This section reviews the enzymatic reactions of β1,3-glycosyltransferase family, transferring sugars via a β1,3-linkage (β1,3-galactosyltransferase; β3GalT, β1,3-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase; β3GnT and β1,3-N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase; β3GalNAcT, β1,3-glucosyltransferase; β3GlcT). |
| Category | Glycosyltransferases & related proteins |
| Protocol Name | Enzyme assay of polypeptide N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase, β1,3-glycosyltransferase, and β1,4-glycosyltransferases. [2] β1,3-glycosyltransferase family |
Authors
 |
Togayachi, Akira
Research Center for Medical Glycoscience, National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST)
Sato, Takashi
Research Center for Medical Glycoscience, National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST)
Narimatsu, Hisashi
*
Research Center for Medical Glycoscience, National Instutute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST)
*To whom correspondence should be addressed.
|
| KeyWords |
|
Reagents
 |
| ● |
Donor substrates (see Note 1):
[Substrates]
・UDP-glucose (Glc)
・UDP-N-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc)
・UDP-galactose (Gal)
・UDP-N-acetylgalactosamine (GalNAc)
(Sigma Aldrich, Calbiochem, GE Healthcare Biosciences Corp etc.)
[Radiolabeled chemicals]
・UDP-[14C]glucose (Glc)
・UDP-[14C]N-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc)
・UDP-[14C]galactose (Gal)
・UDP-[3H] N-acetylgalactosamine (GalNAc)
(American Radiolabeled Chemicals, Inc.) |
| ● |
Acceptor substrates (see Note 2):
Monosaccharides/Oligosaccharides
・Gal-β-pNP (para-nitrophenyl)
・GlcNAc-β-Bz (benzyl)
・GalNAc-α-pNP
・GalNAc-β-Bz
・Fuc-α-pNp
・Galβ1–3(GlcNAcβ1–6)GalNAc(core2)-pNP
・GlcNAcβ1–3GalNAc(core3)-pNP
・GlcNAcβ1–6GalNAc(core6)-pNP
・lactose (Galβ1– 4Glc)
・Lactoside-Bz
・N-acetyllactosamine (LN, Galβ1– 4GlcNAc)
・2LN: (Galβ1– 4GlcNAcβ1–3Galβ1– 4GlcNAc
・3LN: (Galβ1– 4GlcNAcβ1– 3)2Galβ1–4GlcNAc
・4LN: (Galβ1–4GlcNAcβ1–3)3Galβ1–4GlcNAc
・5LN: (Galβ1– 4GlcNAcβ1–3)4Galβ1– 4GlcNAc
・lacto-N-neotetraose (LNnT; Galβ1– 4GlcNAcβ1–3Galβ1– 4Glc)
・agalacto-LNnT (agalacto-LNnT)
・lacto-N-tetraose (LNT; Galβ1–3GlcNAcβ1–3Galβ1–4Glc)
・lacto-N-fucosylpentaose (LNFP) III (Galβ1– 4(Fucα1–3)GlcNAcβ1–3Galβ1– 4Glc),
・LNFP-II (Galβ1– 3(Fucα1– 4)GlcNAcβ1–3Gal1– 4Glc)
・LNFP-V (Galβ1–3GlcNAcβ1– 3Galβ1– 4(Fucα1–3)Glc)
・lacto-N-difucosylhexaose II (Galβ1–3(Fucα1–4)GlcNAcβ1–3Galβ1– 4(Fucα1–3)Glc)
Other acceptor substrates
gycopeptides
・e.g., FITC-conjugated glycopeptides: FITC-AHGVT(-GalNAc) SAPDTR
glycoproteins
・e.g., bovine submaxillary gland mucin (BSM), fetuin, asialofetuin, EGF and TSR domains, or etc.
glycolipids
・LacCer: lactosylceramide, Galβ1– 4Glcβ1–1Cer
・Lc3Cer: lactotriaosylceramide, GlcNAcβ1–3Galβ1– 4Glcβ1–1Cer
・nLc4Cer: neolactotetraosylceramide (paragloboside), Galβ1–4GlcNAcβ1–3Galβ1– 4Glcβ1–1Cer
・nLc5Cer: GlcNAcβ1–3Galβ1– 4GlcNAcβ1–3Galβ1– 4Glcβ1–1Cer
・nLc6Cer: Galβ1–4GlcNAcβ1–3Galβ1–4GlcNAcβ1–3Galβ1–4Glcβ1– 1Cer |
| ● |
Reagents for reaction:
・Cell lysate (enzyme source) or membrane fraction of cells/tissues is prepared in a general method. (Concentration should be optimized for your samples.) (see Note 3)
・Triton X-100
・1 μM/10 nmol of each acceptor mixture (Concentration should be optimized for your samples.)
・50 mM donor substrate (e.g., UDP-GlcNAc, UDP-Gal, UDP-GalNAc, and UDP-Glc, (see Note 4)
・10 mM MnCl2
・5 mM CDP-choline (Enzyme reaction occurs in the presence or absence of CDP-choline. It is better to avoid degradation of donor substrates.)
・0.4% Triton CF-54 (In case of hydrophobic substrates being used, i.e., glycolipids)
・150 mM sodium cacodylate buffer (pH 7.2) (see Note 5) |
|
Instruments
 |
| ● |
|
| ● |
Thermoregulated bath (Incubator) |
|
| Methods |
|
1. |
Preparation of enzyme source
Each enzyme is purified from the culture medium using anti-FLAG M2 agarose affinity gel (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO), since recombinant enzyme is fused with FLAG peptide-tag (Sigma-Aldrich). |
| 1) |
A culture medium (10–50 mL) is mixed with anti-FLAG M2 agarose affinity gel and rotated slowly at 4°C overnight. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 2) |
The gel is then washed 2–5 times with 50 mM Tris buffered saline (TBS; 50 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.4, and 150 mM NaCl) and finally suspended in 100 μL of TBS.
|
Comment 0
|

|
| 3) |
Enzymatic reactions of all glycosyltransferases are carried out using the suspension as an enzyme source.
|
Comment 0
|
|
|
|
2. |
|
| 1) |
Glycosyltransferases are reacted in 20 μL of a basic reaction mixture containing following components.
|
Comment 0
|

|
| 2) |
The reaction mixture is incubated at 37°C for designated periods (usually 16 h). |
Comment 0
|

|
| 3) |
The mixture is heated at 100°C for 3 min to terminate the reaction.
|
Comment 0
|

|
| 4) |
The mixture is centrifuged at 15,000 rpm for 5 min at 4°C and the supernatant is recovered.
|
Comment 0
|

|
| 5) |
The substrate and product are analyzed by the methods as described in section [IV] "General methods for detection of enzyme reaction products". As necessary, the product should be purified with any method (i.e., SepPak C18 column for hydrophobic-labeled substrates, HPLC for any substrates).
|
Comment 0
|
|
|
| Notes | 1. Donor Substrate: For example, UDP-GlcNAc is used as a donor acceptor for b3GnT assay. UDP-Gal and UDP-GalNAc are useful donor substrates for β3GalT and β3GalNAcT assay, respectively. In case radiolabeled chemicals are used, UDP-[14C]glucose (Glc), UDP-[14C]N-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc), UDP-[14C]galactose (Gal), UDP-[3H] N-acetylgalactosamine (GalNAc), UDP-[14C]glucuronic acid (GlcA), GDP-[14C]mannose (Man) and GDP-[14C]fucose (Fuc) (American Radiolabeled Chemicals, Inc., are available and utilized as donor substrates.
2. The various acceptor substrates, such as monosaccharides, oligosaccharides, glycolipids, glycopeptides, and glycoproteins, were purchased from Calbiochem (San Diego, CA), Toronto Research Chemicals Inc. (Toronto, Canada), Seikagaku Corp. (Tokyo, Japan), Takara Bio Inc. (Otsu, Japan), Glycotech (Gaithersburg, MD) or Sigma-Aldrich(St. Louis, MO) etc. Oligosaccharides are fluorescently labeled with 2-aminobenzamide- (2AB) or pyridylamino- (PA) group and used as good acceptors for analysis using radioisotope (scintillation counter), High performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), and MS. Oligosaccharides are fluorescently labeled with nitrophenol (para-Np, ortho-Np) or benzene (Bz) and used as good acceptors for analysis using radioisotope (scintillation counter) and MS.
[Example: polylactosamine synthase (β3GnTs)]
For acceptor substrates: carbohydrate structures including terminal Gal residues on non-reducing end of their structures. For major polylactosamine synthase, β3GnT2 activity, a longer acceptor substrate, such as polylactosamine structure is recommended (at least 2-repeated lactosamine structure and over 3-repeated lactosamine structure is desirable).
[Exampe: type 1 structure synthase (β3GalTs)]
Pyridylaminated agalacto-LNnT (Agalacto-LNnT-PA) as acceptor substrate is prepared, and used for assaying β3Gal-T activity. The LNnT-PA is digested with 20 milliunits/mL streptococcal β-galactosidase (Seikagaku Corp., Tokyo, Japan) to remove the galactose residue at the non- reducing end.
3. For example, cells/tissues are solubilized in a 20 mM HEPES buffer (pH 7.2) at 2%. The total protein (10–20 mg) in the cell homogenates is used for the enzyme reaction.
4. For using a radioactive donor, add 2.5 mM of a radioactive donor substrate for reaction.
5. Reaction is optimized in various buffer systems i.e., MES, HEPES, Tris-HCl and Na-cacodylate buffer at different pH values, approximately pH 7.4. We use 150 mM sodium cacodylate buffer (pH 7.2). |
| Figure & Legends |
Figure & Legends

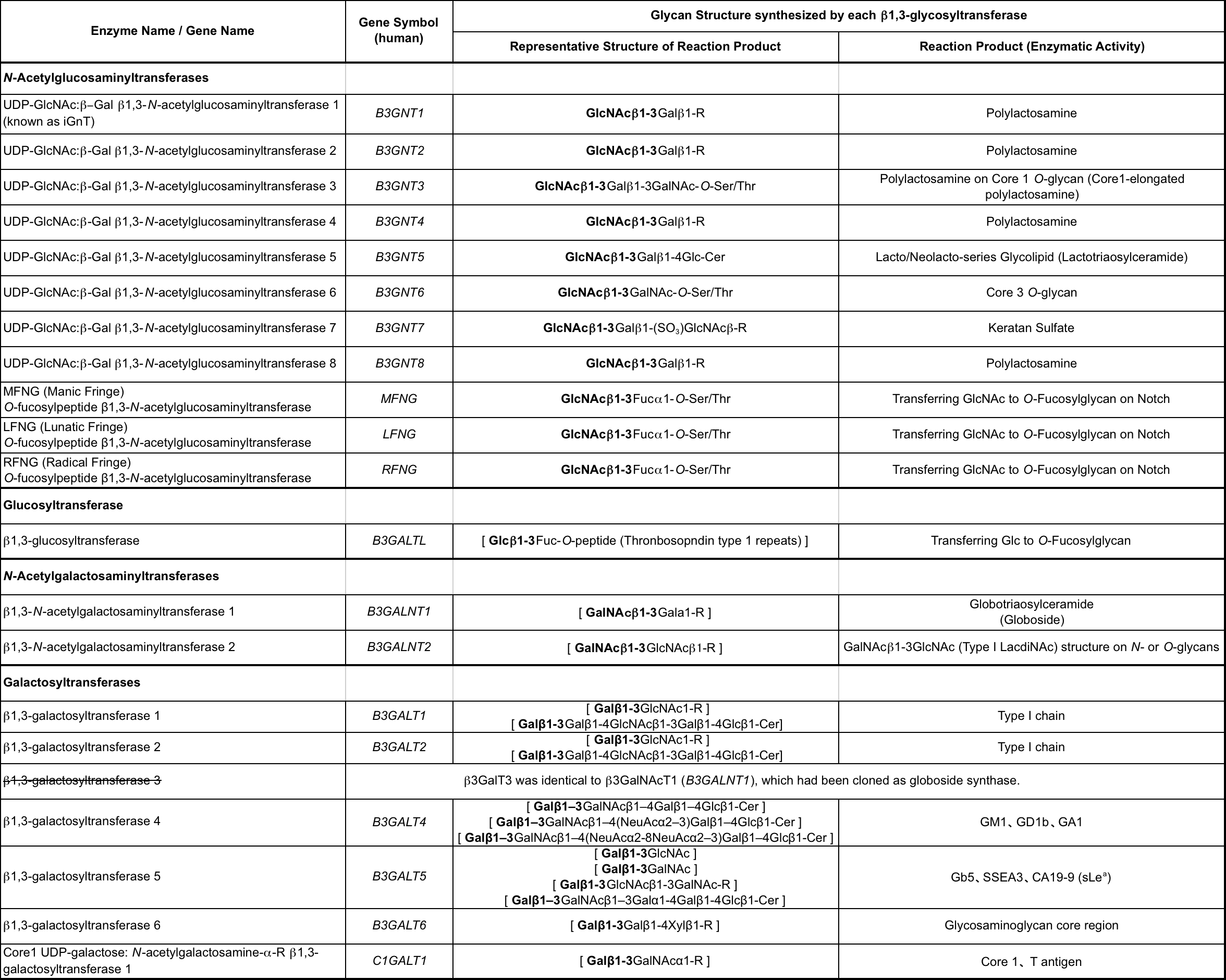
Fig. 1. Table; β1,3-Glycosyltransferases and their enzymatic activity |
| Copyrights |
 Attribution-Non-Commercial Share Alike Attribution-Non-Commercial Share Alike
This work is released underCreative Commons licenses
|
| Date of registration:2017-02-23 15:00:52 |
- Amado, M., Almeida, R., Schwientek, T., and Clausen, H. (1999) Identification and characterization of large galactosyltransferase gene families: galactosyltransferases for all functions. Biochim Biophys Acta 1473, 35–53 [PMID : 10580128]
- Bai, X., Zhou, D., Brown, J. R., Crawford, B. E., Hennet, T., and Esko, J. D. (2001) Biosynthesis of the linkage region of glycosaminoglycans: cloning and activity of galactosyltransferase II, the sixth member of the β 1,3-galactosyltransferase family (β3GalT6). J Biol Chem 276, 48189–48195 [PMID : 11551958]
- Hennet, T., Dinter, A., Kuhnert, P., Mattu, T. S., Rudd, P. M., and Berger, E. G. (1998) Genomic cloning and expression of three murine UDP-galactose: β-N-acetylglucosamine β1,3-galactosyltransferase genes. J Biol Chem 273, 58–65 [PMID : 9417047]
- Hennet, T. (2002) The galactosyltransferase family. Cell Mol Life Sci 59, 1081–95 [PMID : 12222957]
- Hiruma, T., Togayachi, A., Okamura, K., Sato, T., Kikuchi, N., Kwon, Y. D., Nakamura, A., Fujimura, K., Gotoh, M., Tachibana, K., Ishizuka, Y., Noce, T., Nakanishi, H., and Narimatsu, H. (2004) A novel human beta 1,3-N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase that synthesizes a unique carbohydrate structure, GalNAcb1-3GlcNAc. J Biol Chem 279, 14087–14095 [PMID : 14724282]
- Iwai, T., Inaba, N., Naundorf, A., Zhang, Y., Gotoh, M., Iwasaki, H., Kudo, T., Togayachi, A., Ishizuka, Y., Nakanishi, H., and Narimatsu, H. (2002) Molecular cloning and characterization of a novel UDP-GlcNAc:GalNAc-peptide β1,3-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase (β3Gn-T6), an enzyme synthesizing the core 3 structure of O-glycans. J Biol Chem 277, 12802–12809 [PMID : 11821425]
- Miyazaki, H., Fukumoto, S., Okada, M., Hasegawa, T., and Furukawa, K. (1997) Expression cloning of rat cDNA encoding UDP-galactose: GD2 β1,3-galactosyltransferase that determines the expression of GD1b/GM1/GA1. J Biol Chem 272, 24794–24799 [PMID : 9312075]
- Isshiki, S., Togayachi, A., Kudo, T., Nishihara, S., Watanabe, M., Kubota, T., Kitajima, M., Shiraishi, N., Sasaki, K., Andoh, T., and Narimatsu, H. (1999) Cloning, expression, and characterization of a novel UDP-galactose: β-N-acetylglucosamine β1,3-galactosyltransferase (β3Gal-T5) responsible for synthesis of type 1 chain in colorectal and pancreatic epithelia and tumor cells derived therefrom. J Biol Chem 274, 12499–12507 [PMID : 10212226]
- Okajima, T., Nakamura, Y., Uchikawa, M., Haslam, D. B., Numata, S. I., Furukawa, K., Urano, T., and Furukawa, K. (2000) Expression cloning of human globoside synthase cDNAs. Identification of β3Gal-T3 as UDP-N-acetylgalactosamine:globotriaosylceramide β 1,3-N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase. J Biol Chem 275, 40498–40503 [PMID : 10993897]
- Seko, A., and Yamashita, K. (2004) β1,3-N-Acetylglucosaminyltransferase-7 (β3Gn-T7) acts efficiently on keratan sulfate-related glycans. FEBS Lett 556, 216–220 [PMID : 14706853]
- Seko, A., and Yamashita, K. (2008) Activation of β 1,3-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase-2 (β3Gn-T2) by β3Gn-T8. Possible involvement of β3Gn-T8 in increasing poly-N-acetyllactosamine chains in differentiated HL-60 cells. J Biol Chem. 283, 33094–33100.12 [PMID : 18826941]
- Ishida, H., Togayachi, A., Sakai, T., Iwai, T., Hiruma, T., Sato, T., Okubo, R., Inaba, N., Kudo, T., Gotoh, M., Shoda, J., Tanaka, N., and Narimatsu, H. (2005) A novel β1,3-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase (β3Gn-T8), which synthesizes poly-N-acetyllactosamine, is dramatically upregulated in colon cancer. FEBS Lett 579, 71–78 [PMID : 15620693]
- Sato, T., Sato, M., Kiyohara, K., Sogabe, M., Shikanai, T., Kikuchi, N., Togayachi, A., Ishida, H., Ito, H., Kameyama, A., Gotoh, M., and Narimatsu, H. (2006) Molecular cloning and characterization of a novel human β1, 3-glucosyltransferase, which is localized at the endoplasmic reticulum and glucosylates O-linked fucosylglycan on thrombospondin type 1 repeat domain. Glycobiology 16, 1194–1206 [PMID : 16899492]
- Sasaki, K., Kurata-Miura, K., Ujita, M., Angata, K., Nakagawa, S., Sekine, S., Nishi, T., and Fukuda, M. (1997) Expression cloning of cDNA encoding a human β-1,3-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase that is essential for poly-N-acetyllactosamine synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 94, 14294–9 [PMID : 9405606]
- Seko, A., and Yamashita, K. (2005) Characterization of a novel galactose β1,3-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase (β3Gn-T8): the complex formation of β3Gn-T2 and β3Gn-T8 enhances enzymatic activity. Glycobiology 15, 943–51.
- Shiraishi, N., Natsume, A., Togayachi, A., Endo, T., Akashima, T., Yamada, Y., Imai, N., Nakagawa, S., Koizumi, S., Sekine, S., Narimatsu, H., and Sasaki, K. (2001) Identification and characterization of three novel β1,3-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferases structurally related to the β1,3-galactosyltransferase family. J Biol Chem 276, 3498–3507 [PMID : 11042166]
- Togayachi, A., Akashima, T., Ookubo, R., Kudo, T., Nishihara, S., Iwasaki, H., Natsume, A., Mio, H., Inokuchi, J., Irimura, T., Sasaki, K., and Narimatsu, H. (2001) Molecular cloning and characterization of UDP-GlcNAc:lactosylceramide β1,3-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase (β3Gn-T5), an essential enzyme for the expression of HNK-1 and Lewis X epitopes on glycolipids. J Biol Chem 276, 22032–22040 [PMID : 11283017]
- Togayachi, A., Sato, T., and Narimatsu, H. (2006) Comprehensive enzymatic characterization of glycosyltransferases with a β3GT or β4GT motif. Methods Enzymol 416, 91–10 [PMID : 17113861].
- Ujita, M., McAuliffe, J., Schwientek, T., Almeida, R., Hindsgaul, O., Clausen, H., and Fukuda, M. (1998) Synthesis of poly-N-acetyllactosamine in core 2 branched O-glycans. The requirement of novel β-1,4-galactosyltransferase IV and β-1,3-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase. J Biol Chem 273, 34843–34849 [PMID : 9587011]
- Yeh, J. C., Hiraoka, N., Petryniak, B., Nakayama, J., Ellies, L. G., Rabuka, D., Hindsgaul, O., Marth, J. D., Lowe, J. B., and Fukuda, M. (2001) Novel sulfated lymphocyte homing receptors and their control by a Core1 extension b 1,3-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase. Cell 105, 957–969 [PMID : 11439191]
- Zhou, D., Berger, E. G., and Hennet, T. (1999) Molecular cloning of a human UDP-galactose:GlcNAcbeta1,3GalNAc β1, 3-galactosyltransferase gene encoding an O-linked core3-elongation enzyme. Eur J Biochem 263, 571–576 [PMID : 10406968]
- Zhou, D., Dinter, A., Gutierrez Gallego, R., Kamerling, J. P., Vliegenthart, J. F., Berger, E. G., and Hennet, T. (1999) A β-1,3-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase with poly-N-acetyllactosamine synthase activity is structurally related to β-1,3-galactosyltransferases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 96, 406–411 [PMID : 9892646]
- Zhou, D., Henion, T. R., Jungalwala, F. B., Berger, E. G., and Hennet, T. (2000) The β1,3-galactosyltransferase β3GalT-V is a stage-specific embryonic antigen-3 (SSEA-3) synthase. J Biol Chem 275, 22631–22634 [10837462]
|
This work is licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-Non-Commercial Share Alike. Please include the following citation
How to Cite this Work in an article:
Togayachi, Akira,
Sato, Takashi,
Narimatsu, Hisashi,
(2017). GlycoPOD https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD.
Web.26,4,2024 .
How to Cite this Work in Website:
Togayachi, Akira,
Sato, Takashi,
Narimatsu, Hisashi,
(2017).
Enzyme assay of polypeptide N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase, β1,3-glycosyltransferase, and β1,4-glycosyltransferases. [2] β1,3-glycosyltransferase family.
Retrieved 26,4,2024 ,
from https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD/protocolShow.action?nodeId=t241.
html source
Togayachi, Akira,
Sato, Takashi,
Narimatsu, Hisashi,
(2017).
<b>Enzyme assay of polypeptide <em>N-</em>acetylgalactosaminyltransferase, β1,3-glycosyltransferase, and β1,4-glycosyltransferases. [2] β1,3-glycosyltransferase family</b>.
Retrieved 4 26,2024 ,
from <a href="https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD/protocolShow.action?nodeId=t241" target="_blank">https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD/protocolShow.action?nodeId=t241</a>.
Including references that appeared in the References tab in your work is
much appreciated.
For those who wish to reuse the figures/tables, please contact JCGGDB
management office (jcggdb-ml@aist.go.jp).
|
|