General view on engineered mice of glycosyltransferase genes and modifying enzyme genes, and typical examples from our own laboratories were introduced. Todate, a number of glycosyltransferase genes have been isolated and genetic engineering of some of them has been achieved (Furukawa K. et al. 2001; Lowe JB and Marth JD 2003). Depending on the structures and expression patterns of individual genes, detailed constructions and approaches for resulting phenotypes are various. Just standard protocols are presented here as previously reported (Furukawa K. et al. 2006). |
| Category | Glycogene transgenic animals |
| Protocol Name | Mouse (gene-engineered mice) ~Surgical approaches for repair activity: Hypoglossal nerve resection system |
Authors
 |
Furukawa, Koichi
*
Department of Biochemistry II, Nagoya University Graduate School of Medicine
Ohmi, Yuhsuke
Department of Biochemistry II, Graduate School of Medicine, Nagoya University
*To whom correspondence should be addressed.
|
| KeyWords |
|
| Methods |
|
1. |
Mouse (gene-engineered mice) ~Surgical approaches for repair activity: Hypoglossal nerve resection system |
| 1) |
Cleavage of mouse hypoglossal nerve and glycolipid injection: Mice are anesthetized by an intraperitoneal injection of 20 - 30 mg/kg sodium pentobarbital, and the right hypoglossal nerve (RHN) are cleaved. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 2) |
In the glycolipid-injected group, various amount of glycolipid mixture (G-mix) (2 - 0.002 μg) dissolved in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) was injected into the nerve stump site. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 3) |
HRP injection: Ten weeks after these treatments, 20 μL of 30% horseradish peroxidase in sterile saline is injected into various parts of the tongue of mice as described previously (Streit P. and Reubi JC. 1977). |
Comment 0
|

|
| 4) |
Counting of neurons at the hypoglossal nerve nucleus: After 24 h, the animals are anesthetized deeply and perfused intracardially with 0.9% saline containing heparin-Na, and fixed with 10% formalin in 0.1 M phosphate buffer. The lower brain stem is dissected, and 50 μm serial cross-sections are prepared on a freezing microtome. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 5) |
The sections are then incubated with a mixture of 3,3’-diaminobenzidine and hydrogen peroxide at room temperature for 40 min, mounted on 3-aminopropyl-trienthoxysilane (Sigma Aldrich, St. Louis, MO) coated glass slides, and counterstained with 1% cresyl violet. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 6) |
Only cells containing a clearly visible HRP vesicle in the cytoplasm are counted in every fifth section. Same counting procedure is performed for the untreated left hypoglossal nerve (LHN) and its result is used to obtain the percent ratio (RHN/LHN). |
Comment 0
|

|
| 7) |
To follow the time course of neuronal death and nerve regeneration, mice are sacrificed at 2, 4, 6, 8, 10 and 20 weeks after the operation, and served for the histological analyses. An example with GD3 synthase null mice is presented in Fig. 1 (Okada M. et al. 2002). |
Comment 0
|
|
|
| Discussion | We need to keep in mind that cerebellar defects result in performance deficits in the rota-rod test.
To analyze the potential of repair for damaged nervous tissues, various devices have been developed in the central nervous system or peripheral nerves such as sciatic nerve. We have developed an efficient system to estimate nerve repair potential primarily with rat hypoglossal nerve (Itoh M. et al. 1999).
Morphological approaches:
See the reference (Inoue M. et al. 2002)
Detection of low level glycolipids
Efficient histology and immnohistochemistry can be performed using KO mice tissues. See the reference (Okuda T. et al. 2006) |
| Figure & Legends |
Figure & Legends 
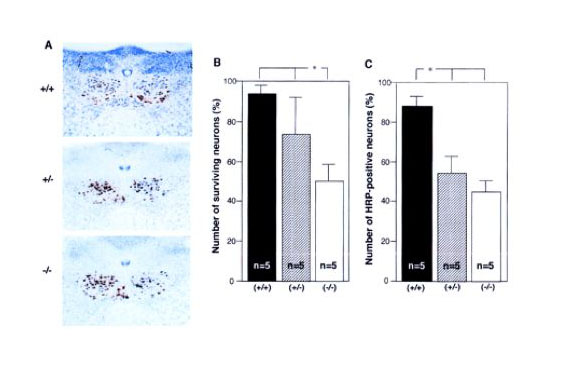
Fig. 1. Reduced regeneration of the axotomized hypoglossal nerves in the mutant mice of GD3 synthase gene
A) HRP-stained patterns of the hypoglossal nerve nuclei in the wild-type (+/+), heterozygote (+/–), and homozygote mice (–/–) at 10 weeks after the nerve resection. Regeneration of the axotomized nerves was examined by staining the sections with 3,3’-diaminobenzidine. B) numbers of surviving neurons 10 weeks after the operation were counted and plotted. C) numbers of HRP-positive neurons were counted and plotted. B and C show the mean ± S.D. (n is as indicated). * represents p < 0.005.
This figure was originally published in J Biol Chem. Okada M, Furukawa K. et al. "b-series Ganglioside deficiency exhibits no definite changes in the neurogenesis and the sensitivity to Fas-mediated apoptosis but impairs regeneration of the lesioned hypoglossal nerve" 2002, 277(3):1633-6. © the American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology. |
| Copyrights |
 Attribution-Non-Commercial Share Alike Attribution-Non-Commercial Share Alike
This work is released underCreative Commons licenses
|
| Date of registration:2014-02-26 17:50:12 |
- Okuda, T., Tokuda, N., Numata, S., Ito, M., Ohta, M., Kawamura, K., Wiels, J., Urano, T., Tajima, O., Furukawa, K., and Furukawa, K.. (2006) Targeted disruption of Gb3/CD77 synthase gene resulted in the complete deletion of globo-series glycosphingolipids and loss of sensitivity to verotoxins. J. Biol. Chem. 281, 10230-5. [PMID : 16476743]
- Inoue, M., Fujii, Y., Furukawa, K., Okada, M., Okumura, K., Hayakawa, T., Furukawa, K., and Sugiura, Y. (2002) Refractory skin injury in complex knock-out mice expressing only the GM3 ganglioside. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 29881-8. [PMID : 12023957]
- Itoh, M., Fukumoto, S., Baba, N., Kuga, Y., Mizuno, A., and Furukawa, K.. (1999) Prevention of the death of the rat axotomized hypoglossal nerve and promotion of its regeneration by bovine brain gangliosides. Glycobiology 9, 1247-52. [PMID : 10536040]
- Streit, P. and Reubi J.C. (1977) A new and sensitive staining method for axonally transported horseradish peroxidase (HRP) in the pigeon visual system. reported horseradish peroxidase (HRP) in the pigeon visual system. Brain Res. 126, 530-7. [PMID : 67876]
- Okada, M., Itoh, Mi. M., Haraguchi, M., Okajima, T., Inoue, M., Oishi, H., Matsuda, Y., Iwamoto, T., Kawano, T., Fukumoto, S., Miyazaki, H., Furukawa, K., Aizawa, S., and Furukawa, K. (2002) b-series Ganglioside deficiency exhibits no definite changes in the neurogenesis and the sensitivity to Fas-mediated apoptosis but impairs regeneration of the lesioned hypoglossal nerve. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 1633-6. [PMID : 11682464]
|
This work is licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-Non-Commercial Share Alike. Please include the following citation
How to Cite this Work in an article:
Furukawa, Koichi,
Ohmi, Yuhsuke,
(2014). GlycoPOD https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD.
Web.25,4,2024 .
How to Cite this Work in Website:
Furukawa, Koichi,
Ohmi, Yuhsuke,
(2014).
Mouse (gene-engineered mice) ~Surgical approaches for repair activity: Hypoglossal nerve resection system.
Retrieved 25,4,2024 ,
from https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD/protocolShow.action?nodeId=t41.
html source
Furukawa, Koichi,
Ohmi, Yuhsuke,
(2014).
<b>Mouse (gene-engineered mice) ~Surgical approaches for repair activity: Hypoglossal nerve resection system</b>.
Retrieved 4 25,2024 ,
from <a href="https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD/protocolShow.action?nodeId=t41" target="_blank">https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD/protocolShow.action?nodeId=t41</a>.
Including references that appeared in the References tab in your work is
much appreciated.
For those who wish to reuse the figures/tables, please contact JCGGDB
management office (jcggdb-ml@aist.go.jp).
|
|