Yeast cell wall consists of β1, 3- and β1, 6-glucans, chitin, and mannoproteins that are hyperglycosylated. The cell wall composition changes by various mutations (Abe et al., 2009, Ram et al., 1994). Therefore, glycan analysis of the cell walls is a powerful tool to evaluate and characterize the mutant cells properties. In this section, we will introduce an assay method for analyzing the glycan content of yeast cell walls. Briefly, cell walls are prepared from yeast cells and are hydrolyzed by trifluoroacetic acid (TFA). Then, the liberated monosaccharides are labeled with 8-aminopyrene-1, 3, 6-trisulfonate (APTS) or 2-aminopyridine (PA), and finally the labeled monosaccharides are analyzed by capillary electrophoresis (CE) or high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). Here, we describe (1) APTS-labeling method for yeast cell wall monosaccharides and (2) detection method of the APTS-labeled monosaccharides by use of CE separation system with laser-induced fluorescence (LIF) detection. |
| Category | Biosynthesis & Metabolism |
| Protocol Name | Assay for glycan contents of yeast cell wall |
Authors
 |
Tomimoto, Kazuya
Health Research Institute, National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST)
Abe, Hiroko
*
Celluer imaging Research Group, Health Research Institute, National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST)
*To whom correspondence should be addressed.
|
| KeyWords |
|
Reagents
 |
| ● |
4 M trifluoroacetic acid (TFA) (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO) |
| ● |
0.2 M CH3COONH4 (Wako Pure Chemical Industries Ltd., Osaka, Japan) |
| ● |
Acetic acid anhydride (Wako Pure Chemical Industries Ltd.) |
| ● |
Labeling Dye (APTS-M (Monosaccharide grade)) (Beckman Coulter, Inc. Brea, CA) |
| ● |
1 M sodium cyanoborohydride (Sigma-Aldrich) |
| ● |
120 mM boric acid buffer (pH 10.2) (Nacalai Tesque Inc., Kyoto, Japan) |
| ● |
Monosaccharides (GlcNAc, Man, Glc) as standards (Sigma-Aldrich) |
|
Instruments
 |
| ● |
Shakemaster Neo (Bio Medical Science Inc., Tokyo, Japan) |
| ● |
Glass beads (0.6 mm in diameter) (Bio Medical Science Inc.) |
| ● |
Centrifugal vacuum evaporator (EYELA, Tokyo, Japan) |
| ● |
Capillary electrophoretic separation system (P/ACE 2100 equipped with laser-induced fluorescence detector) (Beckman Coulter, Inc. ) |
| ● |
20 μm x 30 cm fused silica capillary (Beckman Coulter, Inc. ) |
| ● |
Heat block (Tietech Co., Ltd., Saitama, Japan) |
|
| Methods |
|
1. |
|
| 1) |
Cultivate yeast cells in the YPAD liquid medium until logarithmic growth (OD600=3) and harvest the yeast cells. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 2) |
Wash the cells with 1mL of 10 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.5, containing 1 mM phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride (PMSF). |
Comment 0
|

|
| 3) |
Suspend the cells in 0.5 mL of the same buffer and then add glass beads up to the meniscus. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 4) |
Shake the samples from step 3) at 4°C for 1 h in a Shakemaster Neo. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 5) |
Add 0.5 mL of 1 M NaCl solution to sample from step 4) and mix well. Collect the lysate of cells broken by step 4) in a new sample tube. Separate cell lysate from glass beads by repeat of this procedure. Then recover the cell wall fraction as a pellet by centrifugation of the cell lysate at 4°C, 1,000 g for 10 min. |
Comment 1
|

|
| 6) |
Wash the pellets twice with 1 mL of 1 M NaCl solution, and next, wash the pellet three times with 1mL of 1 mM PMSF solution. Finally, recover the cell wall pellets by centrifugation at 4°C, 1,000 g for 10 min. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 7) |
Suspend in 0.1 mL of 1mM PMSF solution. |
Comment 0
|
|
|
|
2. |
|
| 1) |
Mix the following components in a 1.5 mL sample tube
Cell walls sample 30 μL
Milli-Q water 70 μL
4 M TFA 100 μL
---------------------------------
Total 200 μL |
Comment 0
|

|
| 3) |
Dry up the sample using an evaporator. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 4) |
Suspend the pellets in 0.1 mL of 0.2 M ammonium acetate and 10 μL of acetic acid anhydride. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 5) |
Incubate at room temperature for 30 min. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 6) |
Dry up the sample using an evaporator. |
Comment 0
|

|
|
|
|
3. |
APTS labeling of monosaccharides liberated from the cell wall and CE separation
|
| 1) |
Add 2 μL of 1 M sodium cyanoborohydride to the sample. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 2) |
Add 2 μL of APTS Labeling Reagent. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 3) |
Incubate the reaction mixture at 60°C for 90 min on a heat block. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 4) |
Add 96 μL of Milli-Q water and then vortex. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 5) |
Add 195 μL of Milli-Q water to 5 μL of sample from step 4), and then transfer into a micro vial for analysis on the CE separation system. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 6) |
Analyze the sample from step 5) using CE separation system. The analysis conditions are as follows. Separation buffer; 120 mM boric acid buffer, Capillary; 20 μm × 30 cm fused silica capillary, Excitation wavelength; 488 nm, Emission wavelength; 520 nm, Temperature: 20°C, Sample Injection; pressure injection 0.5 psi for 20 sec, Electrophoresis condition; 28.0 kv, 15 min, normal polarity. |
Comment 1
|
|
|
| Notes | PALSTATION Pyridylamination Reagent Kit for monosaccharides was formerly supplied by Takara Bio Inc., Otsu, Japan, but the supply is now discontinued. |
| Discussion | The method described in this report facilitates evaluation and characterization various yeast mutants (see Fig. 1 and 2). For example, TIY20 strain can produce proteins with a mammalian-type high mannose structure, Man8GlcNAc2 (M8), by genetic manipulation. YAB103 is a derivative strain from TIY20 (Abe et al., 2009). A significant alteration in the cell wall composition of these strains was observed (Fig. 1 and 2); glucose content of YAB103 was significantly higher than that of the wild type strain. |
| Figure & Legends |
Figure & Legends

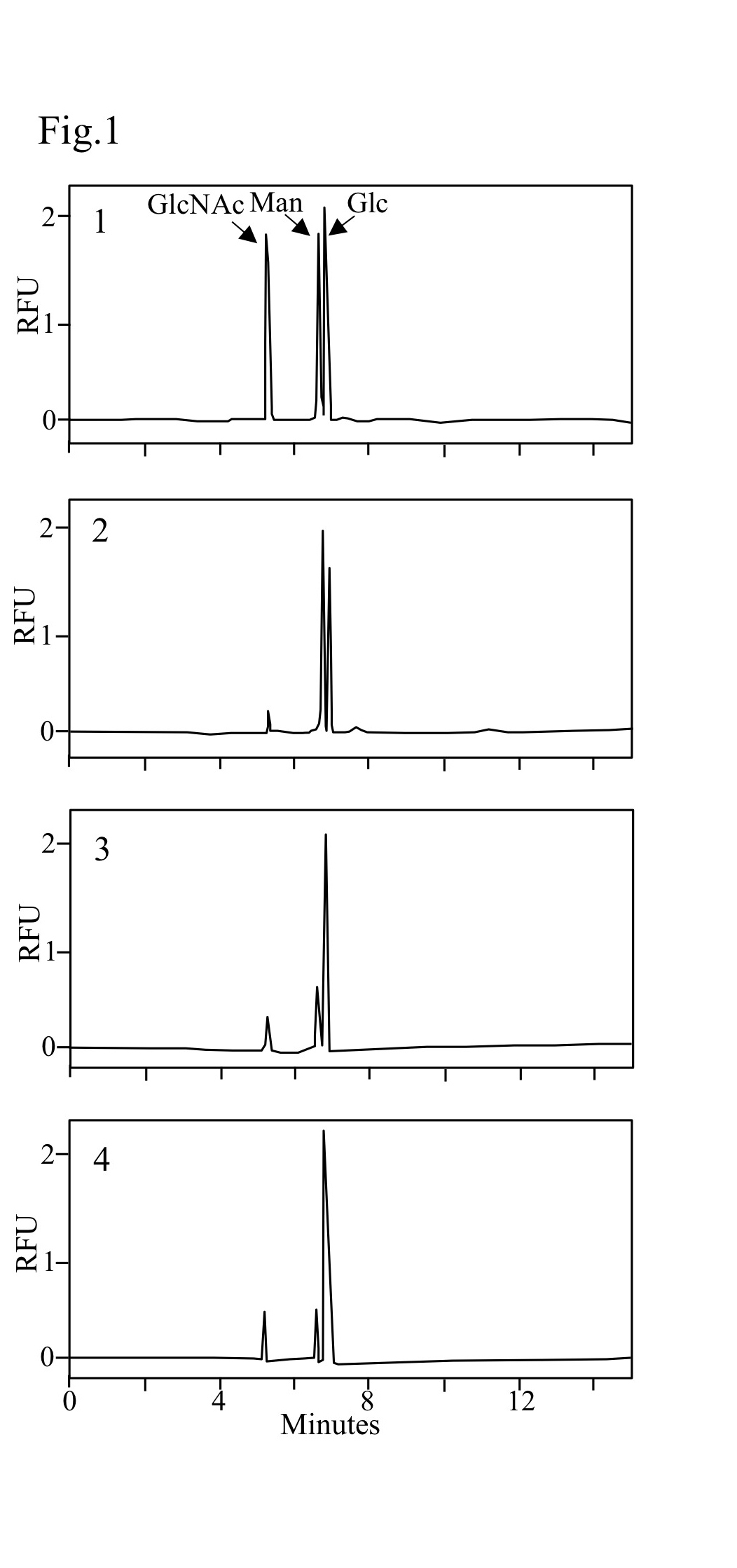
Fig. 1. Electropherograms of ATPS-labeled monosaccharides
1. ATPS-labeled monosaccharides (GlcNAc, Man, Glc) mixture. 2. ATPS-labeled monosaccharides from cell wall of wild type cells. 3. ATPS-labeled monosaccharides from cell wall of TIY20 (mannosylation mutant) cells. 4. ATPS-labeled monosaccharides from cell wall of YAB103 (mannosylation mutant) cells. RFU, relative fluorescence unit.

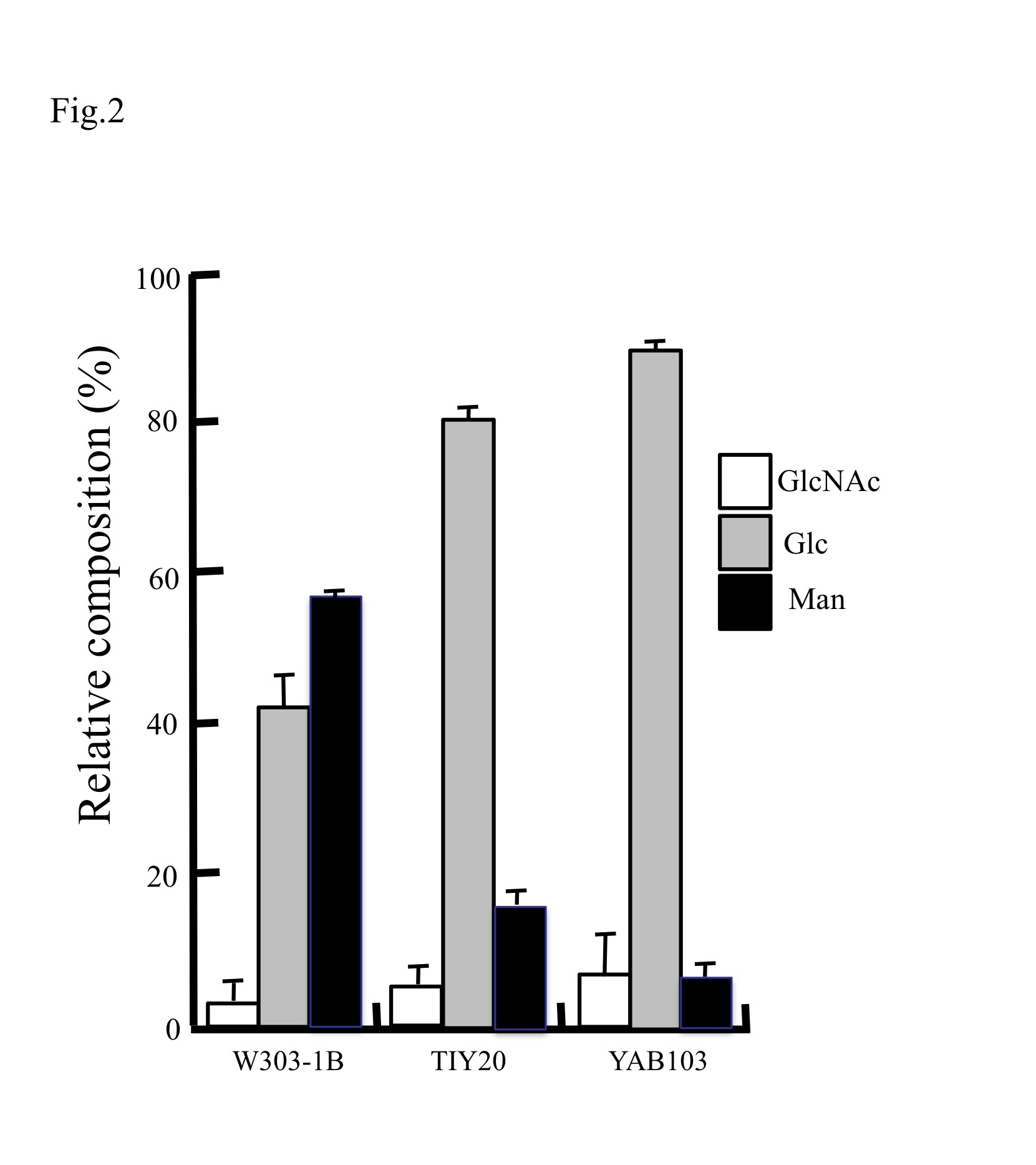
Fig. 2. Relative cell wall composition of different S. cerevisiae mutants
Relative amounts of each component in the cell walls of each strain are plotted. Data represent means ± standard deviation for three independent experiments. |
| Copyrights |
 Attribution-Non-Commercial Share Alike Attribution-Non-Commercial Share Alike
This work is released underCreative Commons licenses
|
| Date of registration:2014-12-11 14:33:43 |
- Abe, H., Fujita, Y., Chiba, Y., Jigami, Y., and Nakayama, K. (2009) Upregulation of genes involved in gluconeogenesis and the glyoxylate cycle suppressed the drug sensitivity of an N-glycan-deficient Saccharomyces cerevisiae mutant. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 73, 1398–1403 [PMID : 19502721]
- Ram, A. F., Wolters, A., Ten Hoopen, R., and Klis, F. M. (1994) A new approach for isolating cell wall mutants in Saccharomyces cerevisiae by screening for hypersensitivity to calcofluor white. Yeast 10, 1019–1030 [PMID : 7992502]
- Chen, F. T., Dobashi, T. S., and Evangelista, R. A. (1998) Quantitative analysis of sugar constituents of glycoproteins by capillary electrophoresis. Glycobiology 8, 1045–1052 [PMID : 9751791]
- Abe, H., Takaoka, Y., Chiba, Y., Sato, N., Ohgiya, S., Itadani, A., Hirashima, M., Shimoda, C., Jigami, Y., and Nakayama, K. (2009) Development of valuable yeast strains using a novel mutagenesis technique for the effective production of therapeutic glycoproteins. Glycobiology 19, 428–436 [PMID : 19129247]
|
This work is licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-Non-Commercial Share Alike. Please include the following citation
How to Cite this Work in an article:
Tomimoto, Kazuya,
Abe, Hiroko,
(2014). GlycoPOD https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD.
Web.23,4,2024 .
How to Cite this Work in Website:
Tomimoto, Kazuya,
Abe, Hiroko,
(2014).
Assay for glycan contents of yeast cell wall.
Retrieved 23,4,2024 ,
from https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD/protocolShow.action?nodeId=t168.
html source
Tomimoto, Kazuya,
Abe, Hiroko,
(2014).
<b>Assay for glycan contents of yeast cell wall</b>.
Retrieved 4 23,2024 ,
from <a href="https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD/protocolShow.action?nodeId=t168" target="_blank">https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD/protocolShow.action?nodeId=t168</a>.
Including references that appeared in the References tab in your work is
much appreciated.
For those who wish to reuse the figures/tables, please contact JCGGDB
management office (jcggdb-ml@aist.go.jp).
|
|