Since it is difficult to characterize the structure of intact glycosaminoglycan (GAG) chains which are long, variously sulfated, and complicated polysaccharides, in practice they are enzymatically or chemically dissected into disaccharides, which are then subjected to analysis using HPLC. |
| Category | Glycosaminoglycans |
| Protocol Name | HPLC analysis of glycosaminoglycans |
Authors
 |
Yamada, Shuhei
*
Department of Pathobiochemistry, Faculty of Pharmacy, Meijo University
Toyoda, Hidenao
Laboratory of Bio-analytical Chemistry, College of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Ritsumeikan University
*To whom correspondence should be addressed.
|
| KeyWords |
|
Reagents
 |
| ● |
Chondroitinase ABC (a conventional preparation) from Proteus vulgaris (Seikagaku Corp., Tokyo, Japan) |
| ● |
Chondroitinase AC-II from Arthrobacter aurescens (Seikagaku Corp.) |
| ● |
Heparinase from Flavobacterium heparinum (Seikagaku Corp.) |
| ● |
Heparitinases I and II from Flavobacterium heparinum (Seikagaku Corp.) |
| ● |
Unsaturated chondro-disaccharide kit (C kit) (for HPLC) (Seikagaku Corp.) |
| ● |
Unsaturated HS/HEP-disaccharide kit (H kit) (for HPLC) (Seikagaku Corp.) |
| ● |
2-Aminobenzamide (2AB) (Nacalai Tesque Inc., Kyoto, Japan) |
| ● |
NaCNBH4 (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO) |
| ● |
2-Cyanoacetamide (Sigma-Aldrich) |
| ● |
Tetra-n-butylammonium hydrogen sulfate (Sigma-Aldrich) |
|
Instruments
 |
| ● |
YMC-Pack PA-03 (4.6 mm i.d. x 250mm) (YMC Co., Ltd., Kyoto, Japan) |
| ● |
Senshu Pak DOCOSIL A column (4.6 mm i.d. x 150 mm, 5 μm) (Senshu Scientific Co., Ltd., Tokyo, Japan) |
| ● |
Speed Vac Concentrator (Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., Waltham, MA) |
| ● |
Ultrafree-MC (Merck Millipore, Billerica, MA) |
| ● |
HPLC system (LC-20 Series: Shimadzu Corp., Kyoto, Japan) |
| ● |
HPLC system (L-2000 Series: Hitachi High-Tech Science Corp., Tokyo, Japan) |
|
| Methods |
|
1. |
HPLC analysis of GAG di- and oligosaccharides (precolumn-labeling) |
| 1) |
Enzymatic digestion of GAGs:
Incubate heparin (Hep)/heparan sulfate (HS) (25-250 ng) with a mixture of heparinase and heparitinase (1 mIU each) in a total volume of 20 μL of 20 mM acetate-Na buffer, pH 7.0, containing 2 mM Ca(CH3COO)2 at 37˚C for 1 h.
Incubate chondroitin sulfate (CS)/dermatan sulfate (DS) or hyaluronan (HA) (25-250 ng) with a mixture of chondroitinases ABC and AC-II (1 mIU each) in a total volume of 20 μL of 50 mM acetate-Na buffer, pH 6.0, at 37˚C for 30 min. |
Comment 1
|

|
| 2) |
Terminate the reactions by boiling at 100 ˚C for 1 min. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 3) |
Lyophilize the sample by Speed Vac. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 4) |
Add 5 μL of the 2AB-derivatization reagent mixture (0.35 M 2AB/1.0 M NaCNBH4/30% (v/v) acetic acid in dimethyl sulfoxide) and incubate at 65˚C for 2 h to label the reducing end with a fluorophore. |
Comment 1
|

|
| 5) |
Dilute the reaction mixture with distilled water to 200 μL and transfer it to a glass tube. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 6) |
Remove the excess 2AB reagent by extraction with an equivalent volume of chloroform 5 times. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 7) |
Analyze an aliquot (40 μL) of the aqueous phase by HPLC on an amine-bound silica PA-03 column using a linear gradient of NaH2PO4 from 16 to 530 mM at a flow rate of 1 mL/min, monitored by measuring fluorescence with excitation and emission wavelengths of 330 and 420 nm, respectively. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 8) |
Identify and quantify the eluted peaks by comparing with the elution positions of authentic standards (Fig. 1 and 2). |
Comment 0
|
|
|
|
2. |
HPLC analysis of GAG di- and oligosaccharides (postcolumn-labeling) |
| 1) |
Enzymatic digestion of GAGs:
Incubate Hep/HS (1-250 ng) with a mixture of heparinase and heparitinases I and II (1 mIU each) in a total volume of 15 μL of 25 mM sodium acetate buffer, pH 7.0, containing 2 mM calcium acetate at 37˚C for 16 h.
Incubate CS/DS or HA (1-250 ng) with a mixture of chondroitinases ABC and AC-II (5 mIU each) in a total volume of 15 μL of 25 mM Tris-acetate buffer, pH 8.0, at 37˚C for 3 h. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 2) |
Terminate the reactions by boiling at 100˚C for 1 min. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 4) |
Add 10 μL of distilled water, then inject 8 μL of the sample into the postcolumn HPLC system. The flow diagram and HPLC conditions are shown in Fig. 3. Typical chromatograms are shown in Fig. 4. |
Comment 0
|
|
|
| Figure & Legends |
Figure & Legends

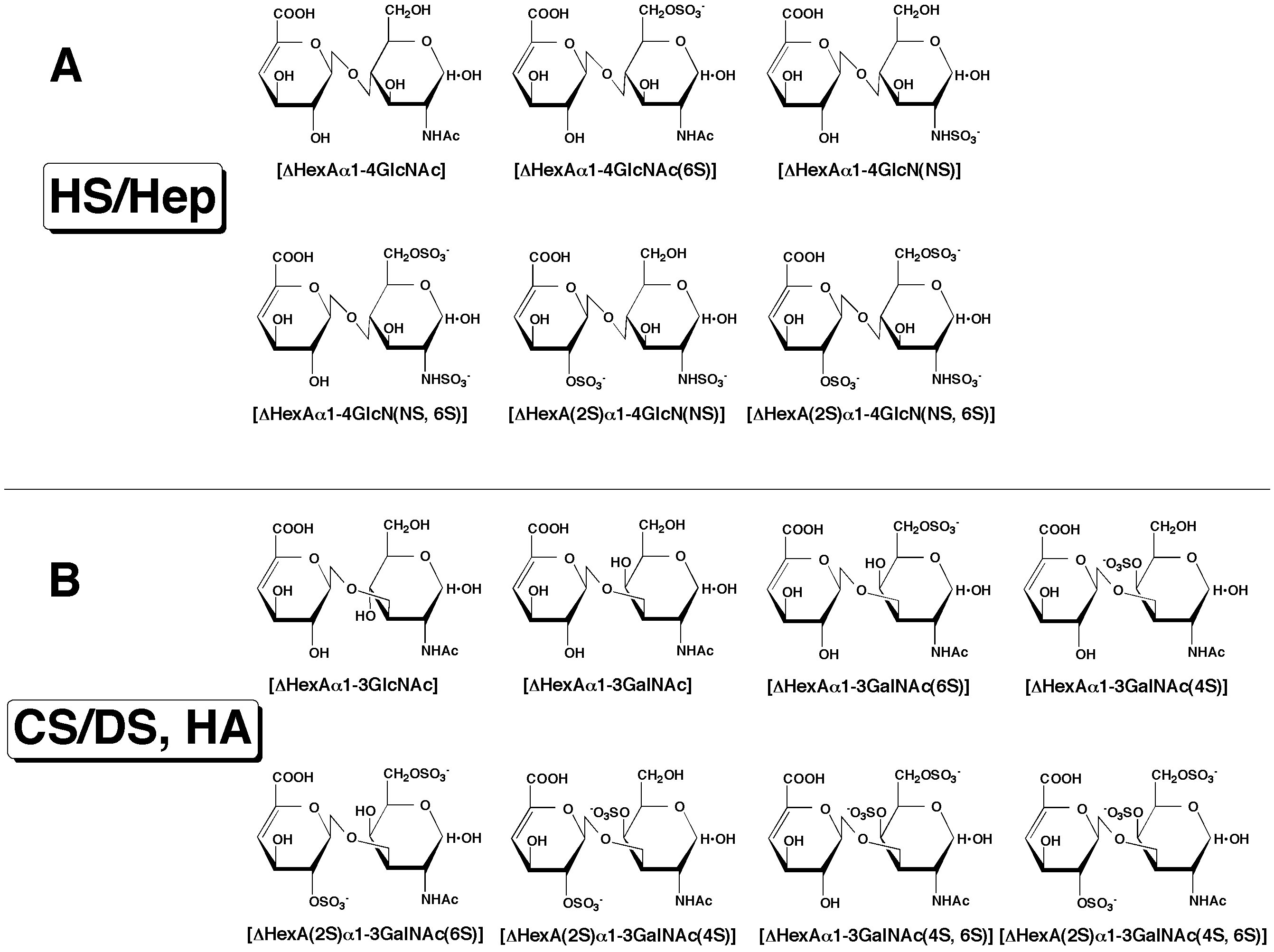
Fig. 1. Structure of unsaturated disaccharides
The structure of unsaturated disaccharides derived from HS/Hep (A) as well as CS/DS and HA (B) is given. Treatment with bacterial eliminases converts the original uronic acid structure in the polysaccharides into an artificial structure, the 4,5-unsaturated uronic acid, 4-deoxy-α-L-threo-hex-4-enepyranosyluronic acid (ΔHexA). GalNAc, GlcNAc, GlcN, 2S, 4S, 6S, and NS represent N-acetylgalactosamine, N-acetylglucosamine, glucosamine, 2-O-sulfate, 4-O-sulfate, 6-O-sulfate, and 2-N-sulfate, respectively.

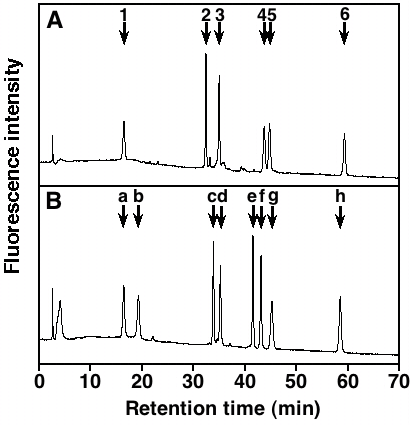
Fig. 2. HPLC profile of the 2AB-labeled unsaturated disaccharide standards
Elution positions of the 2AB-derivatives of the standard disaccharides derived from HS/Hep (A) as well as CS/DS and HA (B) are shown. 1, ΔHexAα1-4GlcNAc; 2, ΔHexAα1-4GlcNAc(6S); 3, ΔHexAα1-4GlcN(NS); 4, ΔHexAα1-4GlcN(NS, 6S); 5, ΔHexA(2S)α1-4GlcN(NS); 6, ΔHexA(2S)α1-4GlcN(NS, 6S); a, ΔHexAα1-3GlcNAc; b, ΔHexAα1-3GalNAc; c, ΔHexAα1-3GalNAc(6S); d, ΔHexAα1-3GalNAc(4S); e, ΔHexA(2S)α1-3GalNAc(6S); f, ΔHexA(2S)α1-3GalNAc(4S); g, ΔHexAα1-3GalNAc(4S, 6S); h, ΔHexA(2S)α1-3GalNAc(4S, 6S). The HPLC analysis was carried out on an amine-bound silica PA-03 column under isocratic conditions with 16 mM of NaH2PO4 for the first 10 min followed by a linear gradient from 16 to 538 mM NaH2PO4 over 60 min.

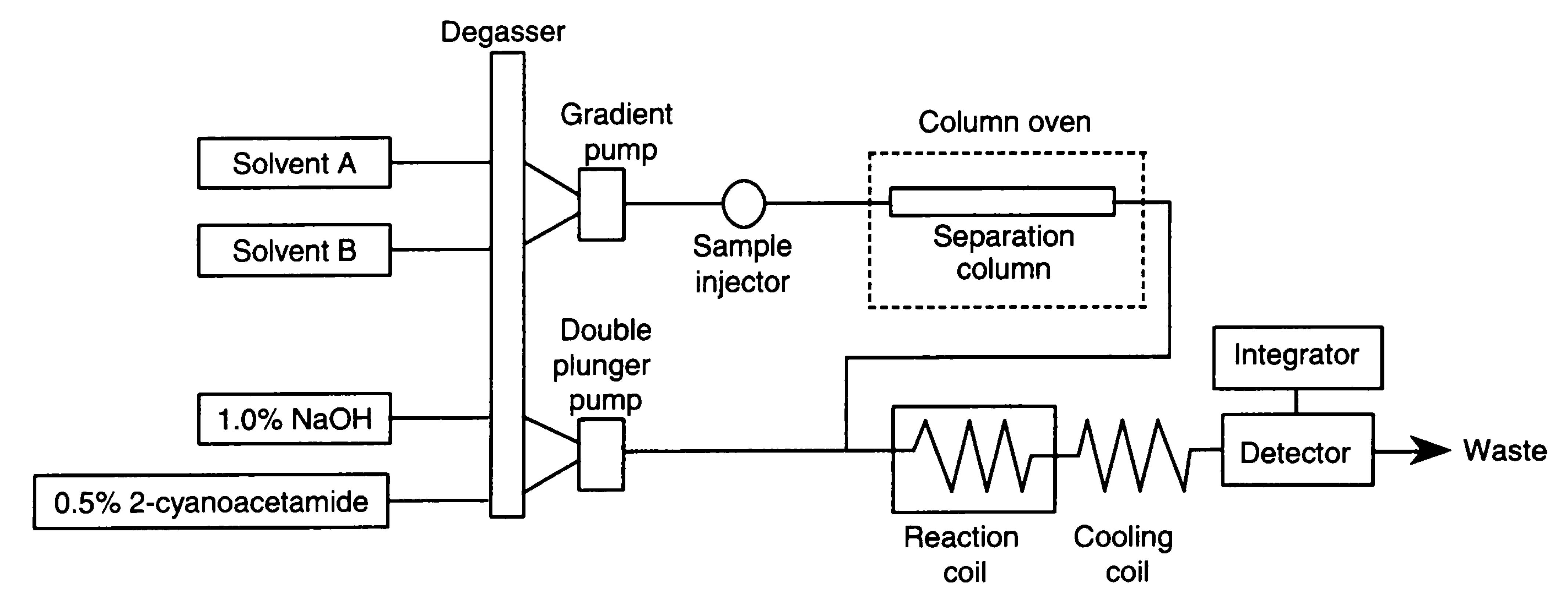
Fig. 3. Flow diagram of the postcolumn HPLC system for analyzing the unsaturated disaccharides
The sample is separated on a C22 reversed phase column (4.6 mm i.d. x 150 mm) at 55˚C with a NaCl gradient (flow rate, 1.1 mL/min). The column eluate is then mixed with 0.5% 2-cyanoacetamide and 1.0% NaOH, supplied by the double-plunger pump (flow rate, 0.35 mL/min), and reacted at 125˚C to form fluorescence products. Reaction coil, 0.5 mm i.d. x 10 m; cooling coil, 0.25 mm i.d. x 2 m; detection, excitation 346 nm, emission 410 nm. Solvent A is 1.2 mM tetra-n-butylammonium hydrogen sulfate in 8.5% acetonitrile. Solvent B is 0.2 M NaCl in solvent A. Gradient program: 0-10 min, 1-4% B; 10-11 min 4-15% B; 11-20 min, 15-25% B; 20-22 min, 25-53%; 22-29 min, 53% B; equilibration with 1% B for 20 min.

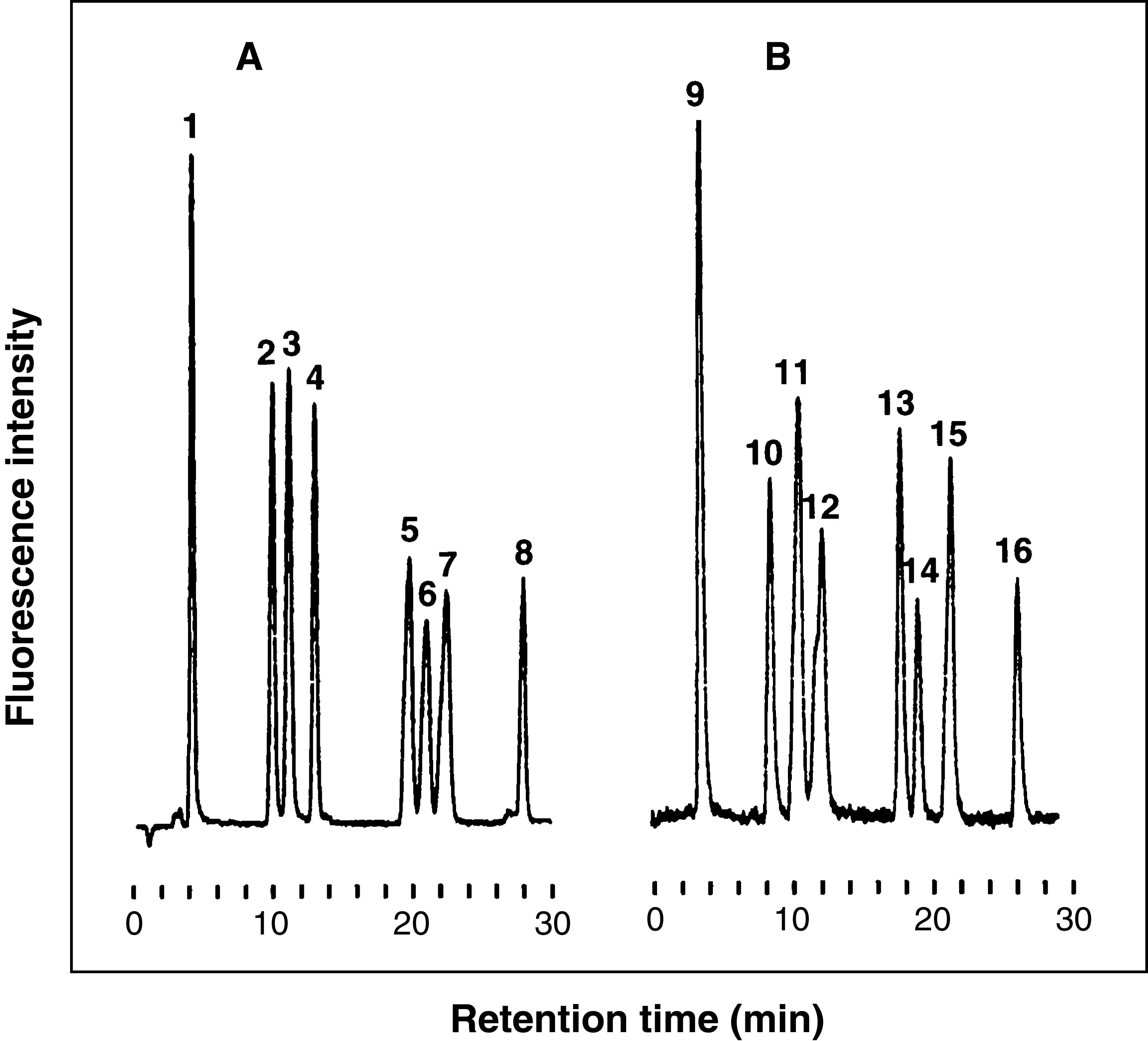
Fig. 4. Typical chromatograms of unsaturated disaccharides derived from CS/DS (A) and HS/Hep (B)
(A) Sample size (5 μL, 5 ng of each sugar). Peaks: 1, ΔHexAα1-3GalNAc; 2, ΔHexAα1-3GalNAc(4S); 3, ΔHexAα1-3GalNAc(6S); 4, ΔHexA(2S)α1-3GalNAc; 5, ΔHexAα1-3GalNAc(4S, 6S); 6, ΔHexA(2S)α1-3GalNAc(4S); 7, ΔHexA(2S)α1-3GalNAc(6S); 8, ΔHexA(2S)α1-3GalNAc(4S, 6S). (B) Sample size (5 μL, 5 ng of each sugar). Peaks: 9, ΔHexAα1-4GlcNAc; 10, ΔHexAα1-4GlcN(NS); 11, ΔHexAα1-4GlcNAc(6S); 12, ΔHexA(2S)α1-4GlcNAc; 13, ΔHexAα1-4GlcN(NS, 6S); 14, ΔHexA(2S)α1-4GlcN(NS); 15, ΔHexA(2S)α1-4GlcNAc(6S); 16, ΔHexA(2S)α1-4GlcN(NS, 6S).
|
| Copyrights |
 Attribution-Non-Commercial Share Alike Attribution-Non-Commercial Share Alike
This work is released underCreative Commons licenses
|
| Date of registration:2014-03-31 11:34:22 |
- Kinoshita, A., and Sugahara, K. (1999) Microanalysis of glycosaminoglycan-derived oligosaccharides labeled with a fluorophore 2-aminobenzamide by high-performance liquid chromatography: application to disaccharide composition analysis and exosequencing of oligosaccharides. Anal Biochem 269, 367-378 [PMID : 10222012]
- Kawashima, H., Atarashi, K., Hirose, M., Hirose, J., Yamada, S., Sugahara, K., and Miyasaka, M. (2002) Oversulfated chondroitin/dermatan sulfates containing GlcAβ1/IdoAα1-3GalNAc(4,6-O-disulfate) interact with L- and P-selectin and chemokines. J Biol Chem 277, 12921-12930 [PMID : 11821431]
- Sugahara, K., Okumura, Y., and Yamashina, I. (1989) The Engelbreth-Holm-Swarm mouse tumor produces undersulfated heparan sulfate and oversulfated galactosaminoglycans. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 162, 189–197 [PMID : 2526630]
- Toyoda, H., Kinoshita-Toyoda, A., Selleck, S.B. (2000) Structural analysis of glycosaminoglycans in Drosophila and Caenorhabditis elegans and demonstration that tout-velu, a Drosophila gene related to EXT tumor suppressors, affects heparan sulfate in vivo. J Biol Chem 275, 2269-2275 [PMID : 10644674]
|
This work is licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-Non-Commercial Share Alike. Please include the following citation
How to Cite this Work in an article:
Yamada, Shuhei,
Toyoda, Hidenao,
(2014). GlycoPOD https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD.
Web.18,4,2024 .
How to Cite this Work in Website:
Yamada, Shuhei,
Toyoda, Hidenao,
(2014).
HPLC analysis of glycosaminoglycans.
Retrieved 18,4,2024 ,
from https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD/protocolShow.action?nodeId=t17.
html source
Yamada, Shuhei,
Toyoda, Hidenao,
(2014).
<b>HPLC analysis of glycosaminoglycans</b>.
Retrieved 4 18,2024 ,
from <a href="https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD/protocolShow.action?nodeId=t17" target="_blank">https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD/protocolShow.action?nodeId=t17</a>.
Including references that appeared in the References tab in your work is
much appreciated.
For those who wish to reuse the figures/tables, please contact JCGGDB
management office (jcggdb-ml@aist.go.jp).
|
|