Hyaluronan is a major macromolecular polysaccharide component of the extracellular matrix in vertebrates and plays important roles in embryonic morphogenesis, cellular regeneration, and tissue remodeling. Abnormalities in hyaluronan accumulation have been implicated in many diseases such as inflammatory disorders, cardiovascular diseases, and cancer. The potential importance of hyaluronan, therefore, has led to the development of specific detection methods.
Cartilage proteoglycan aggrecan binds specifically to hyaluronan to form high-molecular weight aggregates. The globular N-terminal G1 domain of aggrecan has high affinity for a decasaccharide unit of hyaluronan and is responsible for the formation of aggregates1). In aggregates, the binding of the G1 domain to hyaluronan is stabilized by link protein.
The most widely employed hyaluronan probe is a biotinylated hyaluronan binding protein (bHABP) which is a complex of the aggrecan G1 domain/link protein fragments prepared from the cartilage proteoglycan aggregates2). Immunohistochemical analysis with the probe is a generally used method to determine the localization of hyaluronan molecules in tissue sections3). The level of hyaluronan associated with the cell surface is also determined by immunofluorescent staining and flow cytometric analysis using the probe. |
| Category | Glycosaminoglycans |
| Protocol Name | Application of anti-GAG antibody and biotinylated hyaluronan binding protein (bHABP) [1] ~ Detection of hyaluronan using biotinylated hyaluronan binding proteins |
Authors
 |
Itano, Naoki
Department of Molecular Biosciences, Faculty of Life Sciences, Kyoto Sangyo University
|
| KeyWords |
|
Reagents
 |
| ● |
Biotinylated hyaluronan binding protein (bHABP: Seikagaku Corp., Tokyo, Japan) |
| ● |
Hyaluronidase (Streptomyces hyalurolyticus) (Seikagaku Corp.) |
| ● |
Hyaluronidase reaction buffer: 100 mM Sodium acetate buffer, pH 6.0 |
| ● |
Avidin D and biotin solution (Streptavidin /Biotin Blocking kit: Vector Laboratories, Inc., Burlingame, CA) |
| ● |
Fluorophore-conjugated streptavidin (Invitrogen/Life Technologies, Carlsbad, CA) |
| ● |
Peroxidase-conjugated streptavidin (Dako, Glostrup, Denmark) |
| ● |
3% bovine serum albumin (BSA) solution: 3 g BSA, 100 mL PBS |
| ● |
|
| ● |
TAE buffer: 40 mM Tris-HCl buffer, pH 7.9, 5 mM sodium acetate, 0.8 mM sodium EDTA |
| ● |
3MM filter paper (Whatman International Ltd., Kent, UK) |
| ● |
Hybond N+ nylon membrane (GE Healthcare, Little Chalfont, UK) |
| ● |
Skim milk (BD, Franklin, NJ) |
| ● |
Salmon sperm DNA (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO) |
| ● |
TBS: 150 mM NaCl, 20 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.4 |
| ● |
ECL detection system (GE Healthcare) |
| ● |
Ascorbic acid/FeSO4/TAE buffer solution: 176 mg L-ascorbic acid, 13.9 mg FeSO4, 500 mL TAE buffer |
|
Instruments
 |
| ● |
Phase contrast microscope and Fluorescence microscope (Carl Zeiss AG, Jena, Germany) |
| ● |
Flow cytometer equipped with a 5-W argon ion laser emitting 488 nm light at 200 mW (BD, Franklin Lakes, CA) |
| ● |
Centrifuge (Hitachi Koki Co., Ltd. Tokyo, Japan) |
| ● |
Horizontal electrophoresis apparatus (Nihon Eido Co., Ltd., Tokyo, Japan) |
| ● |
Semi-dry blotter (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Hercules, CA) |
|
| Methods |
|
1. |
Immunohistochemistry for hyaluronan using bHABP |
| 1) |
Treat formalin-fixed tissue sections with 3% BSA solution for 1 h at room temperature. |
Comment 1
|

|
| 2) |
Incubate the sections in avidin D solution for 15 min at room temperature to block endogenous biotin or biotin-binding proteins, or nonspecific binding substances present in the section. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 4) |
Incubate the sections in biotin solution for 15 min at room temperature. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 6) |
Incubate in 3% BSA solution containing 2 μg/mL bHABP for 1 h at room temperature. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 8) |
Incubate in 3% BSA solution containing fluorophore-conjugated streptavidin (1/500 dilution) for 30 min at room temperature. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 10) |
Mount the fluorescent specimen with anti-fade mounting medium and seal the slide with nail polish. |
Comment 1
|

|
| 11) |
Examine the specimen under a fluorescence microscope or a confocal microscope. |
Comment 0
|
|
|
|
2. |
Immunofluorescent staining of cell surface hyaluronan |
| 1) |
Grow cells on a chamber slide or a cover glass. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 2) |
Fix the cells in 10% neutral buffered formalin for 10 min at room temperature. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 4) |
Block the samples with 3% BSA solution for 1 h at room temperature. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 5) |
Incubate the samples in 3% BSA solution containing 2 μg/mL bHABP for 1 h at room temperature. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 7) |
Incubate the samples in 3% BSA solution containing fluorophore-conjugated streptavidin (1/500 dilution) for 30 min at room temperature. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 9) |
Mount the fluorescent specimen with anti-fade mounting medium and seal the slide with nail polish. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 10) |
Examine the specimen under a fluorescence microscope or a confocal microscope. |
Comment 0
|
|
|
|
3. |
Flow cytometric analysis for cell surface hyaluronan |
| 1) |
Harvest cells using 5 mM EDTA in PBS. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 3) |
Suspend cells in cold PBS containing 1% FCS. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 4) |
Resuspend cells in cold PBS containing 20 μg/mL bHABP and 1% FCS. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 6) |
Wash twice with cold PBS containing 1% FCS. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 7) |
Resuspend cells in cold PBS containing fluorophore-conjugated streptavidin (1/500 dilution) and 1% FCS. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 9) |
Wash twice with cold HBSS containing 1% FCS. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 10) |
Resuspend cells in cold PBS containing 1% FCS. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 11) |
Analyze positively stained cells by flow cytometer. |
Comment 0
|
|
|
|
4. |
Detection of hyaluronan by transblot analysis4) |
| 1) |
Incubate hyaluronan samples at 37˚C for 1 h with or without 1 TRU of Streptomyces hyaluronidase. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 2) |
Mix 14 μL of the hyaluronan samples with 2 μL of 2 M sucrose/TAE solution. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 3) |
Prepare a 0.5% (w/v) agarose gel (20 × 20 cm) by melting 0.6 g agarose in 108 mL of TAE buffer. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 4) |
Transfer the gel plate to the horizontal electrophoresis apparatus. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 5) |
Apply the sample to each lane of the agarose gel. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 6) |
Electrophorese at 2V/cm for 10 h in TAE buffer at room temperature. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 7) |
Incubate the gel in a freshly prepared ascorbic acid/FeSO4/TAE buffer solution for 30 min at room temperature. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 8) |
Wash twice for each 20 min with TAE buffer. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 9) |
Built up transfer sandwich using two pieces of 3MM filter paper, Hybond N+ nylon membrane, the agarose gel, and two additional pieces of 3MM paper (all papers and membranes were presoaked in TAE buffer). |
Comment 0
|

|
| 10) |
Transfer the hyaluronan molecules from the agarose gel to Hybond N+ membrane at 1.2 mA/cm2 for 4 h at room temperature using semi-dry blotter. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 11) |
Incubate the membrane in PBS containing 10% skim milk and 20 μg/mL denatured salmon sperm DNA at 37°C overnight to block nonspecific binding sites. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 13) |
Incubate the membrane in PBS containing 10 μg/mL bHABP and 1% BSA for 1 h at room temperature. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 14) |
Wash three times with TBS containing 0.05% Tween 20. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 15) |
Incubate the membrane in TBS containing peroxidase-conjugated streptavidin (1/500 dilution) and 1% BSA for 30 min at room temperature. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 16) |
Wash three times with TBS containing 0.05% Tween 20. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 17) |
Detect the HABP-streptavidin complexes by the ECL detection system. |
Comment 0
|
|
|
| Figure & Legends |
Figure & Legends

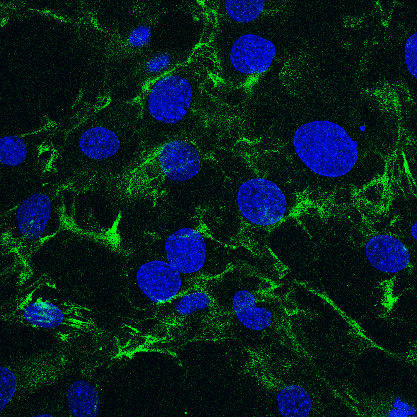
Fig. 1. Immunofluorescence image of the pericellular hyaluronan matrix of cultured stromal fibroblasts.
Hyaluronan is visualized by staining with bHABP (green) and cell nuclei are counterstained with DAPI (blue).

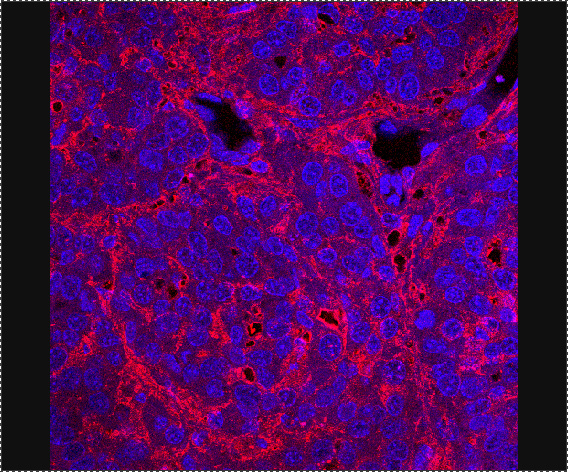
Fig. 2. Immunofluorescence image of the hyaluronan matrix accumulated in spontaneous mammary tumors.
Hyaluronan is visualized by staining with bHABP (red) and cell nuclei are counterstained with DAPI (blue).

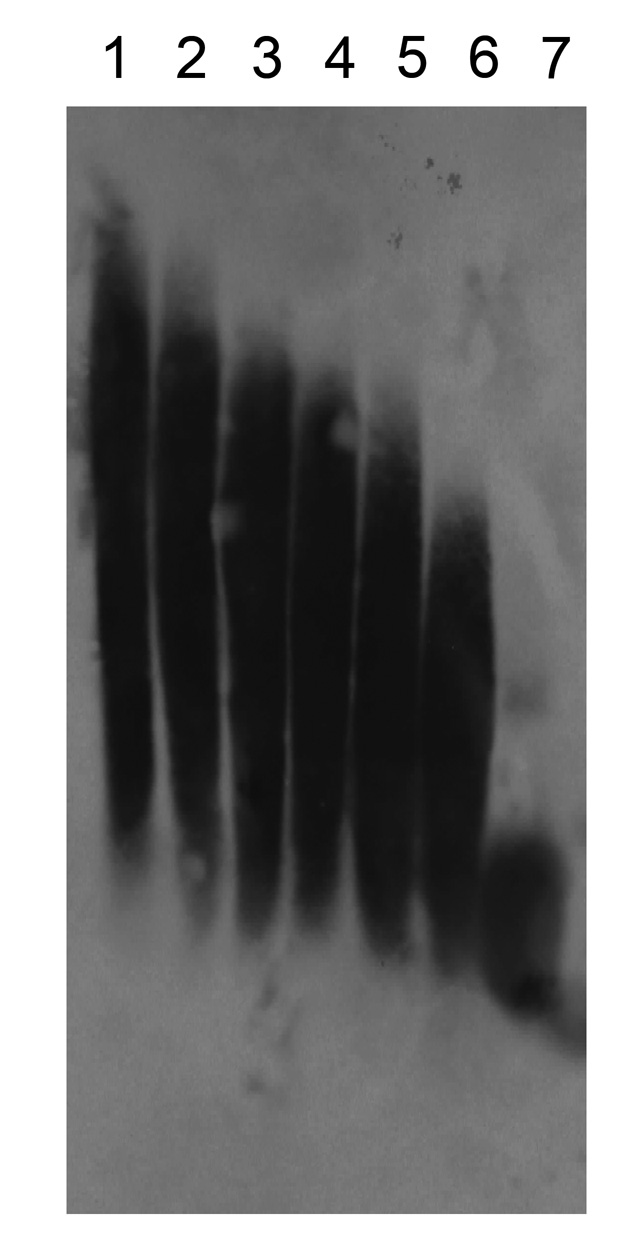
Fig. 3. Transblot analysis of hyaluronan molecules.
Average masses of hyaluronan molecules used are 40 (lane 1), 21.3 (lane 2), 14.1 (lane 3), 9.9 (lane 4), 6.4 (lane 5), 4.6 (lane 6), and 1.0 × 105 Da (lane 7). |
| Copyrights |
 Attribution-Non-Commercial Share Alike Attribution-Non-Commercial Share Alike
This work is released underCreative Commons licenses
|
| Date of registration:2017-02-16 16:33:32 |
- Hardingham, T. E. and Muir, H. (1972) The specific interaction of hyaluronic acid with cartillage proteoglycans. Biochim Biophys Acta. 279, 401–405 [PMID : 4263642]
- Tengblad, A. (1979) Affinity chromatography on immobilized hyaluronate and its application to the isolation of hyaluronate binding properties from cartilage. Biochem Biophys Acta. 578, 281–289 [PMID : 486527]
- Ripellino, J. A., Kilinger, M. M., Margolis, R. U. and Margolis, R. K. (1985). The hyaluronic acid binding region as a specific probe for the localization of hyaluronic acid in tissue sections. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 33, 1066–1086 [PMID : 4045184]
- Itano, N., Sawai, T., Yoshida, M., Lenas, P., Yamada, Y., Imagawa, M., Shinomura, T., Hamaguchi, M., Yoshida, Y., Ohnuki, Y., Miyauchi, S., Spicer, AP., McDonald, JA., and Kimata, K. (1999) Three isoforms of mammalian hyaluronan synthases have distinct enzymatic properties. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 25085–25092 [PMID : 10455188]
|
This work is licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-Non-Commercial Share Alike. Please include the following citation
How to Cite this Work in an article:
Itano, Naoki,
(2017). GlycoPOD https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD.
Web.20,4,2024 .
How to Cite this Work in Website:
Itano, Naoki,
(2017).
Application of anti-GAG antibody and biotinylated hyaluronan binding protein (bHABP) [1] ~ Detection of hyaluronan using biotinylated hyaluronan binding proteins.
Retrieved 20,4,2024 ,
from https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD/protocolShow.action?nodeId=t173.
html source
Itano, Naoki,
(2017).
<b>Application of anti-GAG antibody and biotinylated hyaluronan binding protein (bHABP) [1] ~ Detection of hyaluronan using biotinylated hyaluronan binding proteins</b>.
Retrieved 4 20,2024 ,
from <a href="https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD/protocolShow.action?nodeId=t173" target="_blank">https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD/protocolShow.action?nodeId=t173</a>.
Including references that appeared in the References tab in your work is
much appreciated.
For those who wish to reuse the figures/tables, please contact JCGGDB
management office (jcggdb-ml@aist.go.jp).
|
|