Brain is a unique and highly evolved organ expressing various glycans, which are different from those of other tissues, during development. Many carbohydrates expressed on the neural cell surface have shown pivotal roles in diverse functions including cell-cell interaction and modification of cellular signaling (Kleene and Schachner, 2004; Yanagisawa and Yu, 2007). Knockout mice targeting glycosyltransferases are useful tools to study functions of carbohydrates in vivo during development. However, since brain development is so complicated, in vitro analysis using neurosphere cells is ideal to investigate the function of carbohydrates on neural cells (Angata and Fukuda, 2010). First, we introduce a method for in vitro culture of neurosphere cells containing neural stem cells. By using the cultured neurosphere cells from knockout mice of glycosyltransferases, we can assess the effect of certain carbohydrates on migration of neural cells and differentiation into neurons or glial cells in vitro. |
| Category | Glycogene transgenic animals |
| Protocol Name | Neurosphere culture and in vitro assay |
Authors
 |
Angata, Kiyohiko
Glycoscience and Glycotechnology Research Group, Biotechnology Research Institute for Drug Discovery, Department of Life Science and Biotechnology, National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST)
|
| KeyWords |
|
Reagents
 |
| ● |
For culture of neurosphere cells
· Pregnant mouse (after embryonic day 14)
· L15 medium (Invitrogen/Life Technologies, Carlsbad, CA)
· DME:F12 medium (Invitrogen/Life Technologies)
· B27 supplement (Invitrogen/Life Technologies)
· FGF2 (20 ng/mL)
· EGF (20 ng/mL)
· Tissue culture flasks |
| ● |
For migration assay
· Polyethylenimine (0.01% in 0.15 M sodium borate pH 8.4)
· Mouse laminin (5 μg/mL in PBS)
· 12-well plates
· Neurobasal medium supplemented with B27 (Invitrogen/Life Technologies), glutamine and antibiotics.
· Paraformaldehyde (4% in 0.1 M phosphate buffer pH 7.4) |
| ● |
For differentiation assay
· Polyethylenimine-coated cover glasses
· Normal goat serum (1% in PBS)
· Primary antibodies (nestin, β-III tubulin, GFAP and CNPase, etc.)
· Secondary antibodies (Alexa Fluor ® 488 and 594 goat antibodies for rabbit, mouse or rat)
· Hoechst 33342
· Anti-quenching mounting media
|
|
Instruments
 |
| ● |
Cell culture facility (dissecting microscope, safety cabinet, CO2 incubator, and centrifuge)
|
| ● |
|
|
| Methods |
|
1. |
Culture of neurosphere cells |
| 1) |
Anesthetize pregnant mice with CO2 gas and collect embryos from the uterus. If knockout mice are used for the analyses, cut tails of embryos for genotyping. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 2) |
After cutting head skin and opening a skull, remove brains and place them into cold L15 medium. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 3) |
Under a dissecting microscope, open the brains along the midline of cerebral cortex to cut out ganglionic eminences (GE in Fig. 1) from the left and right semi-sphere of the forebrain. Meninges and visible blood vessels should be carefully removed from the section. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 4) |
Place GE into 0.5 mL DME:F-12/B27 medium and dissociate GE into single cells mechanically by pipetting with a polished Pasteur pipette. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 5) |
Add 4 mL DME:F-12/B27 medium and stand the tubes for 5 min to precipitate non-dissociated cells. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 6) |
Transfer cells except precipitate into a new tube and centrifuge at 300 × g for 5 min. Resuspend the precipitated cells with DME:F-12/B27 medium supplemented with 20 ng/mL FGF2 and 20 ng/mL EGF as mitogens and antibiotics in a tissue culture flask. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 7) |
To keep cells growing, add FGF2 and EGF into the culture medium every other day. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 8) |
At the 6th or 7th day in vitro, the floating neurosphere cells are precipitated and dissociated by pipetting as described above. This step is repeated until neurosphere cells are used for in vitro assays. |
Comment 0
|
|
|
|
2. |
|
| 1) |
Coat 12-well plates with 0.01% polyethylenimine for 2 h. Wash the wells with DDW twice and once with PBS. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 2) |
Then, coat the plates with 5 μg/mL mouse laminin for 2 h at 37°C. Wash the wells with PBS 4 times. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 3) |
Add 500 μL Neurobasal/B27 medium into each well and keep the plates in CO2 incubator. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 4) |
Collect neurospheres on the second or third day after the passage and plate around 50 to 100 spheres into each well. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 5) |
After 48 h, fix the cells by 4% paraformaldehyde. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 6) |
Capture cell images and measure the distance between the migrated cell and the edge of aggregated neurosphere cells (Fig. 1). |
Comment 0
|
|
|
|
3. |
In vitro differentiation assay |
| 1) |
Prepare cover glasses by coating with 0.01% polyethylenimine and 5 μg/mL laminin as described above. Extensively wash the cover glasses for both sides by soaking them in PBS. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 2) |
Collect neurospheres as described above and culture them in the well containing Neurobasal/B27 medium without mitogens. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 3) |
At various days for in vitro culture, fix the cells by 4% paraformaldehyde for staining neural cell markers. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 4) |
After wash the cells with PBS, treat them with 0.25% Triton-X 100 for 10 min and change buffer to 1% normal goat serum. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 5) |
Incubate cells with primary antibodies for neural cell markers to judge differentiation. For example, neural stem cells (nestin), neurons (β-III tubulin), astrocytes (GFAP) and oligodendrocytes (CNPase) are good markers. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 6) |
After washing, react with fluorescence-labeled secondary antibody, followed by Hoechst staining for 5 min. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 7) |
Mount cover glasses with anti-quenching reagent on slide glasses. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 8) |
Under fluorescence microscope, capture images for different colors and count for neurons and glial cells from each neurosphere to calculate differentiation rate to neurons or glial cells. (Fig. 2) |
Comment 0
|
|
|
| Notes |
- Neurosphere cells grow as free-floating spherical clusters. Differentiated cells and other contaminated cells adhere to the bottom of the tissue culture flask so that collecting neurosphere cells is easy for following in vitro assays.
- Addition of mitogens and periodical passage are important, because neurospheres lose neural stem cells and increase more differentiated cells when they grow too much.
- Neurosphere cells before 2 passages are not recommended for in vitro assays to avoid contamination, such as fibroblasts or endothelial cells, from the primary culture.
- Inducer molecules such as BDNF (40 ng/mL), CNTF (50 ng/mL) or PDGF-AA (10 ng/mL) can be added to the culture medium to evaluate the effect of cell surface carbohydrates on differentiation (Angata et al., 2007).
|
| Figure & Legends |
Figure & Legends

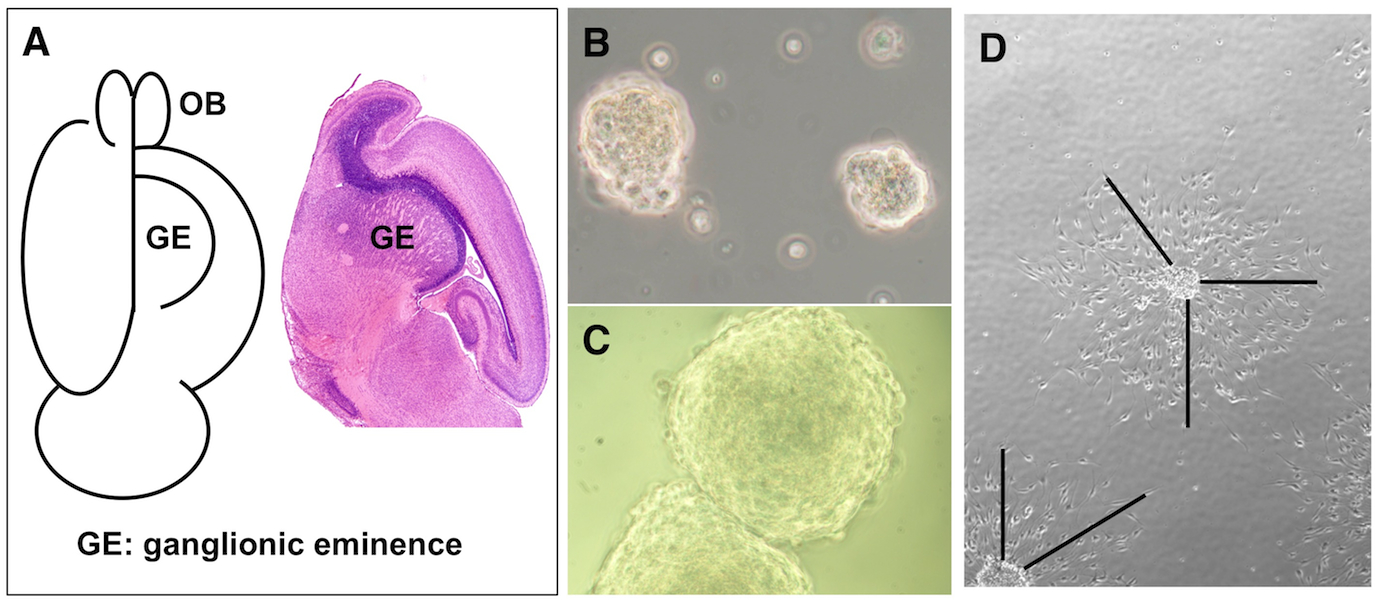
Fig. 1. Neurosphere cells prepared from mouse embryonic brain.
(A) Schematic figure to collect ganglionic eminence (GE). Open the cortex along the center line, GE is present under cerebral cortex (left). Sagittal section of P0 brain is shown (right). OB: olfactory bulb. Neurospheres on the second day (B) and the seventh day (C) after passage are shown. (D) Neurosphere cells cultured for 2 days in 12-well plates were used to measure the length of migration. The distance between edge of the clusters and migrated cells are measured as shown by lines.

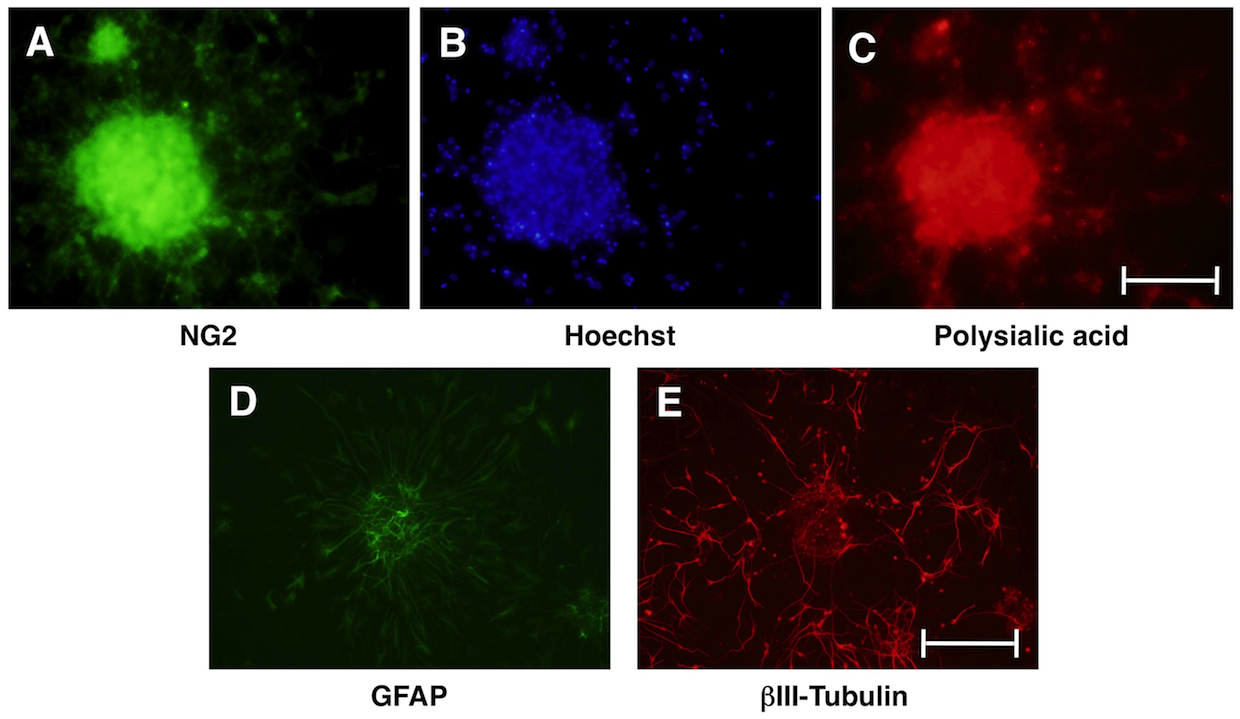
Fig. 2. Differentiation of neurosphere cells.
Neurosphere cells cultured in Neurobasal/B27 medium without mitogens start differentiation. After three days, neurosphere cells were stained with glial cell marker NG2 (green, A), Hoechst (blue, B) and polysialic acid (red, C). At the early point of differentiation, many neurosphere cells express early markers for glial cells and neurons. After seven days, neurosphere cells mainly differentiate into astrocytes expressing GFAP (green, D) and neurons expressing βIII-tubulin (red, E). Scale bars: 0.1 mm in A–C, 0.2 mm in D–E. |
| Copyrights |
 Attribution-Non-Commercial Share Alike Attribution-Non-Commercial Share Alike
This work is released underCreative Commons licenses
|
| Date of registration:2015-01-06 11:39:32 |
- Kleene, R., and Schachner, M. (2004) Glycans and neural cell interactions. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 5, 195–208 [PMID : 14976519]
- Yanagisawa, M., and Yu, R. K. (2007) The expression and functions of glycoconjugates in neural stem cells. Glycobiology 17, 57R–74R [PMID : 17307762]
- Angata, K. and Fukuda, M. (2010) Roles of polysialic acid in migration and differentiation of neural stem cells. Methods Enzymol. 479, 25–36 [PMID : 20816158]
- Angata, K., Huckaby, V., Ranscht, B., Terskikh, A., Marth, J. D. and Fukuda, M. (2007) Polysialic acid-directed migration and differentiation of neural precursors are essential for mouse brain development. Mol. Cell. Biol. 27, 6659–6668 [PMID : 17682066]
|
This work is licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-Non-Commercial Share Alike. Please include the following citation
How to Cite this Work in an article:
Angata, Kiyohiko,
(2015). GlycoPOD https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD.
Web.26,4,2024 .
How to Cite this Work in Website:
Angata, Kiyohiko,
(2015).
Neurosphere culture and in vitro assay.
Retrieved 26,4,2024 ,
from https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD/protocolShow.action?nodeId=t162.
html source
Angata, Kiyohiko,
(2015).
<b>Neurosphere culture and in vitro assay</b>.
Retrieved 4 26,2024 ,
from <a href="https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD/protocolShow.action?nodeId=t162" target="_blank">https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD/protocolShow.action?nodeId=t162</a>.
Including references that appeared in the References tab in your work is
much appreciated.
For those who wish to reuse the figures/tables, please contact JCGGDB
management office (jcggdb-ml@aist.go.jp).
|
|