Glycosyltransferase
Enzyme assay
Analytical method |
| Category | Glycosyltransferases & related proteins |
| Protocol Name | Enzyme assay of polypeptide N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase, β1,3-glycosyltransferase, ang β1,4-glycosyltransferases. [4] General methods for detection of enzyme reaction products |
Authors
 |
Togayachi, Akira
Research Center for Medical Glycoscience, National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST)
Kubota, Tomomi
Research Center for Medical Glycoscience, National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST)
Sato, Takashi
Research Center for Medical Glycoscience, National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST)
Narimatsu, Hisashi
Research Center for Medical Glycoscience, National Instutute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST)
|
| KeyWords |
|
Reagents
 |
| ● |
TSK-gel ODS-80TS column (4.6 × 300 mm; Tosoh Corp., Tokyo, Japan) |
| ● |
PALPAK type R column (4.6 × 250 mm; Takara Bio Inc., Otsu, Japan) |
|
Instruments
 |
|
| Methods |
|
1. |
HPLC for oligosaccharides |
| 1) |
The enzyme reaction is terminated by the boil for 3 min, followed by dilution with water. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 2) |
After centrifugation of the reaction mixtures at 15,000 r.p.m. for 5 min., 10 μL of each supernatant is subjected to HPLC analysis through a TSK-gel ODS-80TS column (4.6 × 300 mm; Tosoh Corp.) or a PALPAK type R column (4.6 × 250 mm; Takara Bio Inc.). |
Comment 0
|

|
| 3) |
The reaction products are eluted with 20 mM ammonium acetate buffer (pH 4.0) at a flow rate of 1.0 mL/min at 25°C. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 4) |
The substrate and product are monitored with a fluorescence spectrophotometer, JASCO FP-920 (JASCO Corporation, Tokyo, Japan). (The substrate and product are detectable with radioisotope, UV, or fluorescence.) |
Comment 0
|
|
|
|
2. |
|
| 1) |
HPLC method using a reverse-phase column is described, as an example. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 2) |
The reaction mixture is filtrated with a 0.22 μm filter. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 3) |
The resulting solution is applied into a C18 reverse column (Waters, 5C18-AR, 4.6×250 mm) equilibrated with 0.05% TFA on the HPLC. The column temperature is 40°C. The flow rate is 1.0 mL/min. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 4) |
The substrate and the products are typically eluted with a 0–50% linear gradient of acetonitrile in 0.05% TFA. Note that the elution conditions will be affected by the peptide sequence, the attached hydrophobic and/or fluorescence tag and the number of attached saccharide. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 5) |
The elution pattern of absorbance at 220 nm or fluorescence is analyzed. Usually, GalNAc attachment will shorten the retention time in the reverse phase chromatography. (Fig. 1.) |
Comment 0
|

|
| 6) |
The eluted peak fractions can be recovered in order to identify the number of GalNAc and the attachment sites (see Protocol Title "Large-scale identification of N-glycosylated peptides using lectin-mediated affinity capture, glycosylation site-specific stable isotope tagging, and LC/MS" by Kaji, Hiroyuki). Typically, the negative control without the donor substrate or the enzyme should be concomitantly analyzed. |
Comment 0
|
|
|
|
3. |
Thin layer chromatography (TLC) for oligosaccharides, especially glycolipids
The product is detectable with radioisotope, a chemical reagent such as orcinol and resorcinol, or fluorescence. |
| 1) |
Reaction products are separated by TLC (Glass HPTLC Silica gel 60 plate ; MERCK MILLIPORE, Germany) with mixtures of chloroform/methanol/water (60: 35: 8). |
Comment 0
|

|
| 2) |
Products and substrate are chemically developed with reagents, such as orcinol or resorcinol solution. Or they are immunostained with lectin or antibody. |
Comment 0
|
|
|
|
4. |
Scintillation counter for various products from radioisotope-labeled donor substrates.
It is necessity to isolate the products from the reaction mixture. For example, use an acceptor substrate which is labeled with hydrophobic residue such as (poly)LacNAc-Bz (Np), and the reacted product is isolated with SepPak C18 cartridge. |
| 1) |
Radioactive products are separated from the free RI-labeled donor substrates using a Sep-Pak Plus C18 cartridge (Waters Corp., Milford, MA). |
Comment 0
|

|
| 2) |
The cartridge is activated by being washed with 1 mL of 100% methanol and then twice with 1 mL of water. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 3) |
The enzyme reaction is terminated by addition of 100 μL of H2O, and the reaction mixture is applied to the equilibrated cartridge and washed twice with 1 mL of water. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 4) |
The radioactive product is eluted with 1 mL of 100% methanol. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 5) |
The eluted solution is added to 5 mL of liquid scintillation cocktail (GE Healthcare, Little Chalfont, UK). |
Comment 0
|

|
| 6) |
The radioactivity is measured with a liquid scintillation counter (Beckman Coulter, Inc. Brea CA). |
Comment 0
|
|
|
|
5. |
SDS-PAGE for glycopeptides and glycoproteins
It is required that the substrate/product is labeled with radioisotope or fluorescence. |
| 1) |
The enzyme reaction is performed at 37°C for 1–24 h. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 2) |
After incubation at 37°C for 16 h, the enzyme reaction is terminated by treatment at 100°C for 3 min, and then the reaction mixture is subjected to 10% SDS-PAGE. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 3) |
The radioactive intensities of the bands obtained are measured with an FLA-3000 Imaging Analyzer (Fujifilm, Tokyo, Japan). |
Comment 0
|

|
| 4) |
Or they are blotted to PVDF membrane and are immunostained with lectin or antibody. |
Comment 0
|
|
|
| Figure & Legends |
Figure & Legends

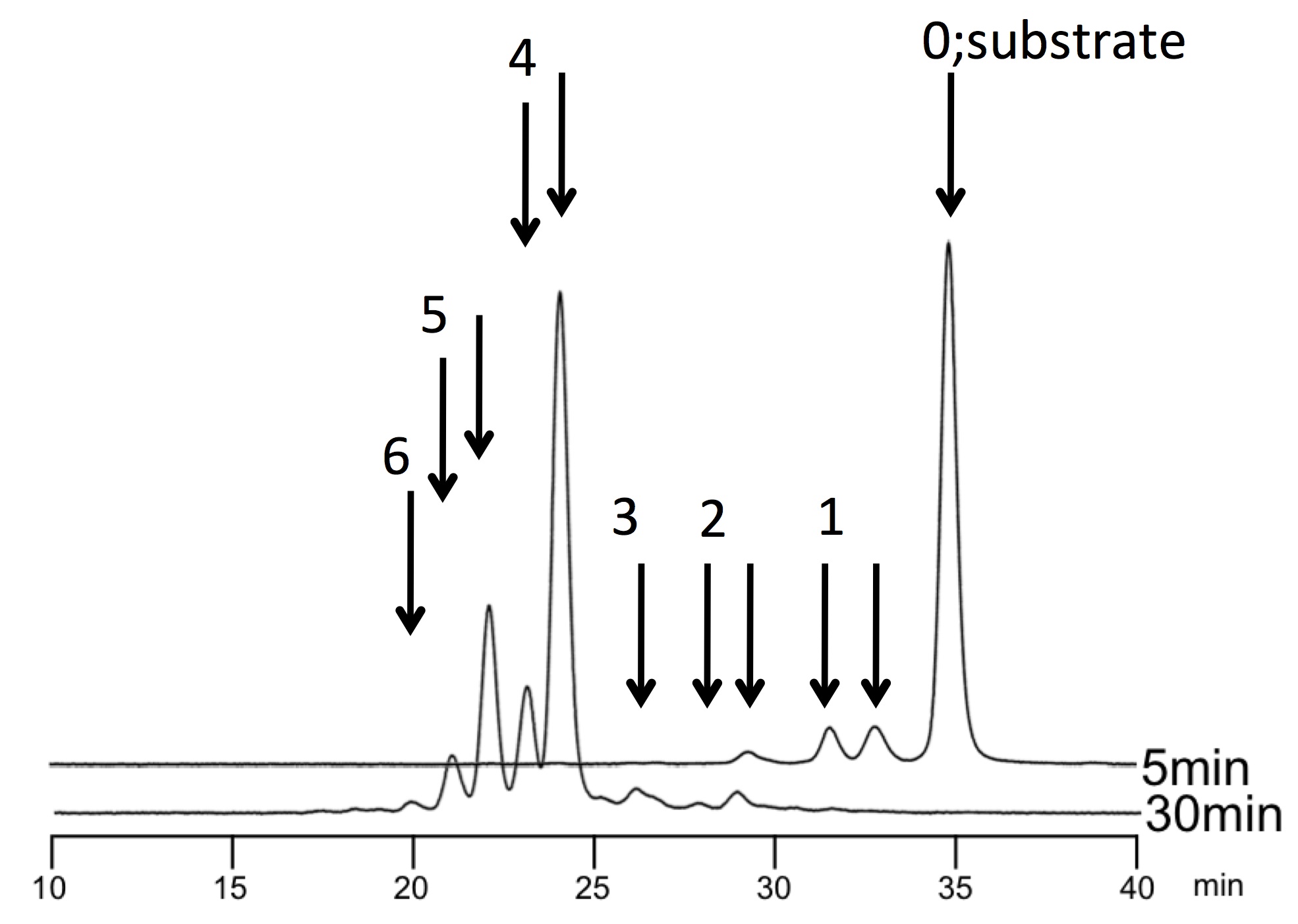
Fig. 1. [Example] HPLC elution pattern of the reaction products by pp-GalNAc-T2 and T10 on the IgA hinge peptide. The reaction time is 5 min and 30 min for upper and lower lines, respectively. The numbers with arrows represent the number of GalNAc incorporated. Note that the divided peaks with same number indicate the different Ser/Thr modified.
In many cases, pp-GalNAc-T reaction is a sequential multiple reaction. Further analysis to determine the number of GalNAc and their sites will be demanded, which could be identified by MS and peptide sequencer, respectively. |
| Copyrights |
 Attribution-Non-Commercial Share Alike Attribution-Non-Commercial Share Alike
This work is released underCreative Commons licenses
|
| Date of registration:2017-02-23 15:01:46 |
- Iwasaki, H, Zhang, Y, Tachibana, K, Gotoh, M, Kikuchi, N, Kwon, Y-D, Togayachi, A, Kudo, T, Kubota, T, Narimatsu, H (2003) Initiation of O-glycan synthesis in IgA1 hinge region is determined by a single enzyme, UDP-N-acetyl-α-D-galactosamine: polypeptide N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase 2. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 5513–5621 [PMID : 12438318]
- Cheng, L, Tachibana, K, Zhang, Y, Guo, J-M, Tachibana, K, Kameyama, A, Wang, H, Hiruma, T, Iwasaki, H, Togayachi, A, Kudo, T, Narimatsu, H (2002) Characterization of a novel human UDP-GalNAc transferase, pp-GalNAc-T10. FEBS Letters 531, 115–121 [PMID : 12417297]
- Amado, M., Almeida, R., Schwientek, T., and Clausen, H. (1999) Identification and characterization of large galactosyltransferase gene families: galactosyltransferases for all functions. Biochim Biophys Acta 1473, 35–53 [PMID : 10580128]
- Bai, X., Zhou, D., Brown, J. R., Crawford, B. E., Hennet, T., and Esko, J. D. (2001) Biosynthesis of the linkage region of glycosaminoglycans: cloning and activity of galactosyltransferase II, the sixth member of the β 1,3-galactosyltransferase family (β3GalT6). J Biol Chem 276, 48189–48195 [PMID : 11551958]
- Hennet, T., Dinter, A., Kuhnert, P., Mattu, T. S., Rudd, P. M., and Berger, E. G. (1998) Genomic cloning and expression of three murine UDP-galactose: b-N-acetylglucosamine b1,3-galactosyltransferase genes. J Biol Chem 273, 58–65 [PMID : 9417047]
- Hennet, T. (2002) The galactosyltransferase family. Cell Mol Life Sci 59, 1081–95
- Hiruma, T., Togayachi, A., Okamura, K., Sato, T., Kikuchi, N., Kwon, Y. D., Nakamura, A., Fujimura, K., Gotoh, M., Tachibana, K., Ishizuka, Y., Noce, T., Nakanishi, H., and Narimatsu, H. (2004) A novel human β1,3-N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase that synthesizes a unique carbohydrate structure, GalNAcb1-3GlcNAc. J Biol Chem 279, 14087–14095 [PMID : 14724282]
- Iwai, T., Inaba, N., Naundorf, A., Zhang, Y., Gotoh, M., Iwasaki, H., Kudo, T., Togayachi, A., Ishizuka, Y., Nakanishi, H., and Narimatsu, H. (2002) Molecular cloning and characterization of a novel UDP-GlcNAc:GalNAc-peptide b1,3-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase (b3Gn-T6), an enzyme synthesizing the core 3 structure of O-glycans. J Biol Chem 277, 12802–12809 [PMID : 11821425]
- Miyazaki, H., Fukumoto, S., Okada, M., Hasegawa, T., and Furukawa, K. (1997) Expression cloning of rat cDNA encoding UDP-galactose: GD2 β1,3-galactosyltransferase that determines the expression of GD1b/GM1/GA1. J Biol Chem 272, 24794–24799 [PMID : 9312075]
- Isshiki, S., Togayachi, A., Kudo, T., Nishihara, S., Watanabe, M., Kubota, T., Kitajima, M., Shiraishi, N., Sasaki, K., Andoh, T., and Narimatsu, H. (1999) Cloning, expression, and characterization of a novel UDP-galactose: β-N-acetylglucosamine β1,3-galactosyltransferase (β3Gal-T5) responsible for synthesis of type 1 chain in colorectal and pancreatic epithelia and tumor cells derived therefrom. J Biol Chem 274, 12499–12507 [PMID: 10212226]
- Okajima, T., Nakamura, Y., Uchikawa, M., Haslam, D. B., Numata, S. I., Furukawa, K., Urano, T., and Furukawa, K. (2000) Expression cloning of human globoside synthase cDNAs. Identification of β3Gal-T3 as UDP-N-acetylgalactosamine:globotriaosylceramide β1,3-N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase. J Biol Chem 275, 40498–40503 [PMID : 10993897]
- Seko, A., and Yamashita, K. (2004) b1,3-N-Acetylglucosaminyltransferase-7 (b3Gn-T7) acts efficiently on keratan sulfate-related glycans. FEBS Lett 556, 216–220 [PMID : 14703853]
- Seko, A., and Yamashita, K. (2008) Activation of β1,3-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase-2 (b3Gn-T2) by b3Gn-T8. Possible involvement of b3Gn-T8 in increasing poly-N-acetyllactosamine chains in differentiated HL-60 cells. J Biol Chem. 283, 33094–33100 [PMID : 18826941]
- Ishida, H., Togayachi, A., Sakai, T., Iwai, T., Hiruma, T., Sato, T., Okubo, R., Inaba, N., Kudo, T., Gotoh, M., Shoda, J., Tanaka, N., and Narimatsu, H. (2005) A novel b1,3-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase (b3Gn-T8), which synthesizes poly-N-acetyllactosamine, is dramatically upregulated in colon cancer. FEBS Lett 579, 71–78 [PMID : 15620693]
- Sato, T., Sato, M., Kiyohara, K., Sogabe, M., Shikanai, T., Kikuchi, N., Togayachi, A., Ishida, H., Ito, H., Kameyama, A., Gotoh, M., and Narimatsu, H. (2006) Molecular cloning and characterization of a novel human b1,3-glucosyltransferase, which is localized at the endoplasmic reticulum and glucosylates O-linked fucosylglycan on thrombospondin type 1 repeat domain. Glycobiology 16, 1194–1206 [PMID : 16899492]
- l Sasaki, K., Kurata-Miura, K., Ujita, M., Angata, K., Nakagawa, S., Sekine, S., Nishi, T., and Fukuda, M. (1997) Expression cloning of cDNA encoding a human b-1,3-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase that is essential for poly-N-acetyllactosamine synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 94, 14294–9.
- l Seko, A., and Yamashita, K. (2005) Characterization of a novel galactose b1,3-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase (b3Gn-T8): the complex formation of b3Gn-T2 and b3Gn-T8 enhances enzymatic activity. Glycobiology 15, 943–51 [PMID : 15917431]
- l Shiraishi, N., Natsume, A., Togayachi, A., Endo, T., Akashima, T., Yamada, Y., Imai, N., Nakagawa, S., Koizumi, S., Sekine, S., Narimatsu, H., and Sasaki, K. (2001) Identification and characterization of three novel beta 1,3-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferases structurally related to the beta 1,3-galactosyltransferase family. J Biol Chem 276, 3498–3507 [PMID : 11042166]
- Togayachi, A., Akashima, T., Ookubo, R., Kudo, T., Nishihara, S., Iwasaki, H., Natsume, A., Mio, H., Inokuchi, J., Irimura, T., Sasaki, K., and Narimatsu, H. (2001) Molecular cloning and characterization of UDP-GlcNAc:lactosylceramide b1,3-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase (b3Gn-T5), an essential enzyme for the expression of HNK-1 and Lewis X epitopes on glycolipids. J Biol Chem 276, 22032–22040 [PMID : 11283017]
- Togayachi, A., Sato, T., and Narimatsu, H. (2006) Comprehensive enzymatic characterization of glycosyltransferases with a b3GT or b4GT motif. Methods Enzymol 416, 91–102 [PMID : 17113861]
- Ujita, M., McAuliffe, J., Schwientek, T., Almeida, R., Hindsgaul, O., Clausen, H., and Fukuda, M. (1998) Synthesis of poly-N-acetyllactosamine in core 2 branched O-glycans. The requirement of novel b-1,4-galactosyltransferase IV and b-1,3-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase. J Biol Chem 273, 34843–34849 [PMID : 9857011]
- Yeh, J. C., Hiraoka, N., Petryniak, B., Nakayama, J., Ellies, L. G., Rabuka, D., Hindsgaul, O., Marth, J. D., Lowe, J. B., and Fukuda, M. (2001) Novel sulfated lymphocyte homing receptors and their control by a Core1 extension b 1,3-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase. Cell 105, 957–969 [PMID : 11439191]
- Zhou, D., Berger, E. G., and Hennet, T. (1999) Molecular cloning of a human UDP-galactose:GlcNAcbeta1,3GalNAc b1, 3-galactosyltransferase gene encoding an O-linked core3-elongation enzyme. Eur J Biochem 263, 571–576 [PMID : 10406968]
- Zhou, D., Dinter, A., Gutierrez Gallego, R., Kamerling, J. P., Vliegenthart, J. F., Berger, E. G., and Hennet, T. (1999) A b-1,3-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase with poly-N-acetyllactosamine synthase activity is structurally related to b-1,3-galactosyltransferases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 96, 406–411 [PMID : 9892646]
- Zhou, D., Henion, T. R., Jungalwala, F. B., Berger, E. G., and Hennet, T. (2000) The b1,3-galactosyltransferase b3GalT-V is a stage-specific embryonic antigen-3 (SSEA-3) synthase. J Biol Chem 275, 22631–22634 [PMID : 10837462]
|
This work is licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-Non-Commercial Share Alike. Please include the following citation
How to Cite this Work in an article:
Togayachi, Akira,
Kubota, Tomomi,
Sato, Takashi,
Narimatsu, Hisashi,
(2017). GlycoPOD https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD.
Web.20,4,2024 .
How to Cite this Work in Website:
Togayachi, Akira,
Kubota, Tomomi,
Sato, Takashi,
Narimatsu, Hisashi,
(2017).
Enzyme assay of polypeptide N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase, β1,3-glycosyltransferase, ang β1,4-glycosyltransferases. [4] General methods for detection of enzyme reaction products.
Retrieved 20,4,2024 ,
from https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD/protocolShow.action?nodeId=t243.
html source
Togayachi, Akira,
Kubota, Tomomi,
Sato, Takashi,
Narimatsu, Hisashi,
(2017).
<b>Enzyme assay of polypeptide <em>N-</em>acetylgalactosaminyltransferase, β1,3-glycosyltransferase, ang β1,4-glycosyltransferases. [4] General methods for detection of enzyme reaction products</b>.
Retrieved 4 20,2024 ,
from <a href="https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD/protocolShow.action?nodeId=t243" target="_blank">https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD/protocolShow.action?nodeId=t243</a>.
Including references that appeared in the References tab in your work is
much appreciated.
For those who wish to reuse the figures/tables, please contact JCGGDB
management office (jcggdb-ml@aist.go.jp).
|
|