Glycoproteins are attached to a variety of oligosaccharides differing in their monosaccharide compositions, sequences, branches, linkages and modifications. Liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry (LC/MS) is a powerful tool for the separation and characterization of the glycans (Ruhaak et al. 2009; Morelle et al. 2006; Zaia 2004). Here we present the procedure for profiling of N-glycans by LC/MS. |
| Category | Isolation & structural analysis of glycans |
| Protocol Name | N-Glycan profiling by LC/MS |
Authors
 |
Kuribayashi, Ryosuke
Division of Biological Chemistry and Biologicals, National Institute of Health Sciences
Nakazawa, Shiori
Division of Biological Chemistry and Biologicals, National Institute of Health Sciences
Kawasaki, Nana
*
Division of Biological Chemistry and Biologicals, National Institute of Health Sciences
*To whom correspondence should be addressed.
|
| KeyWords |
|
Reagents
 |
| ● |
N-Glycosidase F (Roche Diagnostics GmbH, Mannheim, Germany) |
| ● |
Sodium tetrahydroborate (NaBH4, Wako Pure Chemical Industries Ltd., Osaka, Japan) |
| ● |
Ultrapure water (Merck Millipore, Billerica, MA) |
| ● |
Acetonitrile (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO) |
|
Instruments
 |
| ● |
HPLC: Paradigm MS4 (Bruker-Michrom Inc., Auburn, CA) |
| ● |
Mass spectrometer : LTQ-FT (Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., Waltham, MA) |
|
| Methods |
|
1. |
|
| 1) |
Dissolve a glycoprotein (12 μg) in 50 μL of 0.5 M Tris-HCl (pH 8.6) containing 8 M guanidine hydrochloride, and incubate it with 2 μL of 1 M dithiothreitol at 65°C for 30 min. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 2) |
Add 4.8 μL of 1 M sodium monoiodoacetate, and incubate the mixture at 25°C for 40 min in the dark. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 3) |
Remove the excess reagent by gel filtration with Sephadex G-25 (e. g., PD-10 column, GE Healthcare, Little Chalfont, UK), and lyophilize the eluate.
|
Comment 0
|

|
| 4) |
Dissolve the glycoprotein in 50 μL of 50 μM phosphate buffer (pH 8.0)/10 mM EDTA, and incubate the sample with 5 units of N-Glycosidase F at 37°C for 24 h.
|
Comment 0
|

|
| 5) |
Add cold ethanol (final concentration: 60%) to precipitate the deglycosylated protein, and incubate it −20°C for 2 h.
|
Comment 0
|

|
| 6) |
Centrifuge the sample at 15,000 × g for 15 min, and dry the supernatant by SpeedVac. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 7) |
Dissolve the oligosaccharides in 250 μL of 0.5 M NaBH4, and incubate it at 25°C for 16 h.
|
Comment 0
|

|
| 8) |
Terminate the reaction with diluted acetic acid and, extract the borohydrate-reduced oligosaccharides with a solid-phase tip (e. g. an ENVI carb C cartrige, Supelco/Sigma-Aldrich, Bellefonte, PA).
|
Comment 0
|

|
| 9) |
Dry the eluate, and dissolve the borohydrate-reduced oligosaccharides in water (30 μL).
|
Comment 0
|
|
|
|
2. |
|
| 1) |
Equilibrate a graphitized carbon column (e. g. HyperCarb 0.075 – 0.2 mM i. d. × 150 mM, 5μM, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) with 95% of mobile phase A at an appropriate flow rate (0.2–3 mL/min) for 20–30 min. Mobile phase A: 5 mM NH4HCO3/ 2% acetonitrile; mobile phase B: 5 mM NH4HCO3/ 80% acetonitrile
|
Comment 0
|

|
| 2) |
Attach the nanospray tip to the outlet of the column, and set it on the x-y-z translational stage (AMR Inc., Tokyo, Japan). |
Comment 0
|

|
| 3) |
Apply a voltage of 2.5 kV to the tip, and check the stable spray with the mobile phase.
|
Comment 0
|

|
| 4) |
Pass a sample (2 μL) through the cartridge into a LC injector valve, and start simultaneously both the chromatography gradient and mass spectrometer data collection. Acquire mass spectra at a range of m/z 800–2,000 and MS/MS spectra in a data-dependent manner. Gradient: 8−50% of mobile phase B in 60 min, linear. Collision energy: 25% |
Comment 0
|
|
|
| Initial amount | |
| Figure & Legends |
Figure & Legends

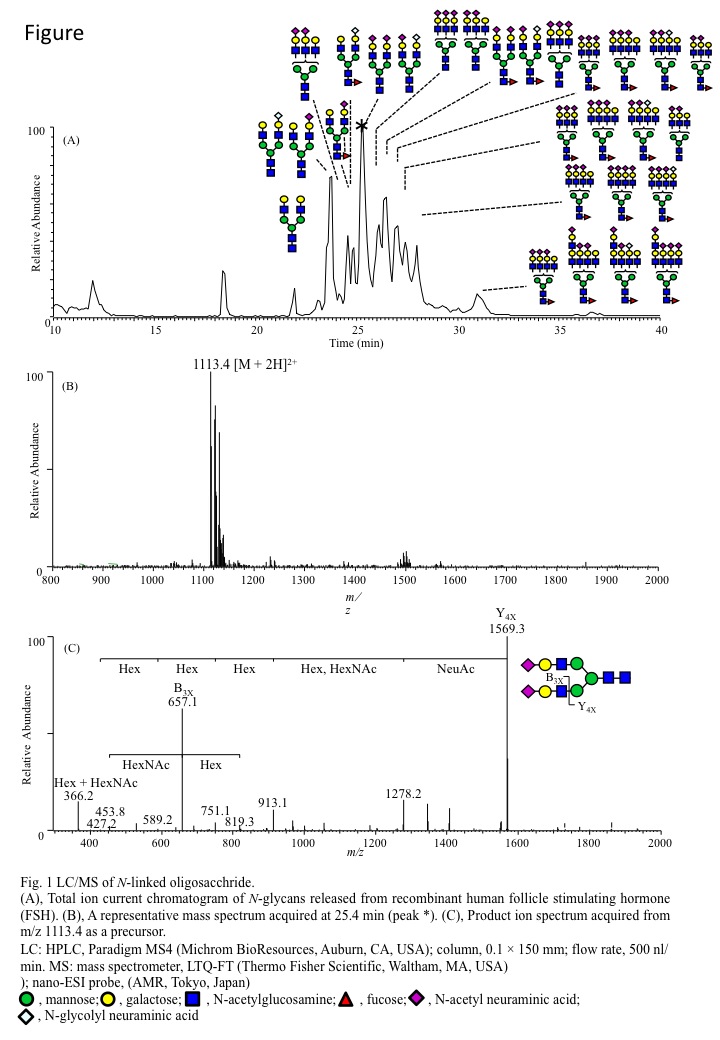
(A), Total ion current chromatogram of N-glycans released from recombinant human follicle stimulating hormone (FSH).
(B), A representative mass spectrum acquired at 25.4 min (peak *).
(C), Product ion spectrum acquired from m/z 1113.4 as a precursor.
LC: HPLC, Paradigm MS4 (Bruker-Michrom Inc., Auburn, CA); column, 0.1 × 150 mm; flow rate, 500 nL/min. MS: mass spectrometer, LTQ-FT (Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc.); nano-ESI probe, (AMR Inc.) |
| Copyrights |
 Attribution-Non-Commercial Share Alike Attribution-Non-Commercial Share Alike
This work is released underCreative Commons licenses
|
| Date of registration:2015-05-08 15:07:08 |
- Ruhaak, L.R., Deelder, A.M., and Wuhrer, M. (2009) Oligosaccharide analysis by graphitized carbon liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Anal Bioanal Chem. 394, 163–74 [PMID : 19247642]
- Morelle, W., Canis, K., Chirat, F., Faid, V., and Michalski, J.C. (2006) The use of mass spectrometry for the proteomic analysis of glycosylation. Proteomics. 6, 3993–4015 [PMID : 16786490]
- Zaia, J. (2004) Mass spectrometry of oligosaccharides. Mass Spectrom Rev. 23, 161–227 [PMID : 14966796]
|
This work is licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-Non-Commercial Share Alike. Please include the following citation
How to Cite this Work in an article:
Kuribayashi, Ryosuke,
Nakazawa, Shiori,
Kawasaki, Nana,
(2015). GlycoPOD https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD.
Web.25,4,2024 .
How to Cite this Work in Website:
Kuribayashi, Ryosuke,
Nakazawa, Shiori,
Kawasaki, Nana,
(2015).
N-Glycan profiling by LC/MS.
Retrieved 25,4,2024 ,
from https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD/protocolShow.action?nodeId=t194.
html source
Kuribayashi, Ryosuke,
Nakazawa, Shiori,
Kawasaki, Nana,
(2015).
<b><em>N</em>-Glycan profiling by LC/MS</b>.
Retrieved 4 25,2024 ,
from <a href="https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD/protocolShow.action?nodeId=t194" target="_blank">https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD/protocolShow.action?nodeId=t194</a>.
Including references that appeared in the References tab in your work is
much appreciated.
For those who wish to reuse the figures/tables, please contact JCGGDB
management office (jcggdb-ml@aist.go.jp).
|
|