Ceramidase (EC 3.5.1.23, CDase) catalyzes the hydrolysis of the N-acyl linkage between sphingosine and fatty acids in ceramide. Based on optimal pH and primary structure, CDases are classified into three groups: acid, neutral, and alkaline enzymes. The first neutral CDase was first purified and cloned from Pseudomonas aeruginosa1) 2). Since then, neutral CDases with an optimal pH of 6.5–8.5 have been cloned from Drosophila, zebrafish, rat, mouse, and human. Here, methods for the hydrolysis of ceramide by Pseudomonas CDase and detection of CDase activity from Pseudomonas aeruginosa and mammalian cells or tissues are described. |
| Category | Glycosidases & related proteins |
| Protocol Name | Hydrolysis of ceramide by ceramidase (CDase) and measurement of CDase activity |
Authors
 |
Okino, Nozomu
*
Department of Bioscience and Biotechnology, Graduate School of Bioresource and Bioenvironmental Sciences, Kyushu University
Ito, Makoto
Department of Bioscience and Biotechnology, Graduate School of Bioresource and Bioenvironmental Sciences, Kyushu University
*To whom correspondence should be addressed.
|
| KeyWords |
|
Reagents
 |
| ● |
|
| ● |
C12-NBD-Cer (Avanti Polar Lipids, Inc., Alabaster, AL) |
| ● |
TLC plate (Silicagel 60, 20 × 20 cm, Merck Millipore, Billerica, MA) |
| ● |
|
| ● |
|
| ● |
CHCl3-MeOH mixture (C/M, volume/volume) |
| ● |
Ninhydrin reagent:
Dissolve 250 mg of ninhydrin in 100 mL of water-saturated n-butanol. Store the reagent in a refrigerator. |
|
Instruments
 |
| ● |
TLC developing chamber (inside, to 24 cm × to 11 cm × to 21 cm) |
| ● |
|
| ● |
TLC Chromatoscanner (CS-9300, Shimadzu Corp., Kyoto, Japan) |
| ● |
UV transiluminator or AE-6935B Visirays (ATTO Corporation, Tokyo, Japan) |
|
| Methods |
|
1. |
Hydrolysis of ceramide by CDase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa |
| 1) |
Dissolve the ceramide ( to 10 nmol) in 10 μL of 50 mM Tris-HCl buffer, pH 8.5, containing 1.0%(w/v) Triton X-100 and 5 mM CaCl2. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 2) |
Add 10 μL of Pseudomonas CDase (to 1 mU) and incubate at 37°C for an appropriate period. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 3) |
Stop the reaction by adding 50 μL of chloroform/methanol (2:1, v/v). After vortexing for a few seconds, centrifuge at 16,000 x g for 1 min. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 4) |
Remove the upper phase and dry the lower phase. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 5) |
Dissolve the sample in 20 μL of chloroform/methanol (2:1, v/v) and apply to a TLC plate. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 6) |
Develop the TLC plate with chloroform, methanol, and 25% ammonia (14:6:1, v/v/v) in a TLC chamber. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 7) |
Dry the plate, heat on a hot plate at 110°C for 5 min, and spray on the ninhydrin reagent. Ninhydrin reagent can detect free amino groups of sphingosine derived from the enzymatic reaction. |
Comment 0
|
|
|
|
2. |
Detection of CDase activity from Pseudomonas aeruginosa |
| 1) |
Dissolve 1 nmol of C12-NBD-Cer in 10 μL of 2× reaction buffer (50 mM Tris-HCl buffer, pH 8.5 containing 0.5%(w/v) Triton X-100 and 5 mM CaCl2). |
Comment 0
|

|
| 2) |
Add 10 μL of CDase and incubate at 37°C for an appropriate period (~1 h). |
Comment 0
|

|
| 3) |
Stop the reaction by adding 50 μL of chloroform/methanol (2:1, v/v). After vortexing for a few seconds, centrifuge at 16,000 × g for 1 min. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 4) |
Apply 5 μL of the lower phase to a TLC plate. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 5) |
Develop the TLC plate with chloroform, methanol, and 25% ammonia (14:6:1, v/v/v) in a TLC chamber. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 6) |
Dry the plate and visualize C12-NBD-Cer and C12-NBD-fatty acid with an AE-6935B Visirays or UV transilluminator. Quantifying the C12-NBD-fatty acid released by the actions of the enzyme and the remaining C12-NBD-Cer with a Shimadzu CS-9300 chromatoscanner (excitation, 475 nm; emission, 525 nm). One enzyme unit of CDase is the amount capable of catalyzing the release of 1 μmol of C12-NBD-fatty acid/min from C12-NBD-Cer. |
Comment 0
|
|
|
|
3. |
Detection of CDase activity from mammalian cells or tissues |
| 1) |
When mammalian cells or tissues are used for the enzyme source3) 4) 5), 50 mM Tris-HCl buffer, pH 7.5 containing 2%(w/v) sodium cholate should be used for the 2× reaction buffer.
|
Comment 0
|
|
|
| Figure & Legends |
Figure & Legends

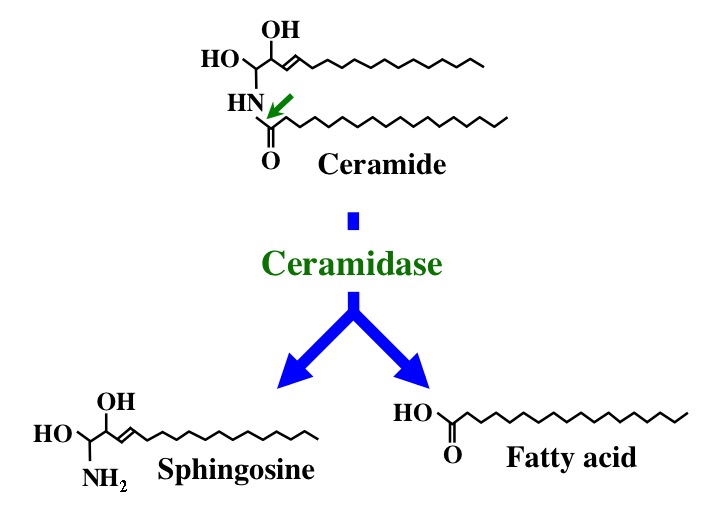
Fig. 1. Action mode of CDase. |
| Copyrights |
 Attribution-Non-Commercial Share Alike Attribution-Non-Commercial Share Alike
This work is released underCreative Commons licenses
|
| Date of registration:2014-07-31 10:42:31 |
- Okino, N., Tani, M., Imayama, S., and Ito, M. (1998) Purification and characterization of a novel ceramidase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Journal of Biological Chemistry 273, 14368–14373 [PMID : 9603946]
- Okino, N., Ichinose, S., Omori, A., Imayama, S., Nakamura, T., and Ito, M. (1999) Molecular cloning, sequencing, and expression of the gene encoding alkaline ceramidase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Cloning of a ceramidase homologue from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Journal of Biological Chemistry 274, 36616–36622 [PMID : 10593963]
- Tani, M., Okino, N., Mitsutake, S., Tanigawa, T., Izu, H., and Ito, M. (2000) Purification and characterization of a neutral ceramidase from mouse liver. A single protein catalyzes the reversible reaction in which ceramide is both hydrolyzed and synthesized. Journal of Biological Chemistry 275, 3462–3468 [PMID : 10652340]
- Tani, M., Okino, N., Mori, K., Tanigawa, T., Izu, H., and Ito, M. (2000) Molecular cloning of the full-length cDNA encoding mouse neutral ceramidase. A novel but highly conserved gene family of neutral/alkaline ceramidases. Journal of Biological Chemistry 275, 11229–11234 [PMID : 10753931]
- Mitsutake, S., Tani, M., Okino, N., Mori, K., Ichinose, S., Omori, A., Iida, H., Nakamura, T., and Ito, M. (2001) Purification, characterization, molecular cloning, and subcellular distribution of neutral ceramidase of rat kidney. Journal of Biological Chemistry 276, 26249–26259 [PMID : 11328816]
|
This work is licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-Non-Commercial Share Alike. Please include the following citation
How to Cite this Work in an article:
Okino, Nozomu,
Ito, Makoto,
(2014). GlycoPOD https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD.
Web.25,4,2024 .
How to Cite this Work in Website:
Okino, Nozomu,
Ito, Makoto,
(2014).
Hydrolysis of ceramide by ceramidase (CDase) and measurement of CDase activity.
Retrieved 25,4,2024 ,
from https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD/protocolShow.action?nodeId=t178.
html source
Okino, Nozomu,
Ito, Makoto,
(2014).
<b>Hydrolysis of ceramide by ceramidase (CDase) and measurement of CDase activity</b>.
Retrieved 4 25,2024 ,
from <a href="https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD/protocolShow.action?nodeId=t178" target="_blank">https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD/protocolShow.action?nodeId=t178</a>.
Including references that appeared in the References tab in your work is
much appreciated.
For those who wish to reuse the figures/tables, please contact JCGGDB
management office (jcggdb-ml@aist.go.jp).
|
|