Glycosphingolipids consist of complicated hydrophilic carbohydrate moieties and hydrophobic ceramides, which are N-acylated forms of sphingosine. Electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (ESI-MS) is considered to be a soft ionization tool and adequate to quantitatively analyze the fragile glycosphingolipid in detail (Ikeda et al. 2008). Here we report an effective method for targeted analysis of theoretically expected ganglioside and sulfatide molecular species by hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography (HILIC)/ESI-MS with multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) (Ikeda et al. 2010). |
| Category | Glycolipids and related compounds |
| Protocol Name | Detailed analysis of glycosphingolipids at the molecular species level by HILIC/ESI-MS |
Authors
 |
Ikeda, Kazutaka
*
Institute for Advanced Biosciences, Keio University
Taguchi, Ryo
Department of Biomedical Sciences, College of Life and Health Sciences, Chubu University
*To whom correspondence should be addressed.
|
| KeyWords |
|
Reagents
 |
| ● |
acetonitrile (CH3CN) (Wako Pure Chemical Industries Ltd., Osaka, Japan) |
| ● |
ammonium formate (HCOONH4)/1 molar (Wako Pure Chemical Industries Ltd.) |
| ● |
|
| ● |
glycosphingolipid mixture/porcine brain (Avanti Polar Lipids, Inc., Alabaster, AL) |
| ● |
Solvent system for liquid chromatography:
Solvent A: CH3CN / DW (83/17, v/v)+1 mM HCOONH4
Solvent B: CH3CN / DW (50/50, v/v) +50 mM HCOONH4 |
|
Instruments
 |
| ● |
Tandem mass spectrometer: 4000 Q TRAP (AB SCIEX, Framingham, MA) |
| ● |
LC system: UltiMate 3000 nano/cap/micro (Dionex Corporation, Sunnyvale, CA) |
| ● |
Autosampler: HTS PAL (CTC Analytics AG, Zwingen, Switzerland) |
| ● |
Hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography (HILIC) column: Inertsil NH2/150 × 0.5 mm i.d. (GL Sciences Inc., Tokyo, Japan) |
|
| Methods |
|
1. |
Liquid Chromatography (LC) |
| 1) |
Liquid chromatography separations were carried out at 40°C with a flow rate of 15 μL/min.
Typically, 3 μL of sample solution was applied. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 2) |
The gradient consist of holding solvent A/B (100/0, v/v) from 0 to 5 min, then linearly converting solvent A/B (100/0, v/v) to A/B (25/75, v/v) from 5 to 20 min, linearly converting solvent A/B (25/75, v/v) to A/B (10/90, v/v) from 20 to 25 min, holding solvent A/B (10/90, v/v) from 25 to 35 min, then linearly converting solvent A/B (10/90, v/v) to A/B (100/0, v/v) from 35 to 36 min, and holding solvent A/B (100/0, v/v) from 36 to 55 min. |
Comment 0
|
|
|
|
2. |
Electrospray ionization-tandem mass spectrometry (ESI-MS) |
| 1) |
ESI-MS analyes were performed by using 4000 Q TRAP quqdropole-linear ion trap hybrid MS. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 2) |
Tandem mass spectrometry(MS/MS) analyses of ceramide molecular species derived from in-source decay of gangliosides were performed in the positive-ion mode (Ikeda et al. 2008) |
Comment 0
|

|
| 3) |
MRM analyses were performed in the negative-ion mode with the same instrument system used for the LC/ESI-MS analysis (Ikeda et al. 2010) . DP was set at −120 V, and CID conditions for each ganglioside and sulfatide were optimized as shown in Tabe 1. |
Comment 1
|
|
|
| Discussion | In our HILIC/ESI-MS analysis with theoretically expanded MRM, different molecular species of each ganglioside were detected at a time, because each of the carbohydrate moiety rather than the ceramide structure mainly influenced these elution orders. This analysis system was possible to sensitively detect individual ganglioside and sulfatide molecular species including these regioisomers even from about 1×103 nerve cells (Ikeda et al. 2010). |
| Figure & Legends |
Figure & Legends

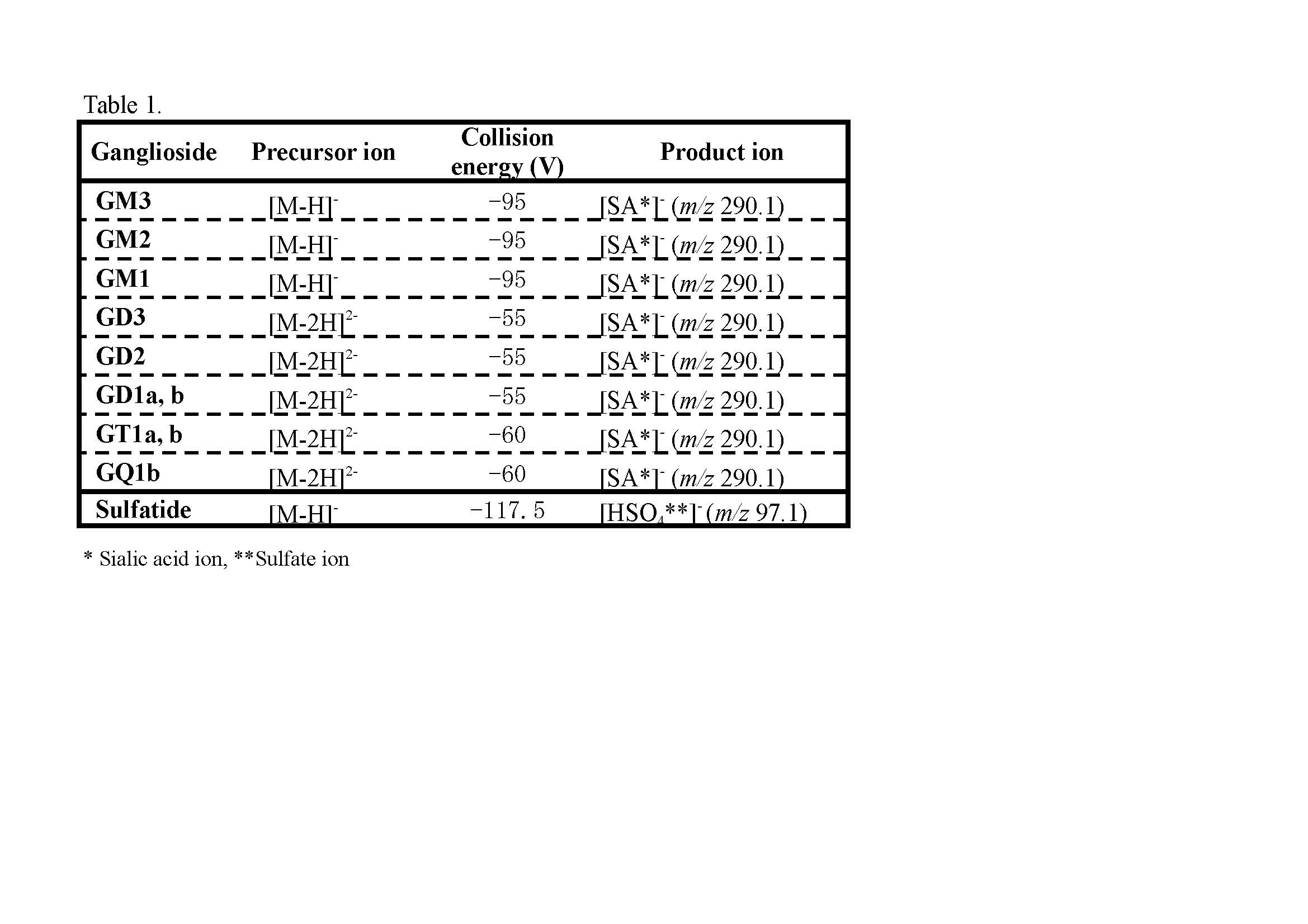

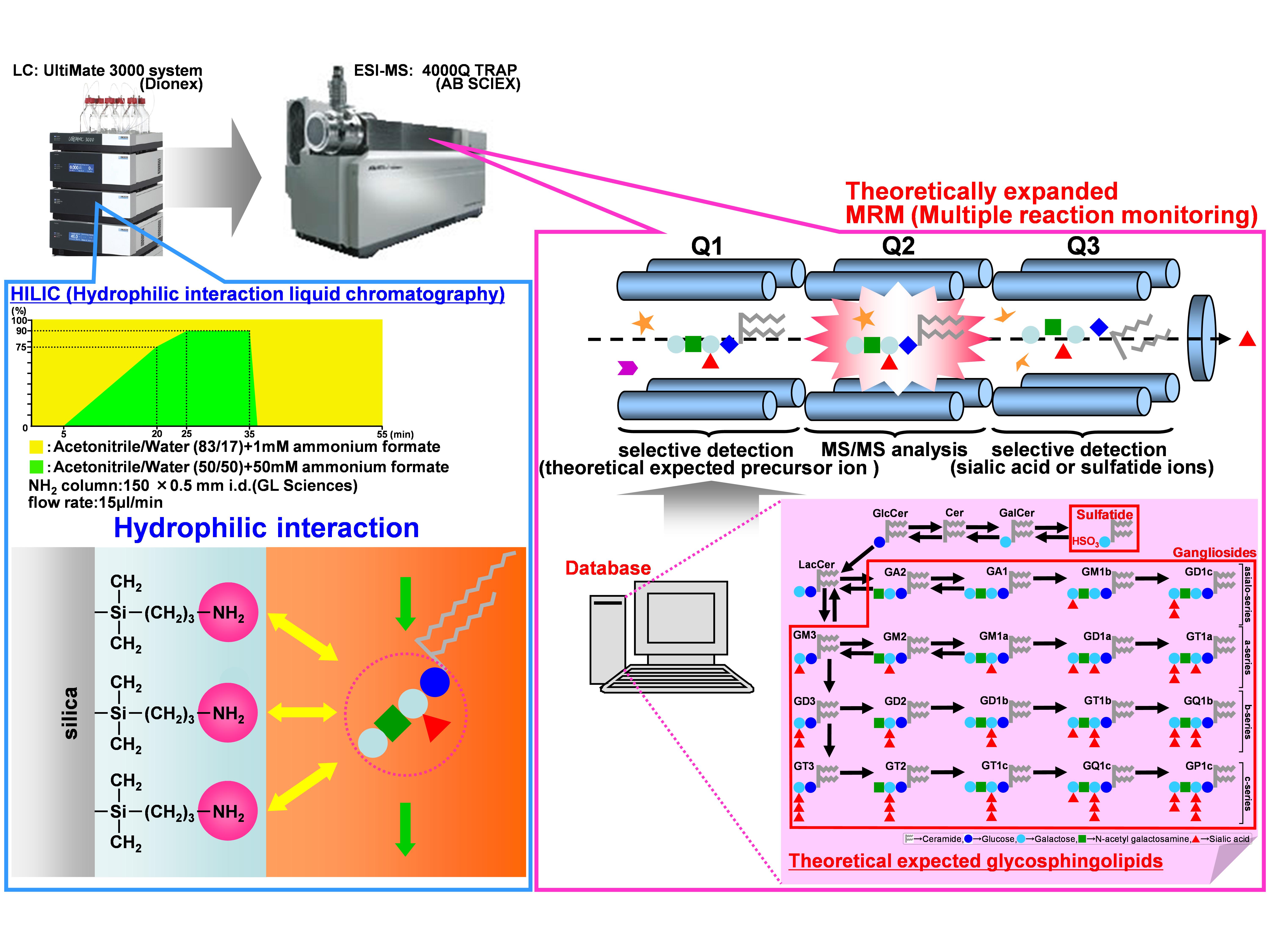
Fig. 1. New analytical strategy for glycosphingolipids by HILIC/ESI-MS with theoretically expanded MRM
Glycosphingolipid mixtures from porcine brain (1.0 μg) were separated by an NH2 column through normal-phase partitioning based on the interaction of carbohydrate hydroxyl groups with the amino phase. A variety of ganglioside and sulfatide molecular species, which were expected from theoretically constructed databases, were analyzed by highly sensitive MRM.
This figure was originally published in BUNSEKI KAGAKU. 61(6): 501–512. 2012 " Establishment of basic lipidomics platforms for discovery of lipid biomarkers" Ikeda K., Taguchi R., Soga T.

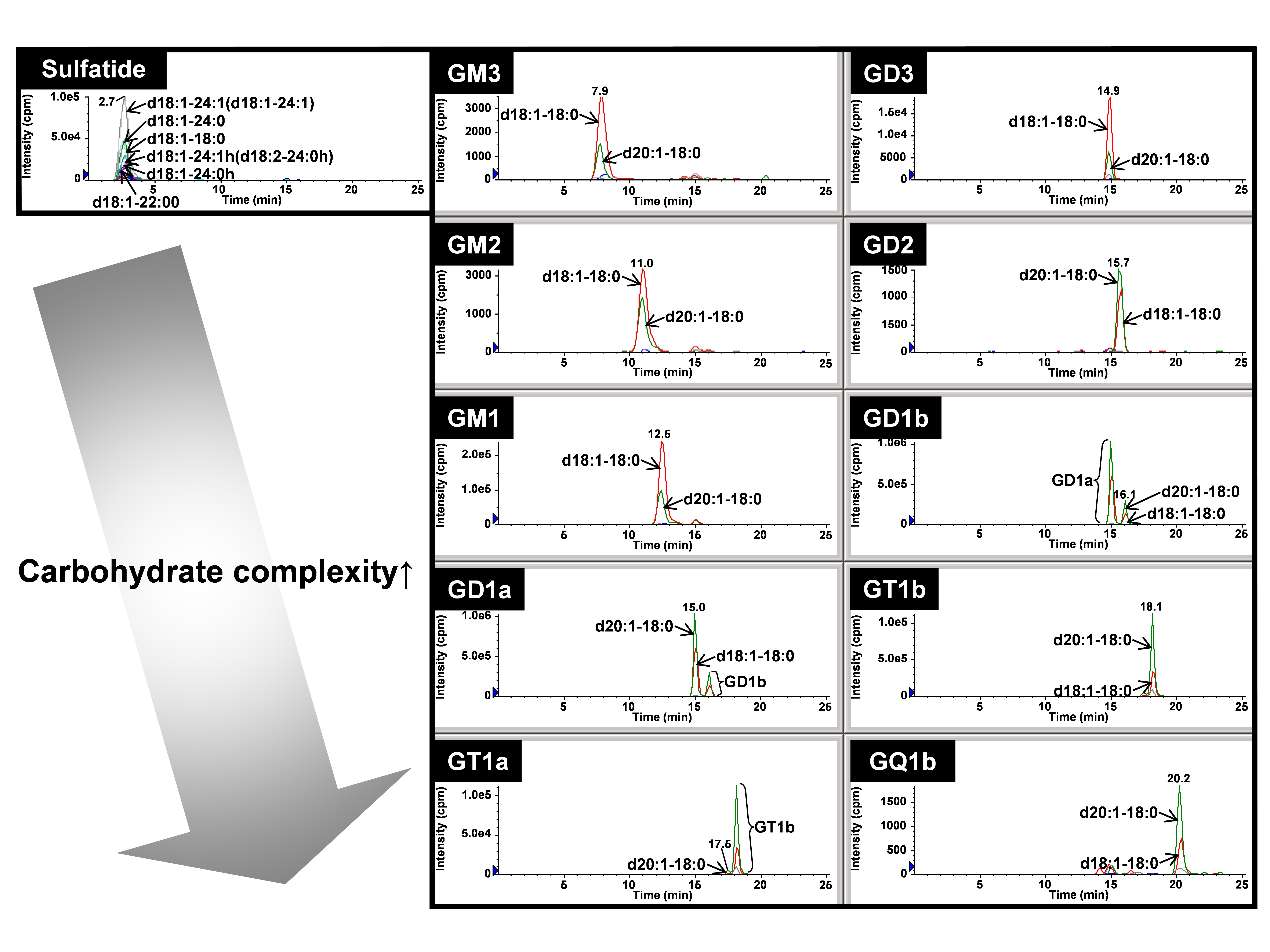
Fig. 2. Quantitative profiling of gangliosides and sulfatides according to carbohydrate types with theoretically expanded MRM
Overlaid chromatograms of major ganglioside and sulfatide molecular species were individually indicated by the selected mass chromatogram extracted from MRM. Each of the lipid classes was detected according to the carbohydrate moieties within 25 min in the following order: sulfatides > GM3 > GM2 > GM1 > GD3 > GD1a > GD2 > GD1b > GT1a > GT1b > GQ1b.
This figure was originally published in BUNSEKI KAGAKU. 61(6): 501–512. 2012 " Establishment of basic lipidomics platforms for discovery of lipid biomarkers" Ikeda K., Taguchi R., Soga T.
|
| Copyrights |
 Attribution-Non-Commercial Share Alike Attribution-Non-Commercial Share Alike
This work is released underCreative Commons licenses
|
| Date of registration:2014-12-16 14:54:46 |
- Ikeda, K., Shimizu, T., and Taguchi, R. (2008) Targeted analysis of ganglioside and sulfatide molecular species by LC/ESI-MS/MS with theoretically expanded multiple reaction monitoring. J. Lipid. Res. 49, 2678–2689 [PMID : 18703820]
- Ikeda, K., and Taguchi, R. (2010) Highly sensitive localization analysis of gangliosides and sulfatides including structural isomers in mouse cerebellum sections by combination of laser microdissection and hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography/electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry with theoretically expanded multiple reaction monitoring. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 24, 2957–2965 [PMID : 20872628]
|
This work is licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-Non-Commercial Share Alike. Please include the following citation
How to Cite this Work in an article:
Ikeda, Kazutaka,
Taguchi, Ryo,
(2014). GlycoPOD https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD.
Web.18,4,2024 .
How to Cite this Work in Website:
Ikeda, Kazutaka,
Taguchi, Ryo,
(2014).
Detailed analysis of glycosphingolipids at the molecular species level by HILIC/ESI-MS.
Retrieved 18,4,2024 ,
from https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD/protocolShow.action?nodeId=t221.
html source
Ikeda, Kazutaka,
Taguchi, Ryo,
(2014).
<b>Detailed analysis of glycosphingolipids at the molecular species level by HILIC/ESI-MS</b>.
Retrieved 4 18,2024 ,
from <a href="https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD/protocolShow.action?nodeId=t221" target="_blank">https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD/protocolShow.action?nodeId=t221</a>.
Including references that appeared in the References tab in your work is
much appreciated.
For those who wish to reuse the figures/tables, please contact JCGGDB
management office (jcggdb-ml@aist.go.jp).
|
|