Various anti-heparan sulfate (HS) antibodies are commercially available for enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISAs), immunohistochemistry, immunoprecipitation, Western blotting, FACS analysis etc. Characteristics of major anti-HS antibodies are summarized in Table 1. F58-10E4 and HepSS-1 predominantly react with highly sulfated regions in HS, but NAH46 specifically interacts with a sequence containing nonsulfated disaccharide units. JM403 recognizes a specific saccharide sequence containing a unique N-unsubstituted glucosamine residue. The epitope structure of F69-3G10 is generated only by treating HS with bacterial heparin (Hep)/HS lyases. Unsaturated uronate is essential for the reactivity of the antibody. As an example, the different reactivity of F58-10E4 and HepSS-1 antibodies toward HS preparations derived from various sources, is shown in this protocol. |
| Category | Glycosaminoglycans |
| Protocol Name | Application of anti-GAG antibody and biotinylated hyaluronan binding protein(bHABP) [1]
~ Characteristics and epitopes for anti-heparan sulfate antibodies |
Authors
 |
Yamada, Shuhei
*
Department of Pathobiochemistry, Faculty of Pharmacy, Meijo University
Kaneiwa, Tomoyuki
Laboratory of Proteoglycan Signaling and Therapeutics, Faculty of Advanced Life Science, Hokkaido University
*To whom correspondence should be addressed.
|
| KeyWords |
|
Reagents
 |
| ● |
Hep and HS from various sources |
| ● |
|
| ● |
0.1 M Phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) |
| ● |
PBS containing 0.05% Tween-20 (PBST) |
| ● |
25 mM Tris buffered saline (TBS) |
| ● |
TBS containing 0.05% Tween-20 (TBST) |
| ● |
Bovine serum albumin (BSA) |
| ● |
Anti-HS antibodies (Seikagaku Biobusiness Corp., Tokyo, Japan) |
| ● |
The secondary antibody, anti-mouse IgG+IgM (H+L) conjugated with alkaline phosphatase (Kirkegaard & Perry Laboratories, Inc., Gaithersburg, MD) |
| ● |
2 mg/mL p-Nitrophenyl phosphate (pNPP) in 50 mM carbonate buffer, pH 9.8, containing 0.5 mM MgCl2 |
|
Instruments
 |
| ● |
Streptavidin Plate C8 Transparent (Nunc, Roskilde, Denmark) |
| ● |
Microplate reader (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Hercules, CA) |
| ● |
|
|
| Methods |
|
1. |
ELISA using Streptavidin plates |
| 1) |
Wash the wells with 200 μL of PBS. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 2) |
Add 0.5 μg each of biotinylated Hep/HS in 50 μL of PBS to the wells and incubate at 4˚C overnight. |
Comment 1
|

|
| 3) |
Wash the wells with 200 μL of PBST. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 4) |
Add 200 μL of 3% BSA/PBS for blocking and incubate at room temperature for 1 h. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 5) |
Wash the wells with 200 μL of PBST three times. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 6) |
Add 50 μL of an appropriate concentration of the anti-HS antibody to the wells, and incubate the plate at 37˚C for 1 h. |
Comment 1
|

|
| 7) |
Wash the wells with 200 μl of TBST three times. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 8) |
Add 50 μL of the secondary antibody (diluted 1:2,000 in TBS) and incubate at 37˚C for 1 h. |
Comment 1
|

|
| 9) |
Wash the wells with 200 μL of TBST three times. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 10) |
Add 50 μL of the pNPP solution and incubate at room temperature. |
Comment 1
|

|
| 11) |
Measure the absorbance at 415 nm with a microplate reader (Fig. 1). |
Comment 0
|
|
|
| Figure & Legends |
Figure & Legends
|
Clone
|
Antigen |
Subtype |
Specificity |
References |
| F58-10E4 |
HS-proteoglycans from
human fetal lung fibroblasts
|
mouse IgM |
Mixed HS domains containing both
N-acetylated and N-sulfated disaccharide units
HS saccharide sequence including an
N-unsubstituted glucosamine
|
David et al., 1992;
Leteux et al., 2001; van
den Born et al. 2005
|
| HepSS-1 |
Murine
methylcholanthrene-induced fibrosarcoma
|
mouse IgM |
N-Sulfated HS domains |
Kure and Yoshie, 1986;
van den Born et al., 2005
|
| JM403 |
Rat glomerular
HS-proteoglycans
|
mouse IgM |
HS saccharide sequence rich in glucuronate and
N-unsubstituted glucosamine residues
|
Leteux et al., 2001; van
den Born et al., 1992
|
| NAH46 |
N-Acetyl-heparosan from
Escherichia coli K5
|
mouse IgM |
HS saccharide sequence containing nonsulfated
disaccharide units
|
Suzuki et al., 2008 |
| F69-3G10 |
Heparitinase-digested
HS-proteoglycans from
human fetal lung fibroblasts
|
mouse IgG2b |
HS oligosaccharide containing an
unsaturated uronate at the nonreducing end
|
David et al., 199
|
Table 1. Commercially available anti-HS antibodies

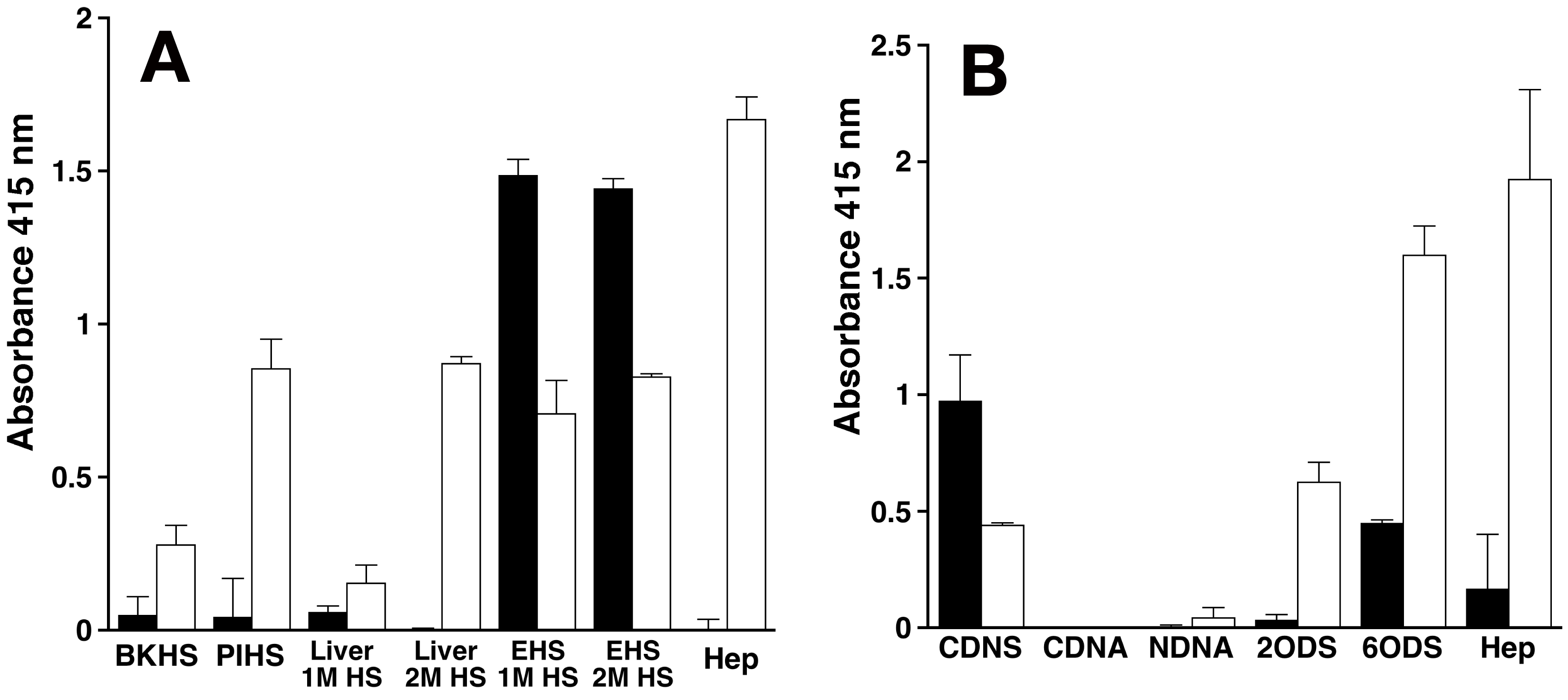
Fig. 1. Reactivity of the anti-HS antibodies, F58-10E4 and HepSS-1, toward various HS/Hep preparations (A) and chemically modified Hep preparations (B).
Closed and open columns show the reactivity of F58-10E4 and HepSS-1, respectively. Two separate experiments were carried out and results are expressed as means ± SDs. Liver 1M HS and Liver 2 M HS are bovine liver HS preparations purified by anion-exchange chromatography with 1 M and 2 M LiCl, respectively. EHS 1M HS and EHS 2 M HS are HS preparations purified from mouse EHS chondrosarcoma by anion-exchange chromatography with 1 M and 2 M LiCl, respectively. BKHS and PIHS stand for bovine kidney and porcine intestinal HS, respectively. The disaccharide composition of these Hep/HS preparations is shown in Table 2. CDNS, CDNA, NDNA, 2ODS, and 6ODS represent completely desulfated N-acetylated Hep, completely desulfated N-sulfated Hep, N-desulfated N-acetylated Hep, 2-O-desulfated Hep, and 6-O-desulfated Hep, respectively.
| Disaccharide |
|
|
|
Bovine liverb |
EHS chondrosarcoma |
| |
BKHSa |
PIHS |
Hep |
1M HS |
2 M HS |
1M HS |
2 M HS |
| |
% |
| ΔHexAd-GlcNAc |
54 |
46 |
5
|
38 |
0 |
30 |
32 |
| ΔHexA-GlcNAc(6S) |
12 |
12 |
4
|
9 |
2 |
0 |
0 |
| ΔHexA-GlcN(NS) |
21 |
32 |
5 |
23 |
11 |
67 |
61 |
| ΔHexA-GlcN(NS,6S) |
5 |
3 |
15 |
6 |
10 |
1 |
7e |
| ΔHexA(2S)-GlcN(NS) |
4 |
2 |
4 |
3 |
4 |
2 |
| ΔHexA(2S)-GlcNAc(6S) |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
6 |
0 |
0 |
| ΔHexA(2S)- GlcN(NS,6S) |
4 |
4 |
67 |
21 |
67 |
0 |
0 |
| total |
100 |
100 |
100 |
100 |
100 |
100 |
100 |
Table 2. Disaccharide composition of various HS and Hep preparations
aBKHS, bovine kidney heparan sulfate; PIHS, porcine intestine heparan sulfate; ΔHexA, GlcNAc, and GlcN stand for unsaturated hexuronic acid, N-acetyl-D-glucosamine, and D-glucosamine, respectively. 2S, 6S, and NS represent 2-O-sulfate, 6-O-sulfate, and 2-N-sulfate, respectively.
bBovine liver 1 M and 2 M HS were purified by anion-exchange chromatography with 1 M and 2 M LiCl, respectively.
cEHS chondrosarcoma 1 M and 2 M HS were purified from mouse EHS chondrosarcoma by anion-exchange chromatography with 1 M and 2 M LiCl, respectively.
dTreatment with bacterial eliminases converts the original uronic acid structure in the polysaccharides into an artificial structure, the 4,5-unsaturated uronic acid, 4-deoxy-α-L-threo-hex-4-enepyranosyluronic acid.
eThe combined proportion of disulfated disaccharide units, ΔHexA-GlcN(NS,6S) and ΔHexA(2S)-GlcN(NS).
|
| Copyrights |
 Attribution-Non-Commercial Share Alike Attribution-Non-Commercial Share Alike
This work is released underCreative Commons licenses
|
| Date of registration:2017-01-23 15:51:46 |
- Kure, S., and Yoshie, O. (1986) A syngeneic monoclonal antibody to murine Meth-A sarcoma (HepSS-1) recognizes heparan sulfate glycosaminoglycan (HS-GAG): cell density and transformation dependent alteration in cell surface HS-GAG defined by HepSS-1. J. Immunol. 137, 3900-3908 [PMID : 2431047]
- David, G., Bai, X.M., Van der Schueren, B., Cassiman, J.J., and Van den Berghe, H. (1992) Developmental changes in heparan sulfate expression: in situ detection with mAbs. J. Cell Biol. 119, 961-975 [PMID : 1385449]
- van den Born, J., van den Heuvel, L.P., Bakker, M.A., Veerkamp, J.H., Assmann, K.J., and Berden, J.H. (1992) A monoclonal antibody against GBM heparan sulfate induces an acute selective proteinuria in rats. Kidney Int. 41, 115-123 [PMID : 1593846]
- Leteux, C., Chai, W., Nagai, K., Herbert, C.G., Lawson, A.M., and Feizi, T. (2001) 10E4 antigen of Scrapie lesions contains an unusual nonsulfated heparan motif. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 12539-12545 [PMID : 11278655]
- van den Born, J., Salmivirta, K., Henttinen, T., Ostman, N., Ishimaru, T., Miyaura S., Yoshida, K., and Salmivirta, M. (2005) Novel heparan sulfate structures revealed by monoclonal antibodies. J. Biol. Chem. 280, 20516-20523 [PMID : 15778504]
- Suzuki, K., Yamamoto, K., Kariya, Y., Maeda, H., Ishimaru, T., Miyaura, S., Fujii, M., Yusa, A., Joo E.J., Kimata, K., Kannagi, R., Kim, Y.S., and Kyogashima, M. (2008) Generation and characterization of a series of monoclonal antibodies that specifically recognize [HexA(+/-2S)-GlcNAc]n epitopes in heparan sulfate. Glycoconj. J. 25, 703-712 [PMID : 18461440]
|
This work is licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-Non-Commercial Share Alike. Please include the following citation
How to Cite this Work in an article:
Yamada, Shuhei,
Kaneiwa, Tomoyuki,
(2017). GlycoPOD https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD.
Web.24,4,2024 .
How to Cite this Work in Website:
Yamada, Shuhei,
Kaneiwa, Tomoyuki,
(2017).
Application of anti-GAG antibody and biotinylated hyaluronan binding protein(bHABP) [1]
~ Characteristics and epitopes for anti-heparan sulfate antibodies.
Retrieved 24,4,2024 ,
from https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD/protocolShow.action?nodeId=t157.
html source
Yamada, Shuhei,
Kaneiwa, Tomoyuki,
(2017).
<b>Application of anti-GAG antibody and biotinylated hyaluronan binding protein(bHABP) [1]
~ Characteristics and epitopes for anti-heparan sulfate antibodies</b>.
Retrieved 4 24,2024 ,
from <a href="https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD/protocolShow.action?nodeId=t157" target="_blank">https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD/protocolShow.action?nodeId=t157</a>.
Including references that appeared in the References tab in your work is
much appreciated.
For those who wish to reuse the figures/tables, please contact JCGGDB
management office (jcggdb-ml@aist.go.jp).
|
|