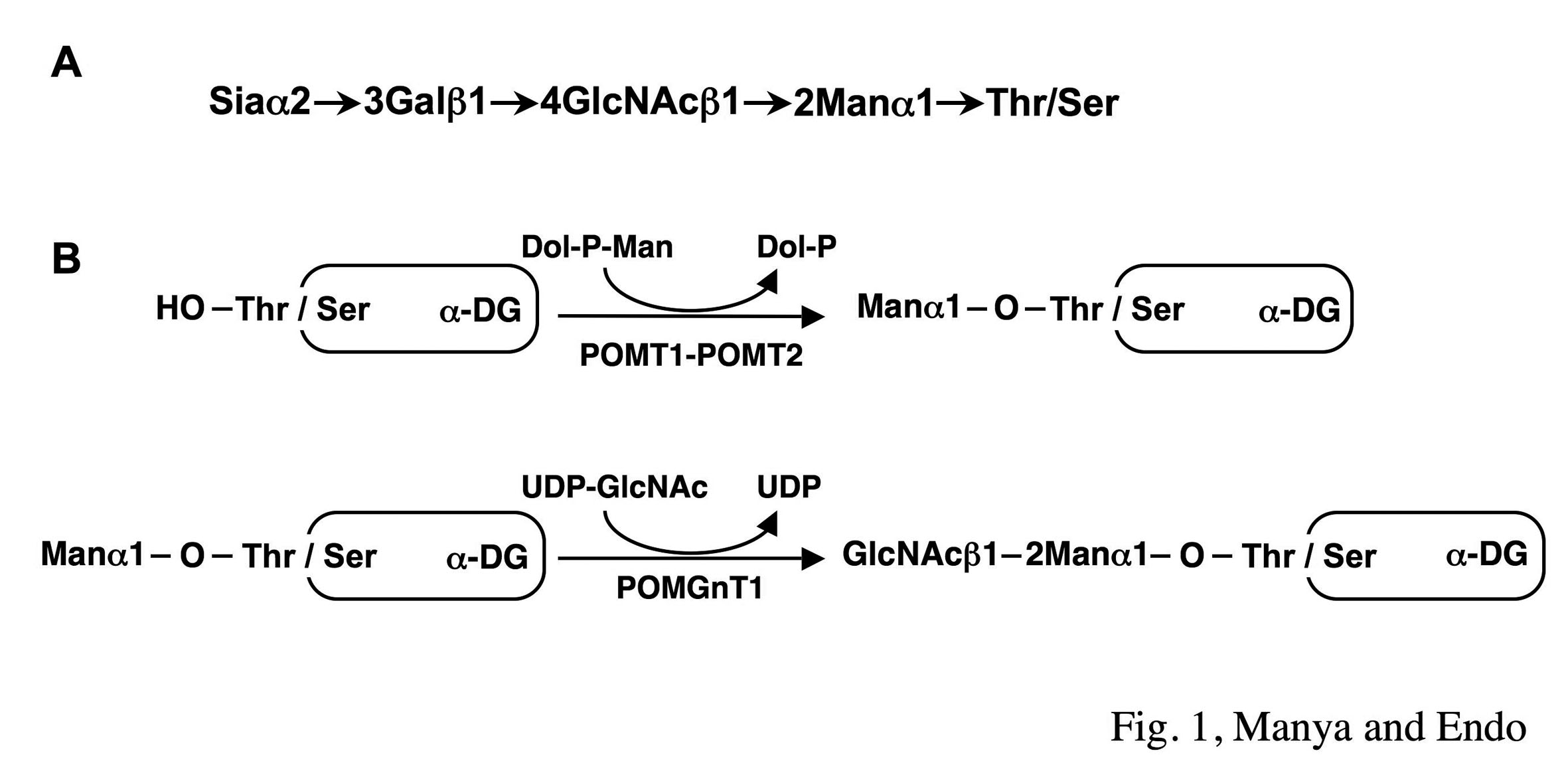
Fig. 1. Structure (A) and biosynthetic pathway (B) of O-mannosylglycan of α-DG
Two homologues, POMT1 and POMT2, are responsible for protein O-mannosylation and POMGnT1 is responsible for GlcNAcβ1-2Man linkage of O-mannosylglycan.

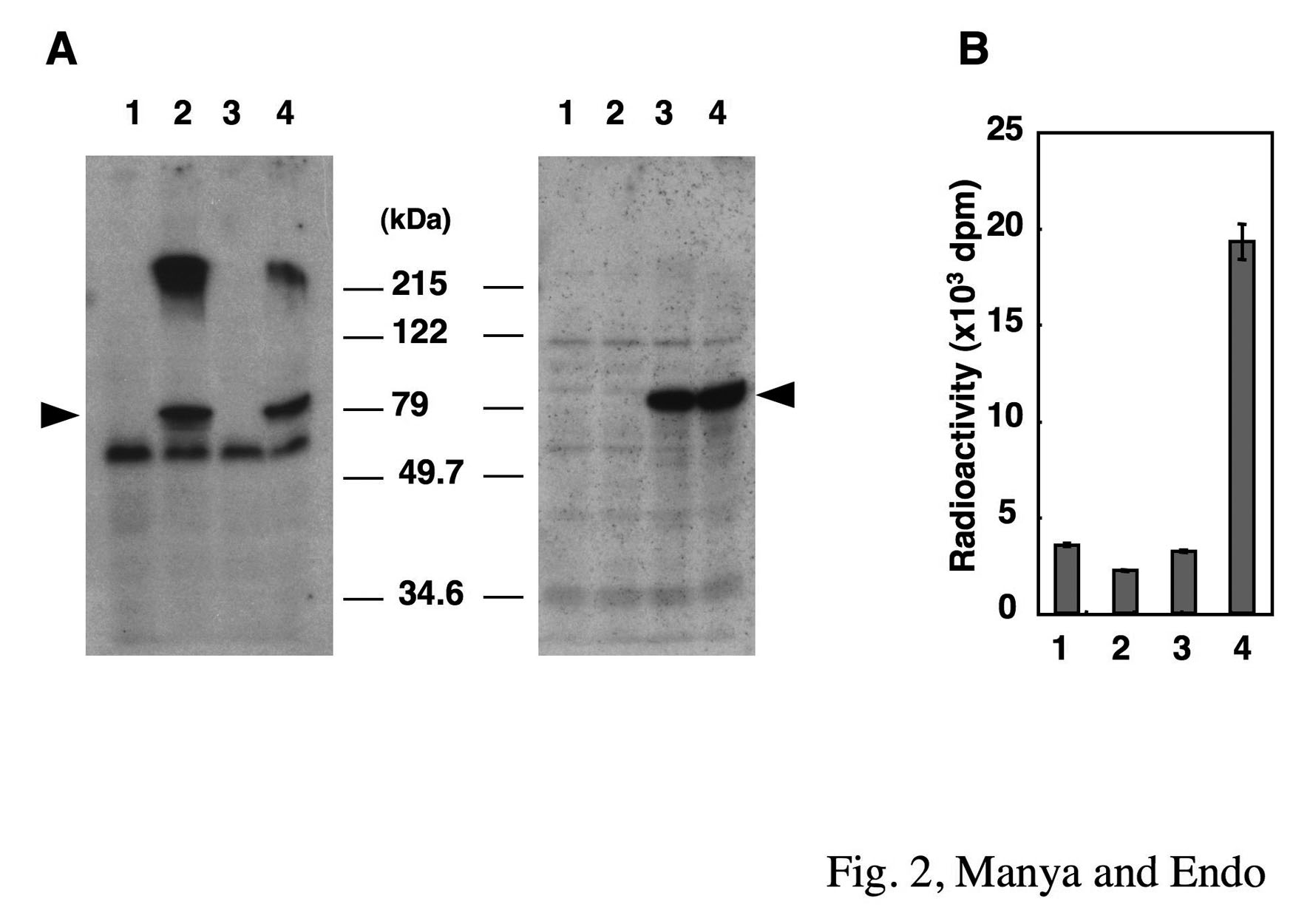
Fig. 2. Western blot analysis of POMT1 and POMT2 (A) and POMT activity of POMT1 and POMT2 (B) expressed in HEK293T cells
Lanes 1, cells transfected with vector alone; lanes 2, cells transfected with human POMT1; lanes 3, cells transfected with human POMT2; lanes 4, cells co-transfected with POMT1 and POMT2. The proteins (20 μg of membrane fraction) were subjected to SDS-PAGE (10% gel), and the separated proteins were transferred to a PVDF membrane. The PVDF membrane was stained with anti-POMT1 (left panel of A) or anti-POMT2 (right panel of A). Arrowheads indicate the positions of the corresponding molecules. Molecular weight standards are shown in the middle.
Reprinted from Methods Enzymol., 417, Endo T, Manya H., Defect in glycosylation that causes muscular dystrophy, 137–52, 2006, with permission from Elsevier. doi:10.1016/S0076-6879(06)17011-1.

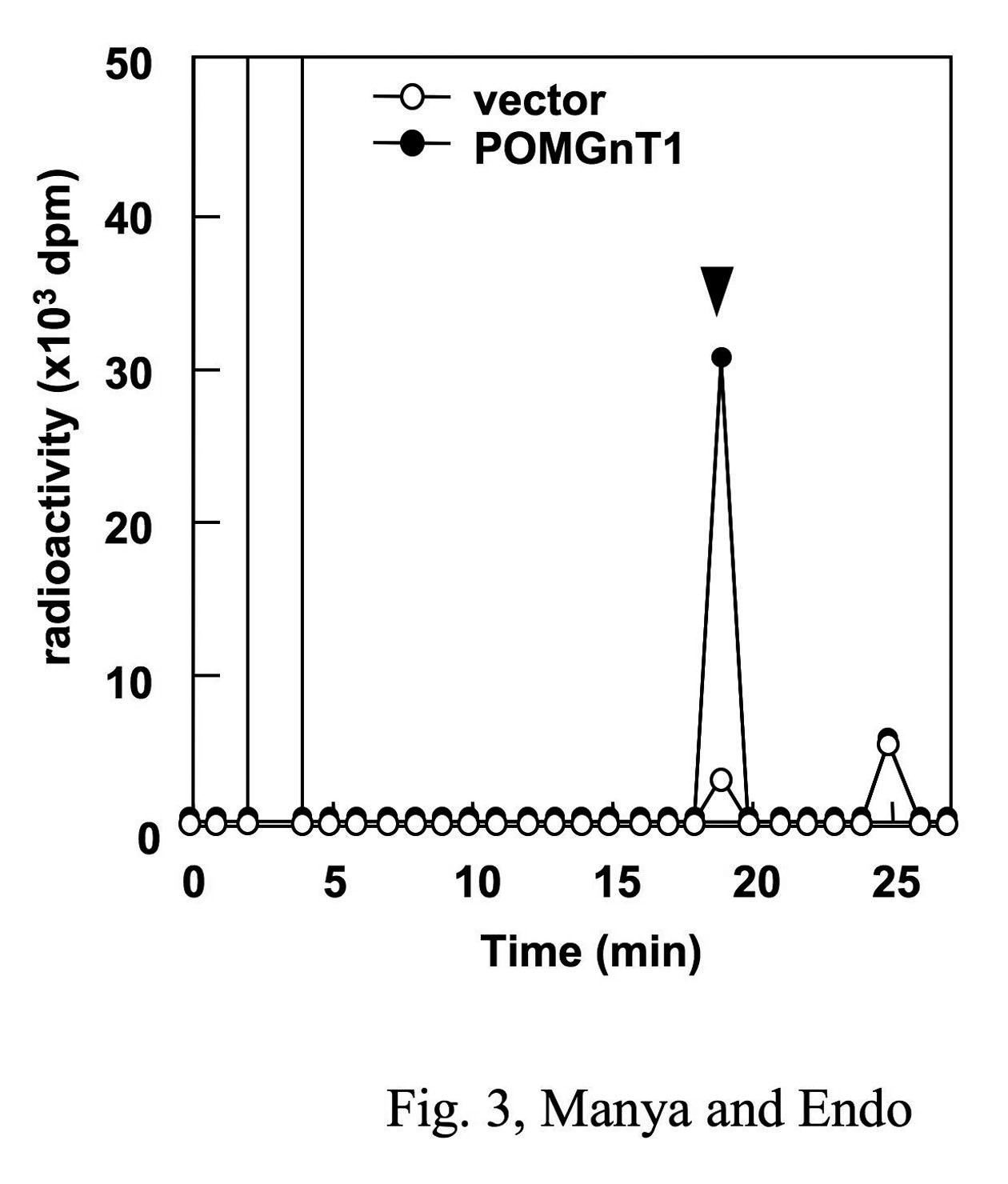
Fig. 3. POMGnT activity expressed in HEK293T cells
UDP-[3H]GlcNAc and mannosylpeptide were reacted with membrane fraction in POMGnT1 reaction buffer and then subjected to reversed-phase HPLC. Arrow indicates the elution position of the mannosylpeptide. Vector (open circle), cells transfected with vector alone; POMGnT1 (closed circle), cells transfected with human POMGnT1.
Reprinted from Methods Enzymol., 417, Endo T, Manya H., Defect in glycosylation that causes muscular dystrophy, 137–52, 2006, with permission from Elsevier. doi:10.1016/S0076-6879(06)17011-1.
|
| Copyrights |
Copyright 2006. Elsevier, for Fig. 2 & Fig. 3 in Figure & Legends
Copyright 2010. Ritsumeikan University, JCGGDB & AIST. for the rest of the contents |
| Date of registration:2014-07-31 09:14:21 |
- Endo, T., and Manya, H. (2006) Defect in glycosylation that causes muscular dystrophy. In Fukuda M (Ed) Methods Enzymol. 417, 137–152, Elsevier, San Diego [PMID : 17132503]
- Manya, H., Chiba, A., Yoshida, A., Wang, X., Chiba, Y., Jigami, Y., Margolis, R.U., and Endo, T. (2004) Demonstration of mammalian protein O-mannosyltransferase activity: coexpression of POMT1 and POMT2 required for enzymatic activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101, 500–505 [PMID : 14699049]
- Manya, H., Chiba, A., Margolis, R.U., and Endo, T. (2006) Molecular cloning and characterization of rat Pomt1 and Pomt2. Glycobiology 16, 863–873 [PMID : 16704966]
- Yoshida, A., Kobayashi, K., Manya, H., Taniguchi, K., Kano, H., Mizuno, M., Inazu, T., Mitsuhashi, H., Takahashi, S., Takeuchi, M., Herrmann, R., Straub, V., Talim, B., Voit, T., Topaloglu, H., Toda, T., and Endo, T. (2001) Muscular dystrophy and neuronal migration disorder caused by mutations in a glycosyltransferase, POMGnT1. Dev Cell. 1, 717–724 [PMID : 11709191]
|
|
For those who wish to reuse the work, please contact JCGGDB management office (jcggdb-ml@aist.go.jp).
|
|