Notch signaling is an evolutionarily conserved mechanism that controls many cell-fate specifications through local cell-cell interactions1). The extracellular domain of Notch receptor contains 36 epidermal growth factor (EGF)-like repeats 2). Some of these EGF-like repeats contain a consensus sequence to be modified by the O-linked tetrasaccharide which is required for control of the interactions between Notch and its ligands 3). First, O-fucosyltransferase 1 (O-fut1) catalyzes the O-fucosylation of this consensus sequence 4) 5) (Fig. 1A). Thereafter, this O-fucose is further elongated and become the O-linked tetrasaccharide 6) (Fig. 1A).
For the O-fucose modification of Notch, GDP-fucose is utilized as the donor of fucose. The GDP-fucose is synthesized in cytosol and is transported into the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and Golgi. Golgi GDP-fucose transporter (Gfr) localize to the Golgi, and ER GDP-fucose transporter (Efr) localize in the ER 7) 8) (Fig. 1B). The Gfr and Efr transport GDP-fucose to the ER and Golgi, respectively (Fig. 1B). O-fut1 catalyzes O-fucosylation of Notch in the ER (Fig. 1B). Additionally, it is also used for O-fucosylation of N-linked glycosylation attached to bulk proteins, including Notch, in the Golgi 9) (Fig. 1B). This modification is catalyzed by Fucosyltransferases (FucT) (Fig. 1B).
We can monitor the level of fucose modifications, if we generate somatic mosaic clones of mutants, such as Gfr, in which the intracellular transport of GDP-fucose is disrupted and detect these modifications by Aleuria Aurantia Lectin (AAL) staining 10) 11) 12). These somatic mosaic clones of mutants can be generates easily in Drosophila wing imaginal discs by FLP/FRT system 13). Here, to understand a role of Gfr in protein fucosylation, we generated somatic mosaic of this mutant and detected fucose modifications by AAL staining. |
| Category | Glycosyltransferases & related proteins |
| Protocol Name | Clonal analysis of Notch O-fucosylation in Drosophila melanogaster |
Authors
 |
Aoyama, Naoki
Division of Experimental Therapeutics, Graduate School of Medicine, Kyoto University
Yamakawa, Tomoko
Department of Biological Sciences, Osaka University
Matsuno, Kenji
*
Department of Biological Sciences, Osaka University
*To whom correspondence should be addressed.
|
| KeyWords |
|
Reagents
 |
| ● |
Phosphate buffered saline (PBS) |
| ● |
Bovine serum albumin (BSA) |
| ● |
PLP fixative solution [2% paraformaldehyde, 0.01 M NaIO4, 0.075 M lysine, 0.037 M NaPO4 (pH 7.2)] |
| ● |
PBS-DT [0.3% (w/v) deoxycholic acid sodium salt monohydrate, 0.3% TritonX (v/v) in PBS] |
| ● |
Biotin-conjugated AAL (Aleuria Aurantia lectin) |
| ● |
Streptavidin-conjugated Alexa 555 |
| ● |
|
|
Instruments
 |
| ● |
Fluorescence microscopy or confocal laser scanning microscopy |
| ● |
|
| ● |
|
|
| Methods |
|
1. |
Generating somatic clones in Drosophila larvae by FLP/FRT system |
| 1) |
Cross hs-flp; FRT82B, Gfr1 / TM6B1, Tb females to FRT82B, ubi-GFP / TM6B, Tb1 males in a plastic vial containing standard fly food at 25°C. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 2) |
After 24–48 h, remove the parental flies from the vial and incubates the vial for 1 h at 37°C. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 3) |
Rear larvae at 25°C 3–4 days, until they develop to the third instar. |
Comment 0
|
|
|
|
2. |
Aleuria aurantia lectin (AAL) staining of the imaginal discs |
| 1) |
Dissect out the wing imaginal discs from the third instar larvae and fix them in PLP fixative solution for 40 min on ice. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 2) |
Wash the sample three times with PBS-DT for 5 min at room temperature. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 3) |
Incubate the sample in PBS containing 1% BSA for 1 h at room temperature. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 4) |
Incubate the sample in PBS containing 1μg/mL biotin-conjugated AAL and 1% BSA for 2 h at room temperature. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 5) |
Wash the sample with PBS-DT for 5 min three times at room temperature. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 6) |
Incubate the sample in PBS containing streptavidin-conjugated Alexa 555 (1:500 dilution) and 1% BSA for 1 h at room temperature. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 7) |
Wash the sample with PBS-DT for 5 min four times at room temperature. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 8) |
Mount samples with 90% glycerol and obtain the images with fluorescence microscopy or confocal laser scanning microscopy. |
Comment 0
|
|
|
| Notes | FLP/FRT system efficiently induces genetic mosaic in Drosophila melanogaster. This system is applicable to most of mutations. |
| Initial amount | Small number of flies is sufficient to perform these experiments. Typically, 10–20 female and male flies are sufficient. |
| Discussion | This method is generally useful to study the functions of other genes involved in protein glycosylation. |
| Figure & Legends |
Figure & Legends

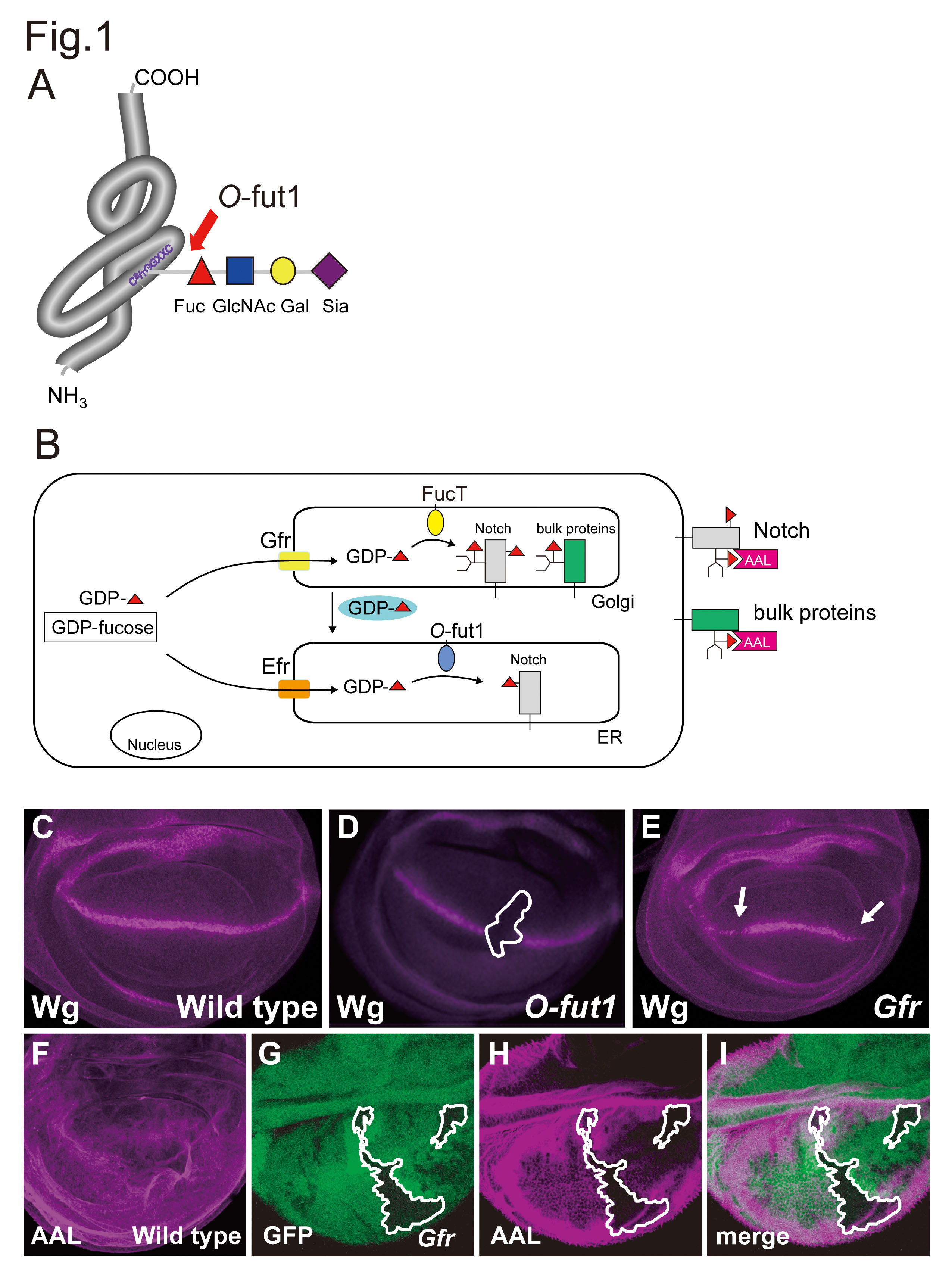
Fig. 1. Mechanisms of Notch O-fucosylation in Drosophila.
(A) The O-linked tetrasaccharide (Sia-α2,3-Gal-β1,4-GlcNAc-β1,3-Fuc) is added to the Ser/Thr residue in the C2X4-5S/TC3 consensus sequence that presents in subset of EGF-like repeats of Notch. The first O-fucose is added by O-fut1. (B) GDP-fucose is synthesized in the cytoplasm. GDP-fucose is transported into the lumens of the ER and Golgi by two GDP-fucose transporters, Efr and Gfr, which are specifically localized to the ER and Golgi, respectively. Efr and Gfr redundantly function for the O-fucosylation of Notch EGF-like repeats by O-fut1, which occurs in the lumen of the ER. GDP-fucose that is imported into the Golgi lumen by Gfr is retrogradely transported from the Golgi to the ER. Gfr, but not Efr, also play a major role in the fucosylation of N-glycans, which occur in the Golgi lumen, by FucT. (C) In wild-type, the induction of wingless (wg) gene expression as a stripe across the wing imaginal disc (magenta) requires the activation of Notch signaling. (D) The wg expression was abolished in O-fut1 mutant clone (inside the white line). (E) In the wing imaginal disc of the Gfr homozygote, the expression domain of wg is reduced (arrowheads). (F) ALL staining of a wild-type wing imaginal disc. (G-H) ALL staining (magenta) was diminished in Gfr mutant clone (inside the white line), indicated by the absence of GFP (green).
Fig. 1A was obtained and modified from "Experimental Glycoscience Glycobiology" edited by Taniguchi N. et al. Springer Japan KK. 2008, pp.295–298. The original publication is available at http://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-4-431-77922-3_70.
Fig. 1C & 1E were originally published in Proceeding of the National Academy of Science of the United States of America. Hiroyuki O. Ishikawa et al. "Notch deficiency implicated in the pathogenesis of congenital disorder of glcosylation llc" 2005, 102 (51): 18532–537. © 2012 National Academy of Sciences, U.S.A.
Fig. 1D was originally publlished in Development. Takeshi Sasamura et al. "neurotic, a novel maternal neurogenic gene, encodes an O-fucosyltransferase that is essential for Notch-Delta interactions" 2003, 130 (20): 4785–95.
Fig. 1F was originally published in The Journal of Biological Chemistry. Hiroyuki O. Ishikawa et al. "Two Pathways for Importing GDP-fucose into the Endoplasmic Reticulum Lumen Function Redundantly in the O-Fucosulation of Notch in Drosophila" 2010, 285 (6): 4122–29.
Fig. 1G, 1H, and 1I were originally published in Proceeding of the National Academy of Science of the United States of America. Tomonori Ayukawa et al. "Rescue of Notch signaling in cells incapable of GDB-L-fucose synthesis by gap junction transfer of GDP-L-fucose in Drosophila" 2012, 109 (38):15318–323.

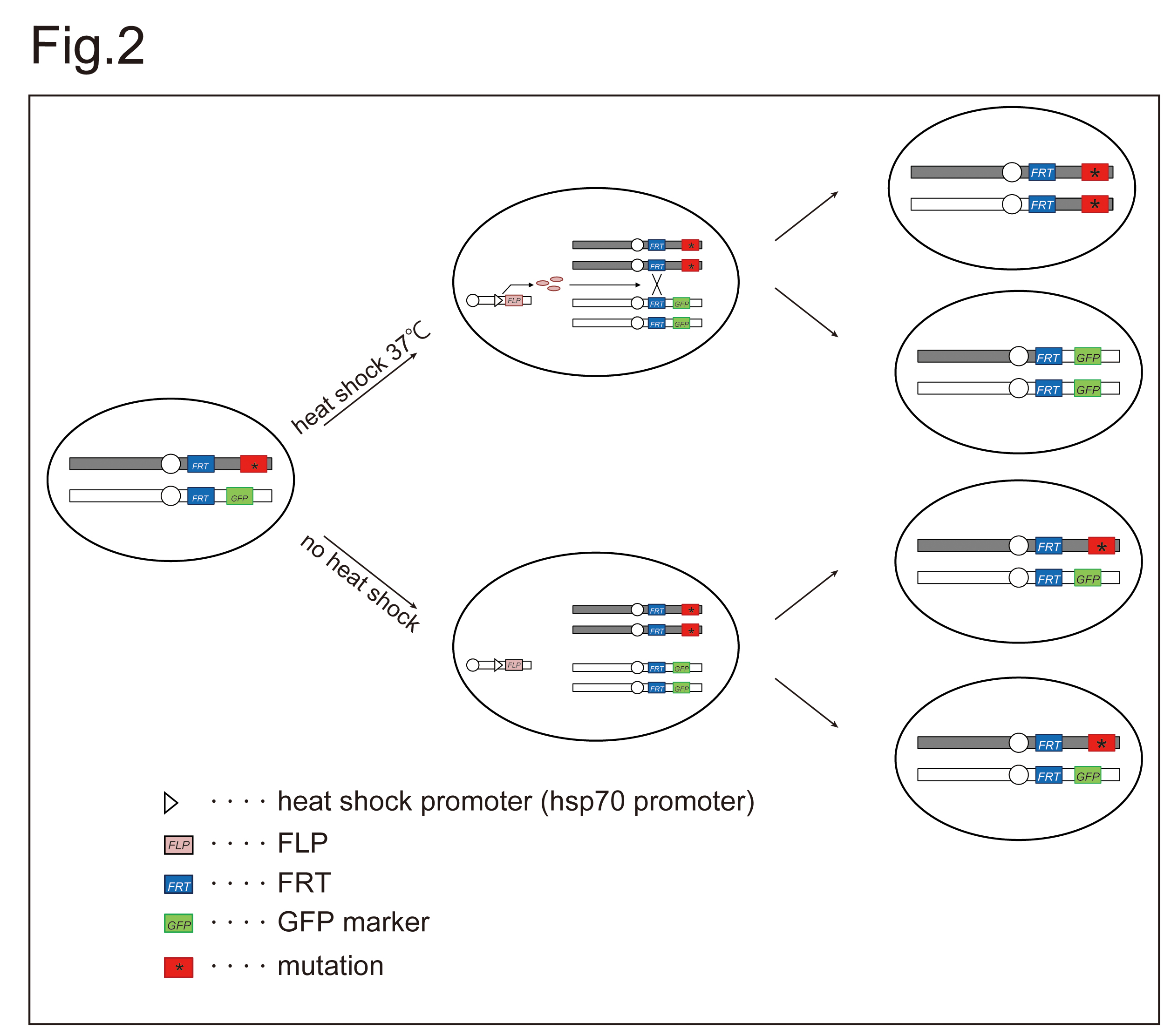
Fig. 2. Mating scheme for generating somatic mosaic clones of a mutant by FLP/FRT system.
Site-specific chromosomal recombination is induced by FLP/FRT system. The expression of FLP, encoding a yeast DNA recombinase, is controlled by hsp70 promoter, which is activated by a heat shock treatment at 37°C for 1 h. The FLP protein induces chromosomal exchange between two FRT sequences in trans. If site-specific recombination between homologous chromosomes is induced between non-sister chromatids, and the daughter chromatids segregate appropriately after replication, the region of the chromosome arm that lies distal to the FRT site becomes homozygous. Thus, in heterozygous-mutant flies, clonal cells that inherit two copies of the parental mutant chromosome (asterisk in red square) are induced (top in the left). These cells can be distinguished based on the absence of GFP marker (GFP in green square). |
| Copyrights |
 Attribution-Non-Commercial Share Alike Attribution-Non-Commercial Share Alike
This work is released underCreative Commons licenses
|
| Date of registration:2016-10-25 13:57:22 |
- Artavanis-Tsakonas, S., Rand, M.D., and Lake, R.J. (1999) Notch Signaling: Cell Fate Control and Signal Integration in Development. Science 284, 770–776 [PMID : 10221902]
- Wharton, K.A., Johansen, K.M., Xu, T., and Artavanis-Tsakonas, S. (1985) Nucleotide Sequence from the Neurogenic Locus Notch Implies a Gene Product That Shares Homology with Proteins Containing Egf-Like Repeats. Cell. 43, 567–81 [PMID : 3935325]
- Rana, N.A., and Haltiwanger, R.S. (2011) Fringe Benefits: Functional and Structural Impacts of O-Glycosylation on the Extracellular Domain of Notch Receptors. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 21, 583–9 [PMID : 21924891]
- Sasamura, T., Sasaki N., Miyashita, F., Nakao, S., Ishikawa, H.O., Ito, M., Kitagawa, M., Harigaya, K., Spana, E., Bilder, D., Perrimon, N., and Matsuno, K. (2003) Neurotic, a Novel Maternal Neurogenic Gene, Encodes an O-Fucosyltransferase That is Essential for Notch-Delta Interactions. Development. 130, 4785–95 [PMID : 12917292]
- Okajima, T., and Irvine, K.D. (2002) Regulation of Notch Signaling by O-Linked Fucose. Cell. 111, 893–904 [PMID : 12526814]
- Moloney, D.J., Shair, L.H., Lu, F.M., Xia, J., Locke, R., Matta, K.L., and Haltiwanger, R.S. (2000) Mammalian Notch1 Is Modified with Two Unusual Forms of O-Linked Glycosylation Found on Epidermal Growth Factor-Like Modules. J Biol Chem. 275, 9604–11 [PMID : 10734111]
- Ishikawa, H.O., Higashi S., Ayukawa, T., Sasamura, T., Kitagawa, M., Harigaya, K., Aoki, K., Ishida, N., Sanai, Y., and Matsuno, K. (2005) Notch Deficiency Implicated in the Pathogenesis of Congenital Disorder of Glycosylation IIc. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 102, 18532–7 [PMID : 16344471]
- Ishikawa, H.O., Ayukawa, T., Nakayama M., Higashi, S., Kamiyama, S., Nishihara, S., Aoki K., Ishida, N., Sanai, Y., Matsuno K. (2010) Two Pathways for Importing Gdp-Fucose into the Endoplasmic Reticulum Lumen Function Redundantly in the O-Fucosylation of Notch in Drosophila. J Biol Chem. 285, 4122–9 [PMID : 19948734]
- Sturla, L., Rampal, R., Haltiwanger, R.S., Fruscione, F., Etzioni, A., Tonetti, M. (2003) Differential Terminal Fucosylation of N-Linked Glycans Versus Protein O-Fucosylation in Leukocyte Adhesion Deficiency Type II (Cdg IIc). J Biol Chem. 278, 26727–33 [PMID : 12738772]
- Lühn, K., Laskowska, A., Pielage, J., Klämbt, C., Ipe, U., Vestweber, D. and Wild, M.K. (2004) Identification and Molecular Cloning of a Functional Gdp-Fucose Transporter in Drosophila Melanogaster. Exp Cell Res. 301, 242–50 [PMID : 15530860]
- Kochibe, N., and Furukawa, K. (1980) Purification and Properties of a Novel Fucose-Specific Hemagglutinin of Aleuria Aurantia. Biochemistry. 19, 2841–6 [PMID : 7397108]
- Ayukawa T., Matsumoto K., Ishikawa HO., Ishio A., Yamakawa T., Aoyama N., Suzuki T., Matsuno K. (2012) Rescue of Notch signaling in cells incapable of GDP-L-fucose synthesis by gap junction transfer of GDP-L-fucose in Drosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 109, 15318–23[PMID : 22949680]
- Xu, T., and Rubin, G.M. (1993) Analysis of Genetic Mosaics in Developing and Adult Drosophila Tissues. Development. 117, 1223–37 [PMID : 8404527]
|
This work is licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-Non-Commercial Share Alike. Please include the following citation
How to Cite this Work in an article:
Aoyama, Naoki,
Yamakawa, Tomoko,
Matsuno, Kenji,
(2016). GlycoPOD https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD.
Web.20,4,2024 .
How to Cite this Work in Website:
Aoyama, Naoki,
Yamakawa, Tomoko,
Matsuno, Kenji,
(2016).
Clonal analysis of Notch O-fucosylation in Drosophila melanogaster.
Retrieved 20,4,2024 ,
from https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD/protocolShow.action?nodeId=t200.
html source
Aoyama, Naoki,
Yamakawa, Tomoko,
Matsuno, Kenji,
(2016).
<b>Clonal analysis of Notch <em>O</em>-fucosylation in <em>Drosophila melanogaster</em></b>.
Retrieved 4 20,2024 ,
from <a href="https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD/protocolShow.action?nodeId=t200" target="_blank">https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD/protocolShow.action?nodeId=t200</a>.
Including references that appeared in the References tab in your work is
much appreciated.
For those who wish to reuse the figures/tables, please contact JCGGDB
management office (jcggdb-ml@aist.go.jp).
|
|