General view on engineered mice of glycosyltransferase genes and modifying enzyme genes, and typical examples from our own laboratories were introduced. Todate, a number of glycosyltransferase genes have been isolated and genetic engineering of some of them has been achieved (Furukawa K. et al. 2001; Lowe JB and Marth JD 2003). Depending on the structures and expression patterns of individual genes, detailed constructions and approaches for resulting phenotypes are various. Just standard protocols are presented here as previously reported (Furukawa K. et al. 2006).
Depending on the step at which the targeted gene product is located, the effects of gene knock-out are various, and approaches required to be done are widely diversed. Here, representative analyses performed for some mutant mice were described.
Construction of targeting gene and generation of homologous recombinant ES cells. An example of a targeting vector for β1,4-GalNAc-T (GM2/GD2 synthase) gene is in the reference (Takamiya K. et al. 1996). |
| Category | Glycogene transgenic animals |
| Protocol Name | Mouse (gene-engineered mice) ~Knock-out strategy |
Authors
 |
Furukawa, Koichi
*
Department of Biochemistry II, Nagoya University Graduate School of Medicine
Ohmi, Yuhsuke
Department of Biochemistry II, Graduate School of Medicine, Nagoya University
*To whom correspondence should be addressed.
|
| KeyWords |
|
Reagents
 |
| ● |
Genome fragments containing significant range of regions encompassing some parts of a glycosyltransferase gene to be disrupted |
| ● |
A vector for insertion of the genome fragment containing units for negative and positive selection |
| ● |
Standard enzymes and competent cells for DNA manipulations (Takara Bio Inc., Otsu, Japan) |
| ● |
|
| ● |
RPMI1640 and fetal calf serum screened for ES cell culture |
| ● |
LIF (Chemicon/Life Technologies, Carlsbad, CA) |
| ● |
Feeder layer cell stock (neo-resistant) (Gibco/Life Technologies, Carlsbad, CA) |
|
Instruments
 |
| ● |
Phase microscope (Olympus, Tokyo, Japan) |
| ● |
Electroporation apparatus (Genepulser, Bio-Rad Laboratories, Carlsbad, CA) |
| ● |
Microinjection apparatus (Olympus, Tokyo, Japan) |
|
| Methods |
|
1. |
Mouse (gene-engineered mice) ~Knock-out strategy |
| 1) |
The targeting plasmid was constructed containing a neomycin-resistant gene (with PGK promoter) inserted into the exon 4. The homologous gene spanned about 7.5 kbp, and diphtheria toxin-A (DT-A) gene is attached. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 2) |
Establishment of homologous recombinant of an ES cell line: The targeting vector (24 nM) is linealized with Not I and is mixed with ES cell (TT2) suspension (1x107), then electroporated at 0.25 kV, 960 μF. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 3) |
At forty-eight hours after electroporation, G418 is added to the medium at the concentration of 150 μg/mL. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 4) |
After 7-8 days, the G418-resistant clones were isolated and subjected to screening for homologous recombination by PCR. The sense primer is 5’-TCGTGCTTTA CGGTATCGCCGCTCCCGATT-3 in 3’ terminus of PGK neo, and the antisense primer was 5’-GGGTGTGGCGGCATACATCT-3’ in the intron of the β1,4-GalNAc-T. The reaction was started one cycle of 95°C (2 min), 55°C (1 min), 74°C (5 min), thereafter 35 cycles of 94°C (1 min), 60°C (30 sec), 74°C (1.5 min) are used. Homologous recombinant clones give a 1.1-kb fragment.
Alternative example: Another example of a targeting construct was shown in Fig. 1, that is generated for knock-out of Gb3/CD77 gene (Okuda T. et al. 2006). Here, the neor gene (Neo) was inserted between two BanI sites, and diphtheria toxin-A gene (DTA) is inserted at both sides as indicated.
For the screening of homologous recombinat clones, Southern blotting is performed, where genomic DNA of neo-resistant clones is digested with EcoRV or BglII and electrophoresed before being hybridized with probe-1, 10.5 kb, wild-type allele; 5.8 kb, recombinant allele (EcoRV); 6.2 kb, wild-type allele; and 7.3 kb, recombinant allele (BglII) (Fig. 2). |
Comment 0
|

|
| 5) |
Northern blotting of α1,4Gal-T was shown in the reference (Okuda T. et al. 2006). mRNA (2.4 kb) is detected with a1,4Gal-T cDNA probe (upper). Ribosomal RNAs detected with ethidiumbromide are shown as the control (bottom). +/+, wild type; +/–, heterozygote; –/–, homozygote. Note complete loss of the transcripts. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 6) |
The products of the enzyme assay (Gb3 synthase) using UDP[14C]galactose and LacCer are analyzed by TLC/autoradiography (left). TLC of neutral glycolipids from kidney tissues with a solvent system chloroform/methanol/water (60:35:8) is visualized by orcinol-H2SO4. |
Comment 0
|
|
|
| Discussion | For the construction of targeting gene, we need to know the deduced enzyme structure and whole domains such as catalytic domain. When the catalytic domain is coded with multiple exons, it seems safety to delete or replace relatively 5’-side in the catalytic domain-coding region. It may be possible to disrupt the exon containing ATG, and render the remainig coding region inactive. |
| Figure & Legends |
Figure & Legends

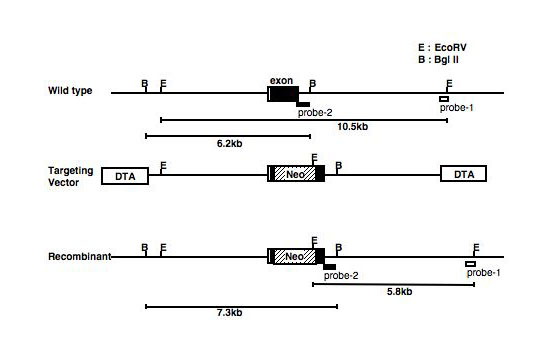
Fig. 1. Another example of a targeting construct
A targeting vector for Gb3/CD77 gene.
This figure was originally published in J Biol Chem. Okuda T, Furukawa K. et al. "Targeted disruption of Gb3/CD77 synthase gene resulted in the complete deletion of globo-series glycosphingolipids and loss of sensitivity to verotoxins" 2006, 281(15):10230-5. © the American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology.

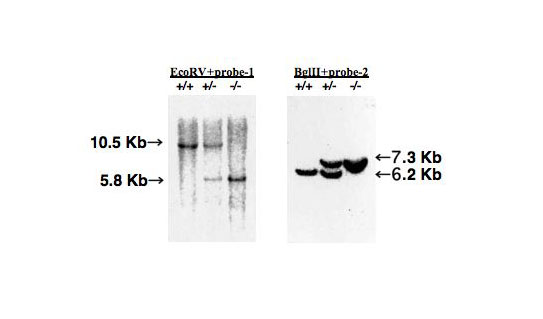
Fig. 2. Southern blotting to confirm homologous recombination of Gb3/CD77 synthase gene
Genomic DNA of neo-resistant clones is digested with EcoRV or BglII and electrophoresed before hybridization with probe-1, 10.5 kb, wild-type allele; 5.8 kb, recombinant allele (EcoRV); 6.2 kb, wild-type allele; and 7.3 kb, recombinant allele (BglII).
This figure was originally published in J Biol Chem. Okuda T, Furukawa K. et al. "Targeted disruption of Gb3/CD77 synthase gene resulted in the complete deletion of globo-series glycosphingolipids and loss of sensitivity to verotoxins" 2006, 281(15):10230-5. © the American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology. |
| Copyrights |
 Attribution-Non-Commercial Share Alike Attribution-Non-Commercial Share Alike
This work is released underCreative Commons licenses
|
| Date of registration:2014-02-26 17:47:22 |
- Takamiya, K., Yamamoto, A., Furukawa, K., Yamashiro, S., Shin, M., Okada, M., Fukumoto, S., Haraguchi, M., Takeda, N., Fujimura, K., Sakae, M., Kishikawa, M., Shiku, H., Furukawa, K., and Aizawa, S. (1996) Mice with disrupted GM2/GD2 synthase gene lack complex gangliosides but exhibit only subtle defects in their nervous system. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 93, 10662-7. [PMID : 8855236]
- Okuda, T., Tokuda, N., Numata, S., Ito, M., Ohta, M., Kawamura, K., Wiels, J., Urano, T., Tajima, O., Furukawa, K., and Furukawa, K. (2006) Targeted disruption of Gb3/CD77 synthase gene resulted in the complete deletion of globo-series glycosphingolipids and loss of sensitivity to verotoxins. J. Biol. Chem. 281, 10230-5. [PMID : 16476743]
|
This work is licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-Non-Commercial Share Alike. Please include the following citation
How to Cite this Work in an article:
Furukawa, Koichi,
Ohmi, Yuhsuke,
(2014). GlycoPOD https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD.
Web.24,4,2024 .
How to Cite this Work in Website:
Furukawa, Koichi,
Ohmi, Yuhsuke,
(2014).
Mouse (gene-engineered mice) ~Knock-out strategy.
Retrieved 24,4,2024 ,
from https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD/protocolShow.action?nodeId=t39.
html source
Furukawa, Koichi,
Ohmi, Yuhsuke,
(2014).
<b>Mouse (gene-engineered mice) ~Knock-out strategy</b>.
Retrieved 4 24,2024 ,
from <a href="https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD/protocolShow.action?nodeId=t39" target="_blank">https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD/protocolShow.action?nodeId=t39</a>.
Including references that appeared in the References tab in your work is
much appreciated.
For those who wish to reuse the figures/tables, please contact JCGGDB
management office (jcggdb-ml@aist.go.jp).
|
|