Sphingolipid ceramide N-deacylase (SCDase) hydrolyzes the N-acyl linkage between fatty acids and sphingosine in the ceramide moiety of various GSLs and sphingomyelin1). SCDase also catalyzes a reverse hydrolysis reaction in which free fatty acids are transferred to various lyso-sphingolipids. |
| Category | Glycosidases & related proteins |
| Protocol Name | Hydrolysis of glycosphingolipids by a sphingolipid ceramide N-deacylase (SCDase) |
Authors
 |
Okino, Nozomu
*
Department of Bioscience and Biotechnology, Graduate School of Bioresource and Bioenvironmental Sciences, Kyushu University
Ito, Makoto
Department of Bioscience and Biotechnology, Graduate School of Bioresource and Bioenvironmental Sciences, Kyushu University
*To whom correspondence should be addressed.
|
| KeyWords |
|
Reagents
 |
| ● |
Sphingolipid ceramide N-deacylase (SCDase) from Pseudomonas sp. TK4 (Takara Bio Inc., Otsu, Japan) |
| ● |
TLC plate (Silicagel 60, 20 × 20 cm, Merck Millipore, Billerica, MA) |
| ● |
|
| ● |
|
| ● |
CHCl3-MeOH mixture (C/M, volume/volume) |
| ● |
Orcinol reagent:
Dissolve 250 mg of orcinol in 50 mL of H2SO4, and make up to 100 mL with DW.
Store the reagent in a refrigerator. |
| ● |
Ninhydrin reagent:
Dissolve 250 mg of ninhydrin in 100 mL of water-saturated n-butanol.
Store the reagent in a refrigerator. |
|
Instruments
 |
| ● |
TLC developing chamber (inside, to 24 cm × to 11 cm × to 21 cm) |
| ● |
|
| ● |
TLC Chromatoscanner (CS-9300, Shimadzu Corp., Kyoto, Japan) |
|
| Methods |
|
1. |
Hydrolysis of glycosphingolipids by a sphingolipid ceramide N-deacylase (SCDase) |
| 1) |
Dissolve the glycosphingolipids (GSLs, to 10 nmol) in 10 μL of 2x reaction buffer (50 mM acetate buffer, pH 6.0 containing 1.6% Triton X-100). |
Comment 0
|

|
| 2) |
Add 10 μL of SCDase (to 1 mU) and incubate at 37°C for an appropriate period (to 1 h). Stop the reaction by heating in a boiling water bath for 5 min. This step can be omitted depending on the purpose of the experiment. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 3) |
Dry the sample with a Speed Vac concentrator. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 4) |
Dissolve the dried sample in a small amount of CHCl3/MeOH (1/2 or 2/1, v/v). |
Comment 0
|

|
| 5) |
Apply the sample to a TLC plate using a micro-syringe. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 6) |
Develop the TLC plate with an appropriate developing solvent in a TLC chamber. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 7) |
GSLs and lyso-GSLs can be visualized by orcinol reagent while only lyso-GSLs can be visualized by ninhydrin reagent. Dry the plate, spray on the orcinol reagent, and heat on a hot plate at 110°C until GSL and lyso-GSL bands can be visualized (to 5 min). Alternatively, heat the TLC plate on a hot plate at 110°C for 5 min, and then spray on the ninhydrin reagent. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 8) |
To calculate the rate of hydrolysis, scan the TLC plate with a Shimadzu CS-9300 chromatoscanner with the reflectance mode set at 540 nm. (The extent of hydrolysis was calculated as follows: hydrolysis (%) = (peak area for lyso-GSLs generated) × 100/(peak area for remaining GSLs + peak area for lyso-GSLs generated). One enzyme unit is defined as the amount capable of catalyzing the release of 1 μmol of lyso-GM1/min from GM1 under the conditions indicated above.) |
Comment 0
|
|
|
| Notes | Rf values are smaller for lyso-GSLs than the parental GSLs. Since lyso-GSLs have one free amino group per molecule, they are also detectable with a ninhydrin reagent. In the case of the SCDase from Shewanella alga G8 2), a 50 mM acetate buffer, pH 6.0 containing 0.4% Triton X-100 and 10 mM CaCl2 should be used for the 2x reaction buffer. The reverse hydrolysis reaction of the SCDase prevents the hydrolysis reaction, but use of an aqueous–organic biphasic system improves the efficiency of hydrolysis 3). We have developed a new method of quantifying GlcCer and GalCer by normal-phase HPLC using O-phtalaldehyde derivatives prepared with SCDase 4). (See “Simultaneous quantification of glucosylceramide and galactosylceramide by HPLC” of GlycoPOD) |
| Figure & Legends |
Figure & Legends

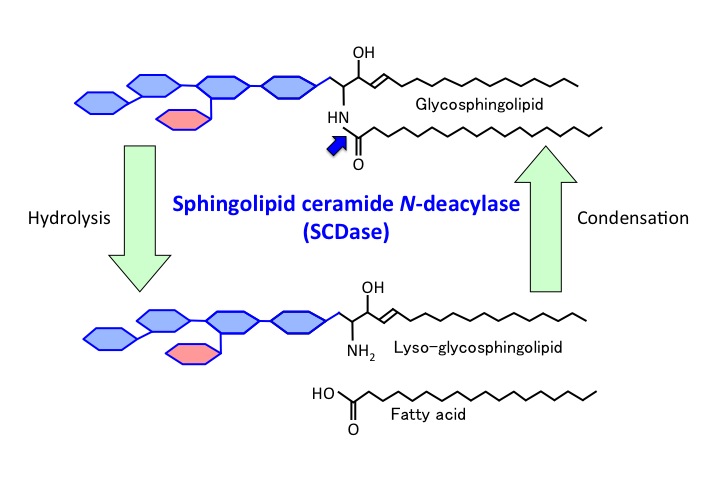
Fig. 1. Action mode of SCDase. |
| Copyrights |
 Attribution-Non-Commercial Share Alike Attribution-Non-Commercial Share Alike
This work is released underCreative Commons licenses
|
| Date of registration:2014-07-31 09:59:24 |
- Ito, M., Kurita, T., and Kita, K. (1995). A novel enzyme that cleaves the N-acyl linkage of ceramides in various glycosphingolipids as well as sphingomyelin to produce their lyso forms. Journal of Biological Chemistry 270, 24370–24374 [PMID : 7592649]
- Furusato, M., Sueyoshi, N., Mitsutake, S., Sakaguchi, K., Kita, K., Okino, N., Ichinose, S., Omori, A., and Ito, M. (2002) Molecular cloning and characterization of sphingolipid ceramide N-deacylase from a marine bacterium, Shewanella alga G8. Journal of Biological Chemistry 227, 17300–17307 [PMID : 11827965]
- Kurita, T., Izu, H., Sano, M., Ito, M., and Kato, I. (2000) Enhancement of hydrolytic activity of sphingolipid ceramide N-deacylase in the aqueous-organic biphasic system. Journal of Lipid Research 41, 846–851 [PMID : 10787446]
- Zama, K., Hayashi, Y., Ito, S., Hirabayashi, Y., Inoue, T., Ohno, K., Okino, N., and Ito, M. (2009) Simultaneous quantification of glucosylceramide and galactosylceramide by normal-phase HPLC using O-phtalaldehyde derivatives prepared with sphingolipid ceramide N-deacylase. Glycobiology 19, 767–775 [PMID : 19411660]
|
This work is licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-Non-Commercial Share Alike. Please include the following citation
How to Cite this Work in an article:
Okino, Nozomu,
Ito, Makoto,
(2014). GlycoPOD https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD.
Web.19,4,2024 .
How to Cite this Work in Website:
Okino, Nozomu,
Ito, Makoto,
(2014).
Hydrolysis of glycosphingolipids by a sphingolipid ceramide N-deacylase (SCDase).
Retrieved 19,4,2024 ,
from https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD/protocolShow.action?nodeId=t177.
html source
Okino, Nozomu,
Ito, Makoto,
(2014).
<b>Hydrolysis of glycosphingolipids by a sphingolipid ceramide <em>N</em>-deacylase (SCDase)</b>.
Retrieved 4 19,2024 ,
from <a href="https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD/protocolShow.action?nodeId=t177" target="_blank">https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD/protocolShow.action?nodeId=t177</a>.
Including references that appeared in the References tab in your work is
much appreciated.
For those who wish to reuse the figures/tables, please contact JCGGDB
management office (jcggdb-ml@aist.go.jp).
|
|