Zebrafish (Danio rerio), a small ~3 cm long tropical fish, has been shown to be a powerful model for investigations of development. Zebrafish are easy to breed with a short generation time, approximately 3 months, and the females can lay hundreds of eggs at weekly intervals. Fertilization is external, allowing easy access to embryos for observation and manipulation. The process of development is easily observed under a dissecting microscope since the eggs are transparent. Despite a lack of technology for gene knockout by homologous recombination, targeted gene knockdown using morpholino antisense oligo (MO) has been successfully applied to zebrafish. Morpholinos are chemically modified oligonucleotides with similar base-stacking abilities to natural genetic material but have a morpholone moiety instead of a ribose (Fig. 1a, green). In addition, a phosphorodiamidate linkage is used, resulting in a neutrally charged backbone (Fig. 1a, red). These two modifications produce a modified and highly soluble polymer capable of hybridizing single-stranded nucleic acid sequences with high affinity and little cellular toxicity and free of most non-specific side effects. MOs inhibit the functions of genes in a sequence-specific manner as translational or splicing blockers (Nasevicius A. et al. 2000, Draper B. W. et al. 2001). MOs in which are designed a 5’ region near the start codon of mRNA of the targeted gene act as a translation blocker. The translation blocker-MOs inhibit progression of the initiation complex, resulting in a blockade of translation from the targeted mRNA (Fig. 1b). MOs targeting the first exon and intron or the last exon and intron boundary of the pre-mRNA alter the splicing site, resulting in the retention of a short stretch of intron (Fig.1d). On the other hand, MOs targeting other exon-intron boundaries can delete part or all of the exon (Fig. 1e). These splicing-blocker MOs have the advantage that the efficacy of gene knockdown can be quantified without use of antibodies. This powerful tool offers the opportunity to pursue sequence-specific gene targeting studies without the necessity for laborious, time-consuming and expensive mutant studies. In this section, we introduce how to inject the MOs into zebrafish embryos and our experimental data showing the knockdown of glucosylceramide synthase (UDP-glucose:ceramide glucosyltransferase, GlcT-1) during the early development of zebrafish. |
| Category | Glycogene transgenic animals |
| Protocol Name | Effective targeted gene knockdown using morpholino antisense oligos in early development of zebrafish |
Authors
 |
Yoshimura, Yukihiro
*
Faculty of Health and Welfare Science, Okayama Prefectural University
Ito, Makoto
Department of Bioscience and Biotechnology, Graduate School of Bioresource and Bioenvironmental Sciences, Kyushu University
*To whom correspondence should be addressed.
|
| KeyWords |
|
Reagents
 |
| ● |
Morpholino oligonucleotide (GeenTools)
MO is dissolved in distilled water at 1–4 mM (stock solution). Before the phenotype is analyzed, the working concentration of MOs and knockdown efficiency must be checked by RT-PCR (splicing-blocker), Western blotting (splicing-, and translation-blocker), or enzymatic assay (if the product of the target gene has enzymatic activity). |
| ● |
E3 embryo medium (5 mM NaCl, 0.17 mM KCl, 0.33 mM CaCl2, 0.33 mM MgSO4, and 10-5% methylene blue) |
|
Instruments
 |
| ● |
Embryos
The night before the injection, place one male and one female separately into a mating box in which each fish is separated by a divider. On the morning of the injection, the fish are put together and usually will mate within 10 min. For efficient knockdown, the injection into embryos should be done at the one- to two-cell stage (approximately 60 min after mating). |
| ● |
Microinjection plate
As zebrafish eggs are fairly buoyant and move easily during injection, it is recommended to use a microinjection plate in which eggs are kept at the correct position for injection. Narrow slope slots (2–3 mm wide, 1–2 mm depth, slope at 30–45°) are made on an acryl plate to use it as a microinjection plate. Alternatively, the microinjection plate can be replaced with 1.5% agarose. |
| ● |
Microinjection needle
To prepare microinjection needles, pull glass capillaries (e.g. GD-1, Narishige Co., Ltd., Tokyo, Japan) on a needle puller (e.g. PC-10, Narishige Co., Ltd.). The diameter of the needle should be thick enough to allow easy penetration of the chorion, however too much diameter may damage the embryo. As the injection should be done within 60 min in after mating, it is recommended that the needles be prepared before starting the experiment. |
| ● |
Microinjection apparatus
A typical microinjection set-up consists of a stereomicroscope, a micromanipulator (e.g. M-152, Narishige Co., Ltd.), and a pneumatic microinjector (e.g. IM-30, Narishige Co., Ltd.) |
| ● |
Forceps (No.5, INOX, Muromachi Kikai Co., Ltd., Tokyo, Japan) |
| ● |
Microloader pipet tips (Eppendorf AG, Hamburg, Germany) |
|
| Methods |
|
1. |
Effective targeted gene knockdown using morpholino antisense oligos in early development of zebrafish |
| 1) |
Attach the microinjection needle to the manipulator before collecting eggs. Fill the needle with a suitable MO solution using a microloader pipet tip (see Comment). Attach the needle with the MO solution to the micromanipulator. |
Comment 1
|

|
| 2) |
Collect the eggs into a 10-cm Petri dish filled with E3 medium or water for culture. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 3) |
Transfer and arrange the eggs within the slots of the microinjection plate (see Comment). Place the plate under a stereomicroscope and make sure that the embryos are at the one- to two-cell stage. |
Comment 1
|

|
| 4) |
Break off the tip of the needle with fine forceps under a stereomicroscope. Use the manipulator to bring the needle tip close to the embryo. Discharge the pressure using the foot switch (e.g. 25 psi, 100 msec) and estimate the volume (diameter) of a droplet from the diameter of the embryo (see Comment *). Adjust the volume by changing the discharge time (see Comment **). |
Comment 1
|

|
| 5) |
Drive the tip of the needle into the yolk of the embryo through the chorion under the control of the micromanipulator. Discharge the solution into the yolk of the embryo (see Comment). |
Comment 1
|

|
| 6) |
Withdraw the tip from the embryo by lifting the needle slowly (see Comment). |
Comment 1
|

|
| 7) |
Move the plate slightly to locate the next embryo, and inject the solution. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 8) |
Tilt the microinjection plate and add E3 medium to the slots to slide the embryos down to a dish filled with E3 medium. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 9) |
Incubate the dish at 28.5°C until the time of observation or harvest (see Comment). |
Comment 1
|
|
|
| Figure & Legends |
Figure & Legends 
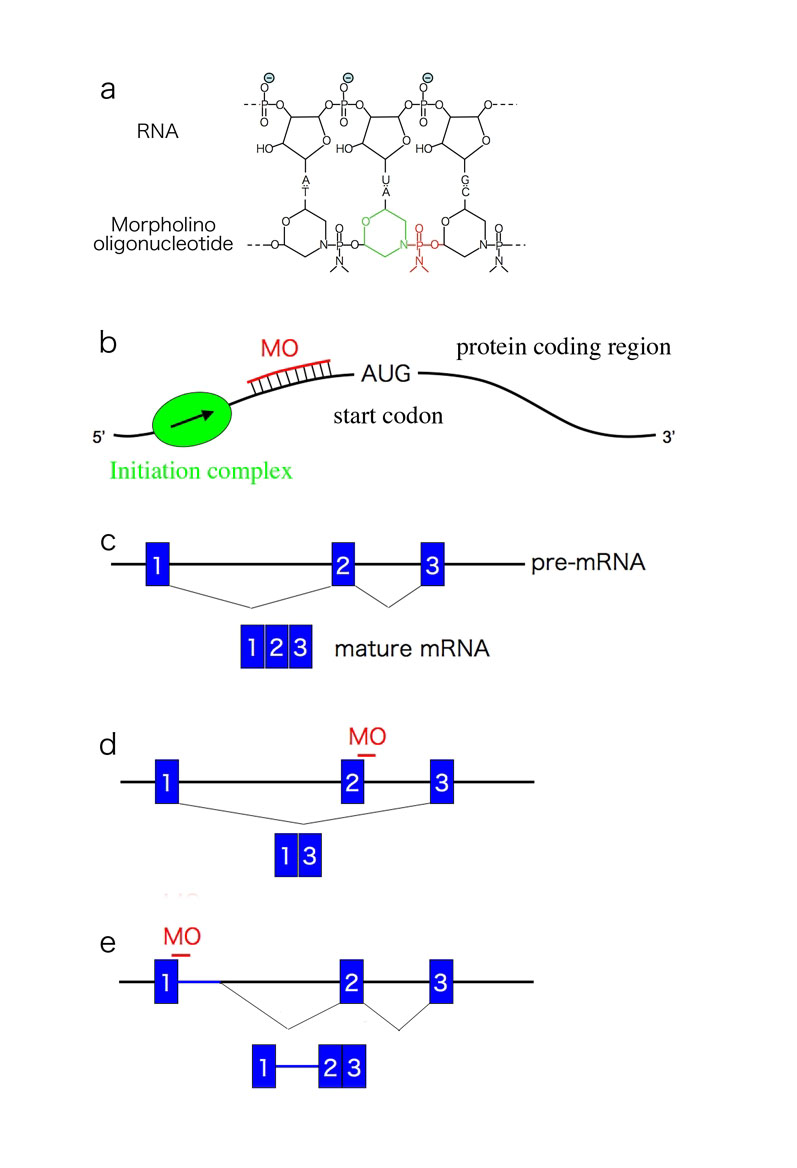
Fig. 1. Structure and mechanism of MOs
a) Structure of MO with target RNA. Note the six-membered morpholino ring (green) and the non-ionic phosphodiemidate link between the two rings (red). b) Inhibition of translation by a translation-inhibitor MO. The MO targets the 5’ of the start codon and inhibits progression of the initiation complex. c-e) Schematic diagram of actions of the splicing- blocker MO. |
| Copyrights |
 Attribution-Non-Commercial Share Alike Attribution-Non-Commercial Share Alike
This work is released underCreative Commons licenses
|
| Date of registration:2015-11-16 14:10:49 |
- Nasevicius, A., and Ekker, S. C. (2000) Effective targetes gene 'knockdown' in zebrafish. Nat. Genet. 26, 216–220 [PMID : 11017081]
- Draper, B. W., Morcos, P. A., and Kimmel, C. B. (2001) Inhibition of zebrafish fgf8 pre-mRNA splicing with morpholino oligos: a quantifiable method for gene knockdown. Genesis 30, 154–156 [PMID : 11477696]
- Komori, H., Ichikawa, S., Hirabayashi, Y., and Ito, M. (2000) Regulation of UDP-glucose: ceramide glucosyltransferase-1 by ceramide. FEBS Lett. 475, 247–250 [PMID : 10869565]
|
This work is licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-Non-Commercial Share Alike. Please include the following citation
How to Cite this Work in an article:
Yoshimura, Yukihiro,
Ito, Makoto,
(2015). GlycoPOD https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD.
Web.19,4,2024 .
How to Cite this Work in Website:
Yoshimura, Yukihiro,
Ito, Makoto,
(2015).
Effective targeted gene knockdown using morpholino antisense oligos in early development of zebrafish.
Retrieved 19,4,2024 ,
from https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD/protocolShow.action?nodeId=t34.
html source
Yoshimura, Yukihiro,
Ito, Makoto,
(2015).
<b>Effective targeted gene knockdown using morpholino antisense oligos in early development of zebrafish</b>.
Retrieved 4 19,2024 ,
from <a href="https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD/protocolShow.action?nodeId=t34" target="_blank">https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD/protocolShow.action?nodeId=t34</a>.
Including references that appeared in the References tab in your work is
much appreciated.
For those who wish to reuse the figures/tables, please contact JCGGDB
management office (jcggdb-ml@aist.go.jp).
|
|