Lectins are carbohydrate-binding proteins that are useful markers for localization and characterization of glycoconjugates, both in vivo and in vitro (Sharma et al., 1995). Here we describe a method for detecting intestinal M-cells and fucosylated columnar epithelial cells (F-ECs) using lectin staining. M cells, one of the antigen entry sites, have unique glycosylation patterns on their apical surface. Murin Peyer’s patch and villous M cells express α(1,2)-fucose and can be detected by staining with a lectin, Ulex europaeus agglutinin-1 (UEA-1). However they do not bind Wheat Germ Aglutinin (WGA), another widely used lectin for staining of intestinal epithelial cells (Clark MA, et. al., 1993). Therefore, M cells are defined as UEA-1+ WGA- cells. α(1,2)-fucosylation is also induced in villous epithelial cells by a variety of intestinal environmental stresses such as colonization by commensal bacteria, mechanical injury or treatment with inflammatory chemicals (Terahara et al., 2011). F-ECs are detected by staining with both WGA and UEA-1. It is thought that F-ECs, which are identified as UEA-1+ WGA+ cells, could be additional entry sites for antigens and various pathogens, and at same time provide a suitable co-habitation environment for symbiotic microorganisms (Goto Y. et al., 2012). |
| Category | Sugar binding proteins |
| Protocol Name | Whole-mount Staining System of Intestinal Epithelial Glycosylation |
Authors
 |
Lamichhane, Aayam
Division of Mucosal Immunology, Department of Microbiology and Immunology, Institute of Medical Science, The University of Tokyo
Goto, Yoshiyuki
Division of Mucosal Immunology, Department of Microbiology and Immunology, Institute of Medical Science, The University of Tokyo
Kiyono, Hiroshi
*
Division of Mucosal Immunology, Department of Microbiology and Immunology, Institute of Medical Science, The University of Tokyo
*To whom correspondence should be addressed.
|
| KeyWords |
|
Reagents
 |
| ● |
Fluorescent dye labeled Ulex Europaeus Agglutinin I (Vector Laboratories, Inc., Burlingame, CA) |
| ● |
Flourescent dye labeled Wheat Germ Agglutinin (WGA) (Invitrogen/Life Technologies, Carlsbad, CA) |
| ● |
1x Phosphate Buffered Saline (PBS) (Nacalai Tesque Inc., Kyoto, Japan, #14249) |
| ● |
4% Para formaldehyde (PFA) - PBS (Nacalai Tesque Inc. #09154) |
| ● |
Aqueous Mounting Medium for Fluorescent Staining (Fluoromount: Diagnostic BioSystems Inc., Pleasanton, CA, Cat. #K024) |
|
Instruments
 |
| ● |
Confocal Microscope (Leica TCS SP2, Leica Microsystems GmbH, Watzlar, Germany) |
|
| Methods |
|
1. |
Extraction of tissue segments |
| 1) |
Euthanize mice and pull out the small intestine. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 2) |
Cut small sections of the tissue from the objective portions of the intestine, e.g. duodenum, jejunum, and ileum. Dissect out small pieces of the tissue such that each segment consists of the apical villus portion. For staining of M cells, cut the sections containing the Peyer`s patch. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 3) |
Put the tissue segments from each portion of the intestine in separate conical tubes with ice cold PBS. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 4) |
Shake the tubes vigorously for about 15 sec to remove feces and mucus. Discard the PBS and pour fresh and cold PBS into the tube. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 5) |
Repeat the above procedure two times. |
Comment 0
|
|
|
|
2. |
Fixation of tissue segments |
| 1) |
Discard PBS after the final wash. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 2) |
Pour 4 mL of 4% PFA-PBS into the tube for fixation of the tissue segments. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 3) |
Place the tubes on ice or in refrigerated environment and incubate for more than 3 h. |
Comment 1
|
|
|
|
3. |
|
| 1) |
Discard the 4% PFA-PBS from the fixed tissue segments. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 2) |
Wash the tissue segments two times with ice-cold PBS. |
Comment 1
|

|
| 3) |
Prepare a premix solution of appropriate fluorescence conjugated UEA-1 and WGA in PBS, such that the final concentration of UEA-1 is 16.0 μg/mL and that of WGA is 12.5 μg/mL. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 4) |
Discard PBS used for the final wash and apply 1 mL of the above premix solution to the tissue segments. |
Comment 1
|

|
| 5) |
Place the tubes with tissue segments on ice, and incubate for more than 3 h. |
Comment 1
|
|
|
|
4. |
|
| 2) |
Wash the tissue segments two times with ice-cold PBS. |
Comment 1
|

|
| 3) |
Place the segments on a glass slide, with the apical luminal surface of small intestinal tissue facing upward. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 4) |
Soak dry the traces of PBS carefully with a bloat paper, such as kim wipe. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 5) |
Apply a drop of aqueous mounting medium for fluorescent staining onto the tissue segment and mount cover glass over it and sandwich the tissue section. The ends of the cover glass should be fixed to the glass slide with a vinyl tape to hold the tissue sections in place. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 6) |
Observe the slide under a confocal microscope with lasers appropriate for the dyes used and acquire images. |
Comment 0
|
|
|
| Notes | We have been using Rhodamine labeled Ulex Europaeus Agglutinin I (Vector Laboratories, Inc. RL-1062), Alexa Fluor® 633 conjugated Wheat Germ Agglutinin (Molecular Probes W21404) with reproducible results. |
| Initial amount | 16.0 μg of UEA-1 and 12.5 μg of WGA for staining of 1 – 2 tissue segments. |
| Figure & Legends |
Figure & Legends

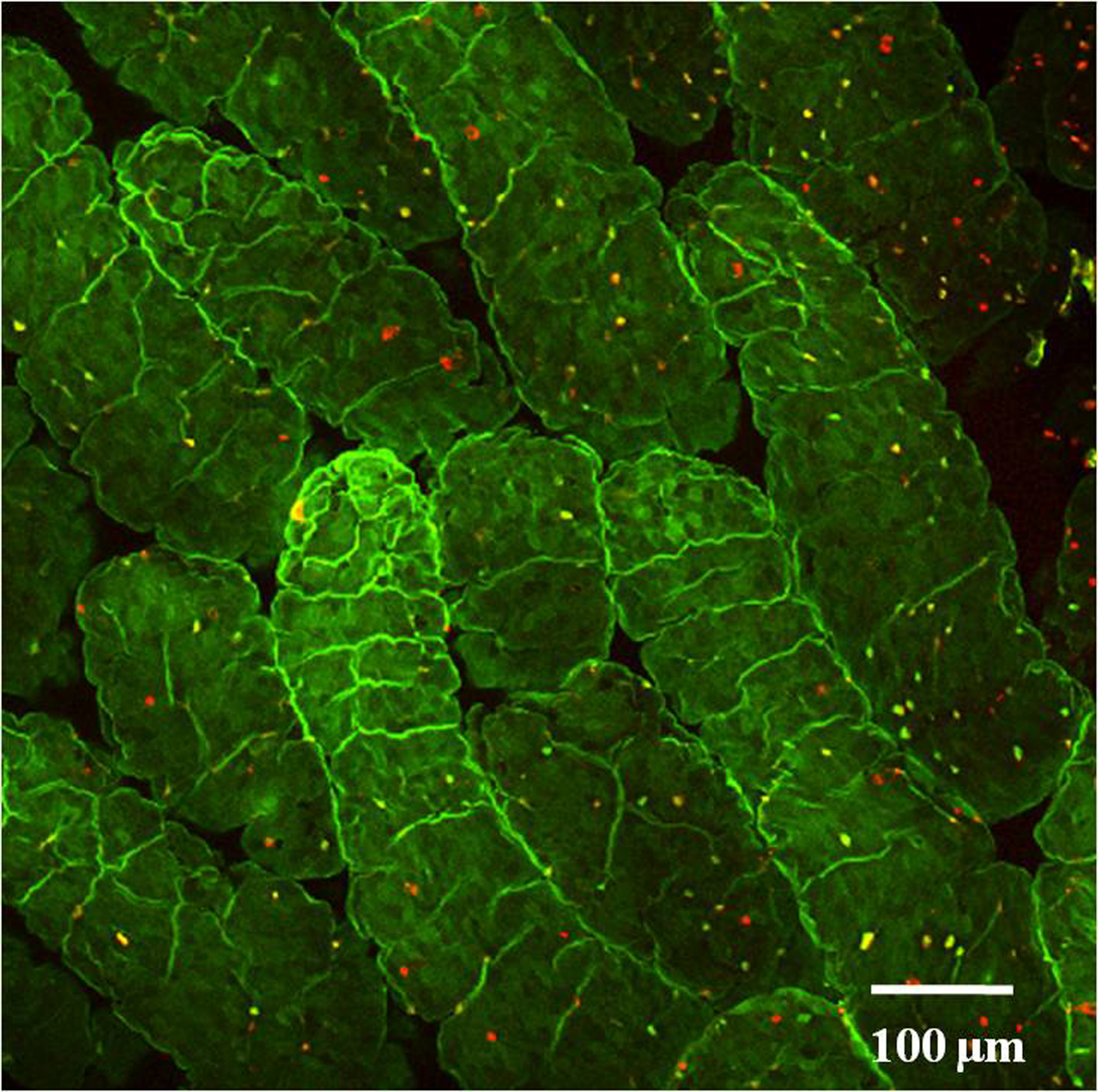
Fig. 1. Whole mount staining of intestinal epithelial cells of proximal duodenum.
Tissue section obtained from a 8 weeks old wild type C57BL/6 mouse was stained with UEA-1 (Red) and WGA (Green) and visualized under a confocal microscope. The number of F-ECs in the proximal duodenum is relatively less.

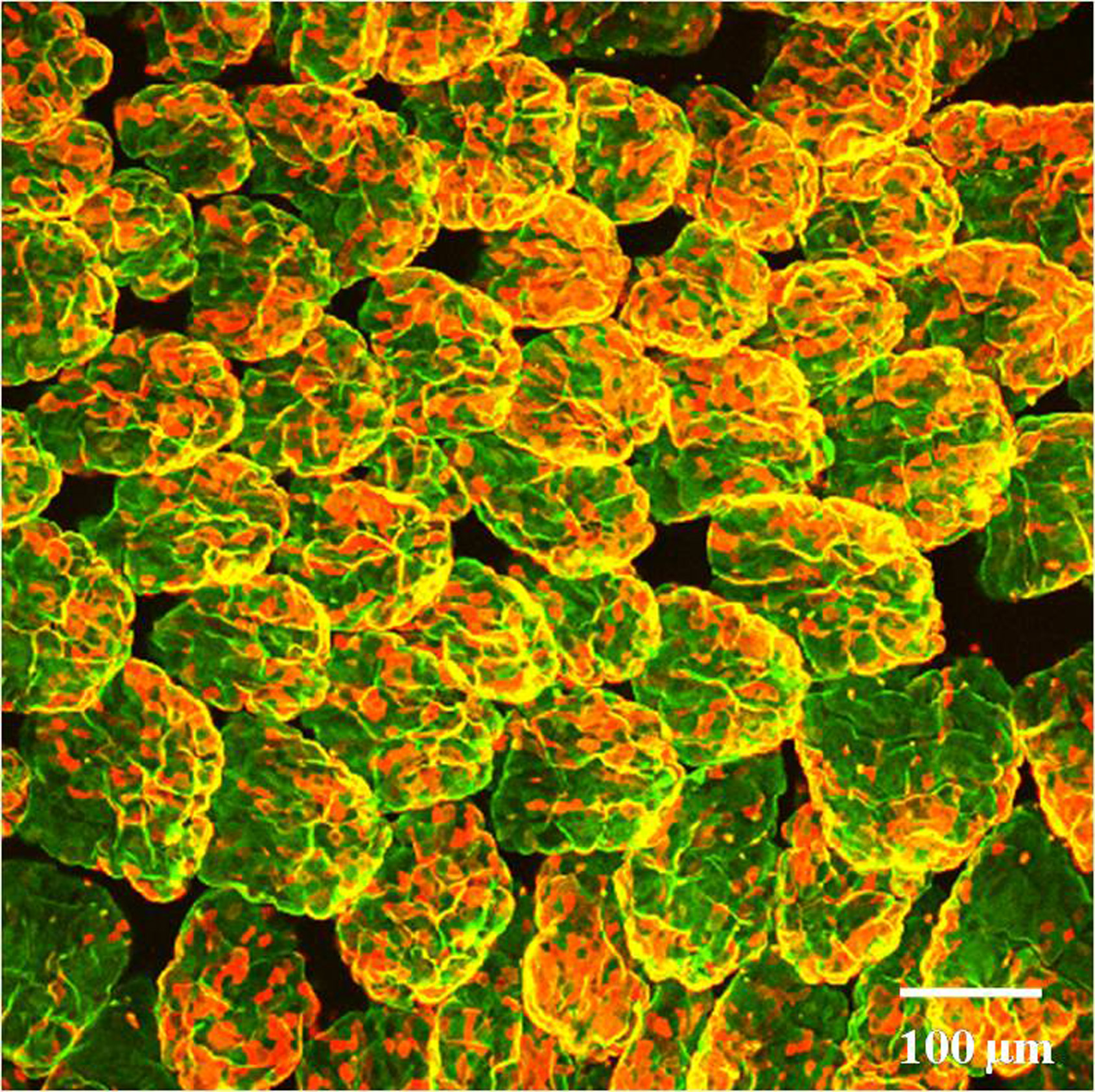
Fig. 2. Whole mount staining of intestinal epithelial cells of distal ileum.
Tissue section obtained from a 8 weeks old wild type C57BL/6 mouse was stained with UEA-1 (Red) and WGA (Green) and visualized under a confocal microscope. A high number of F-ECs can be observed in the distal ileum.

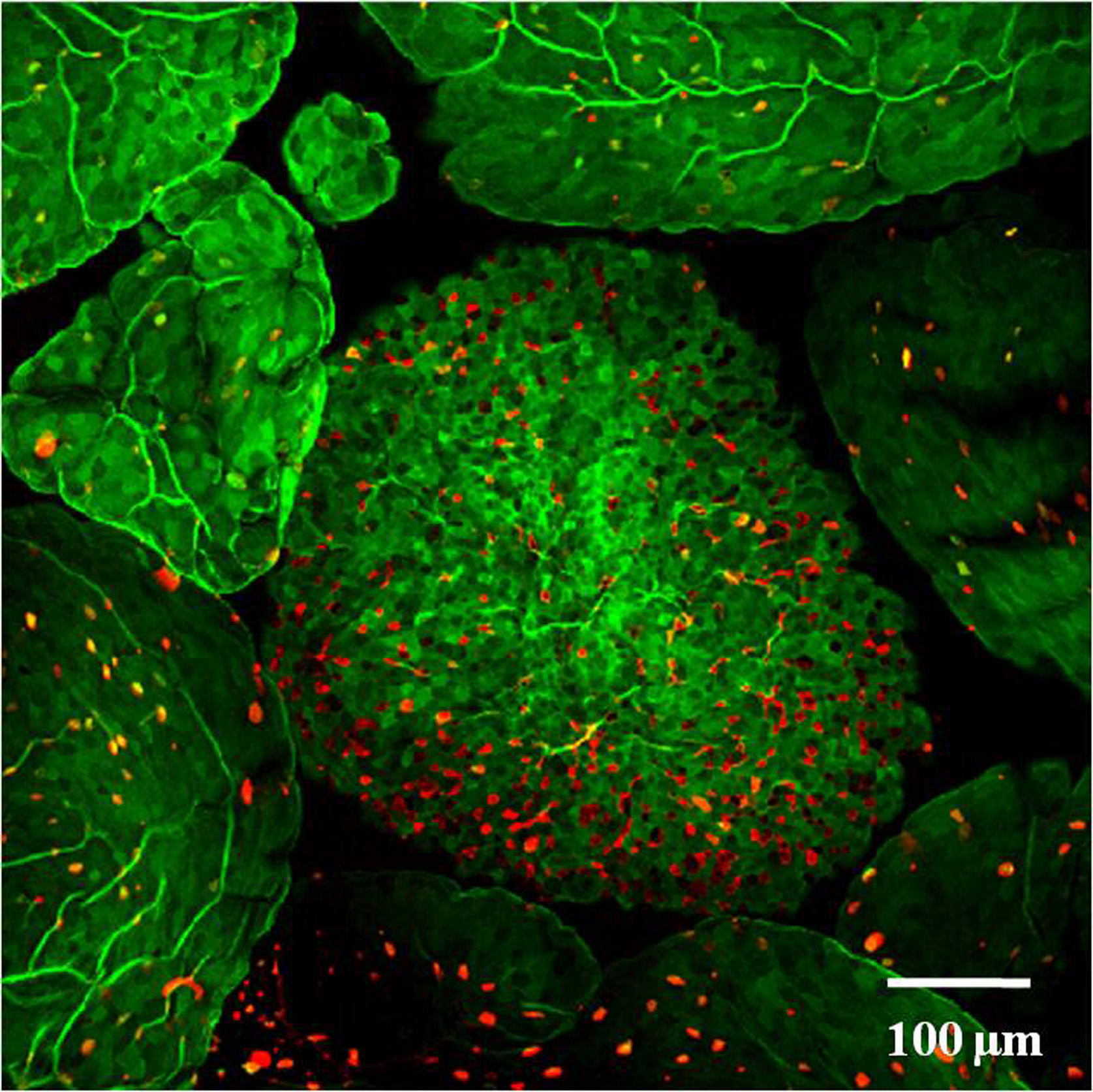
Fig. 3. Whole mount staining of Peyer’s patch M cells.
Peyer’s patch obtained from a 8 weeks old wile type C57BL/6 mouse was stained with UEA-1 (Red) and WGA (Green) and visualized under a confocal microscope. UEA-1+ WGA- cells are identified as M cells. |
| Copyrights |
 Attribution-Non-Commercial Share Alike Attribution-Non-Commercial Share Alike
This work is released underCreative Commons licenses
|
| Date of registration:2014-02-12 15:13:03 |
- Sharma, R., and Schumacher, U. (1995) The influence of diets and gut microflora on lectin binding patterns of intestinal mucins in rats. Lab Invest. 73, 558–564 [PMID : 7474928]
- Terahara, K., Nochi, T., Yoshida, M., Takahashi, Y., Goto, Y., Hatai, H., Kurokawa, S., Jang, M.H., Kweon, M.N., Domino, S.E., Hiroi, T., Yuki, Y., Tsunetsugu-Yokota, Y., Kobayashi, K., and Kiyono, H. (2011) Distinct fucosylation of M cells and epithelial cells by Fut1 and Fut2, respectively, in response to intestinal environmental stress. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 404, 822-828 [PMID : 21172308]
- Clark, M.A., Jepson, M.A., Simmons, N.L., Booth, T.A., and Hirst, B.H. (1993) Differential expression of lectin-binding sites defines mouse intestinal M-cells. J Histochem Cytochem. 41, 1679-1687 [PMID : 7691933]
- Goto, Y., and Kiyono, H. (2012) Epithelial barrier: an interface for the cross-communication between gut flora and immune system. Immunol Rev. 245, 147-163 [PMID : 22168418]
|
This work is licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-Non-Commercial Share Alike. Please include the following citation
How to Cite this Work in an article:
Lamichhane, Aayam,
Goto, Yoshiyuki,
Kiyono, Hiroshi,
(2014). GlycoPOD https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD.
Web.19,4,2024 .
How to Cite this Work in Website:
Lamichhane, Aayam,
Goto, Yoshiyuki,
Kiyono, Hiroshi,
(2014).
Whole-mount Staining System of Intestinal Epithelial Glycosylation.
Retrieved 19,4,2024 ,
from https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD/protocolShow.action?nodeId=t170.
html source
Lamichhane, Aayam,
Goto, Yoshiyuki,
Kiyono, Hiroshi,
(2014).
<b>Whole-mount Staining System of Intestinal Epithelial Glycosylation</b>.
Retrieved 4 19,2024 ,
from <a href="https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD/protocolShow.action?nodeId=t170" target="_blank">https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD/protocolShow.action?nodeId=t170</a>.
Including references that appeared in the References tab in your work is
much appreciated.
For those who wish to reuse the figures/tables, please contact JCGGDB
management office (jcggdb-ml@aist.go.jp).
|
|