UDP-N-acetylglucosamine:α1,3-D-mannoside
β1,4-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferse (GnT-IV) (EC2.4.1.145) catalyzes the transfer of GlcNAc from UDP-GlcNAc to the GlcNAcβ1-2Manα1-3 arm of the core structure of N-glycans through a β1-4 linkage. This enzyme is essential for producing the C-2,4 branch on complex- and hybrid-type N-glycans. The enzyme was first purified from a microsomal fraction solubilized from bovine small intestine (Oguri S, 1997). Two human GnT-IV isozymes (GnT-IVa and GnT-IVb) had been identified, which exhibit different expression profiles among human tissues and cancer cell lines (Yoshida A, 1998, Takamatsu S, 2005). Kinetic analysis showed that both GnT-IV isozymes exhibited similar substrate specificities, although GnT-IVa has higher affinities for sugar chains than GnT-IVb (Oguri S, 2006).
GnT-IV requires divalent cations, especially Mn2+, for activation. The activity is inactivated by EDTA treatment. The addition of 10 mM ME does not affect the activity.
GnT-IV activity can be assayed using a pyridylaminated asialoagalacto-biantennary sugar chain (PA-GnGnbi) which is a common substrate for GnT-III and –V (Nishikawa A, 1990). Since GnT-IV exhibits higher Km for PA-GnGnbi than GnT-III and V, the higher substrate concentration is needed to detect the GnT-IV activity. Therefore, the concentration of acceptor substrate is 0.8 mM in this assay, which is 10-times higher than those of GnT-III and GnT-V (Tokugawa K, 1996). PA-GnGnbi is available commercially, but the costs may be prohibitive for large numbers of assays. |
| Category | Glycosyltransferases & related proteins |
| Protocol Name | Enzyme assay of beta-1,4-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase-IV (GnT-IV) |
Authors
 |
Oguri, Suguru
Department of Bioproduction, Faculty of Bioindustry, Tokyo University of Agriculture
|
| KeyWords |
|
Reagents
 |
| ● |
Human apo-transferrin (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO) |
| ● |
Nonidet P-40 (Nacalai Tesque Inc., Kyoto, Japan) |
| ● |
N-glycosidaese F recombinant (Roche Diagnostics, Basel, Switzerland) |
| ● |
TE-saturated phenol/chloroform (for molecular biology) |
| ● |
Bio-gel P-100 (fine) (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Hercules, CA ) |
| ● |
Toyopearl HW-40F (Tosoh Corporation, Tokyo, Japan) |
| ● |
2-Aminopyridine (Wako Pure Chemical Industries Ltd., Osaka, Japan) |
| ● |
Borane-dimethylamine complex (Wako Pure Chemical Industries Ltd.) |
| ● |
Neuraminidase (Sialidase) from Arthrobacter ureafaciens (Nacalai Tesque Inc., Kyoto, Japan) |
| ● |
β-Galactosidase from Aspergillus sp. (Toyobo Co., Ltd., Osaka, Japan) |
| ● |
PA-GnGnbi (PA-Sugar Chain 012, Takara Bio Inc., Otsu, Japan) |
| ● |
PA-GnGnGntri (PA-Sugar Chain 013, Takara Bio Inc.) |
|
Instruments
 |
| ● |
|
| ● |
|
| ● |
HPLC system with a fluorescent detector |
| ● |
TSK gel ODS-80Tm column (0.46 × 15 cm, Tosoh Corporation) |
|
| Methods |
|
1. |
Preparation of acceptor. Step 1: Release of N-glycans from glycoproteins. |
| 1) |
Dissolve 2.5 g human apo-transferrin in 100 mL of 50 mM Tris-HCl (pH7.2) containing 1% (v/v) β-mercaptoethanol and 2.5% (w/v) SDS. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 2) |
Mix gently with stirring on a magnetic stirrer, and incubate at 60˚C for 2 h. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 3) |
After cooling to room temperature, add 4.0% (w/v) of Nonidet P-40 and 75 U of N-glycosidase F. Add 100 μL of toluene to prevent bacterial growth. Incubate at 37˚C overnight. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 4) |
Add an additional 75 U of N-glycosidase F, incubate at 37˚C overnight. Analyze the aliquot of sample by SDS-PAGE. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 5) |
Divide into 20 mL aliquots in 50 mL conical tubes. Add equal volume of TE-saturated phenol/chloroform solution and mix vigorously by vortex. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 6) |
Centrifuge at 4,000 rpm for 20 min. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 7) |
Transfer the clear aqueous phase to a bottle and lyophilize. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 8) |
Dissolve the lyophilized powder in 20 mL of 50 mM ammonium acetate buffer (no pH adjustment). |
Comment 0
|

|
| 9) |
Apply the sample to a Bio-gel P-100 column (2.5 cm × 70 cm) equilibrated with 50 mM ammonium acetate buffer at the flow-rate of 8 drops/sec. Collect the eluate at 2mL/tube. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 10) |
Detect sugar chains by phenol/H2SO4 method. The sugar chains will be eluted between fractions 130 and 170. Transfer the carbohydrate-positive fractions to a 500 mL bottle and lyophilize. |
Comment 0
|
|
|
|
2. |
Preparation of acceptor. Step 2: Pyridylamination of N-glycans. |
| 1) |
Prepare PA reagent. Dissolve 27 g 2-aminopyridine in 13 mL of glacial acetic acid. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 2) |
Add the PA reagent to the lyophilized sugar chains and stir on a magnetic stirrer until completely dissolved. Wrap the bottle in aluminum foil. Incubate at 90˚C for 1 h by bath. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 3) |
Prepare Reducing reagent. Dissolve 57 g borane-dimethylamine complex and 23 mL of glacial acetic acid in 14mL of water. |
Comment 1
|

|
| 4) |
Add the reducing reagent to the bottle and stir on a magnetic stirrer. Incubate at 80˚C for 1 h in a fume hood. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 5) |
After cooling to room temperature, adjust volume to 250 mL with H2O. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 6) |
Transfer the sample to a separatory funnel. To remove the excess 2-aminopyridine, extract the sample twice with equal volumes of TE-saturated phenol/chloroform, and once with chloroform. The top aqueous phase contains the PA-labeled N-glycans. |
Comment 1
|

|
| 7) |
Concentrate the sample to 40 mL by evaporation with a rotary evaporator. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 8) |
Apply the concentrated sample to a HW-40F column (5 cm × 25 cm) equilibrated with 10 mM ammonium acetate buffer (pH 6.0) at the flow-rate of 2.5 mL/min. Collect the eluate at 5mL/tube. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 9) |
Detect sugar chains by phenol/H2SO4 method. The absorption of eluted PA can be monitored at 300 nm. The PA-labeled N-glycans will be eluted between fractions 40 and 70. Collect the carbohydrate-positive fractions and lyophilize. Analyze the yield of PA-labeled N-glycans by phenol/H2SO4 method and HPLC. |
Comment 0
|
|
|
|
3. |
Preparation of acceptor. Step 3: Sialidase/β-galactosidase treatment of PA-labeled N-glycans. |
| 1) |
Dissolve the lyophilized powder in 10 mL of 0.4 M sodium acetate buffer (pH 5.0) containing 4 mM MgCl2. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 2) |
Add 10 U of neuraminidase and 10 mg of β-galactosidase. Add one drop of toluene to prevent bacterial growth. Incubate at 37˚C overnight. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 3) |
Analyze the aliquots of the sample by HPLC. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 4) |
Purify PA-GnGnbi by reverse-phase HPLC as following condition:
column, Vydac 218TP152010 (10 mm × 250 mm); eluent, 100 mM ammonium acetate (pH 4.0) containing 0.15% n-butanol; flow rate, column temperature, 50˚C; 2.5 mL/min; detection, 300 nm. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 5) |
Confirm the purity of PA-GnGnbi by HPLC. From 2.5 g of human apo-transferrin, 25–30 μmol of PA-GnGnbi was obtained at yield of 43 %. |
Comment 0
|
|
|
|
4. |
|
| 1) |
Prepare 2× GnT-IV reaction buffer: 250 mM MOPS-KOH buffer, 40 mM UDP-GlcNAc, 400 mM GlcNAc, 1% (w/v) Triton X-100, 20 % (v/v) glycerol, 1% (w/v) BSA, 15 mM MnCl2, pH 7.3. Store −20˚C until use. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 2) |
Combine the following components in a thin-walled PCR tube.
2× GnT-IV reaction buffer 5 μL
4 mM PA-GnGnbi 2 μL
Enzyme solution 3 μL
(Total volume 10 μL) |
Comment 1
|

|
| 3) |
Mix gently by pipetting, and incubate at 37˚C for 2 h. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 4) |
Add 30 μL of 10 mM EDTA (pH 7.0), vortex and boil for 2 min. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 5) |
Centrifuge at 15,000 rpm for 15min. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 6) |
Collect the supernatant, and analyze by HPLC. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 7) |
Prepare 10 × stock (1 M ammonium acetate, pH 4.0). Dissolve 7.7 g ammonium acetate in 900 mL of Milli-Q water, and add 52 mL of glacial acetic acid. Titrate with ammonia water to pH 4.0, and add Milli-Q water to make a final volume of 1 L. Store at room temperature. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 8) |
HPLC Buffer (50 mM ammonium acetate, 0.15% n-butanol, pH 4.0). Prepare 1 L of buffer by mixing 50 mL of 10 × stock buffer, 1.5 mL n-butanol, and Milli-Q water. Filtrate the buffer through a 0.45 μm filter prior to use. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 9) |
Analyze 10 μL of the reaction mixture as following condition: column, ODS-80Tm (4.6 mm × 150 mm); eluent, 50 mM ammonium acetate (pH 4.0) containing 0.15% n-butanol; flow-rate, 1.2 mL/min column temperature, 50˚C; detection, Ex = 320 nm, Em = 400 nm |
Comment 1
|
|
|
| Figure & Legends |
Figure & Legends

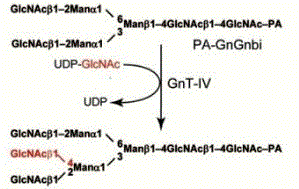
Fig. 1. Reaction catalyzed by GnT-IV

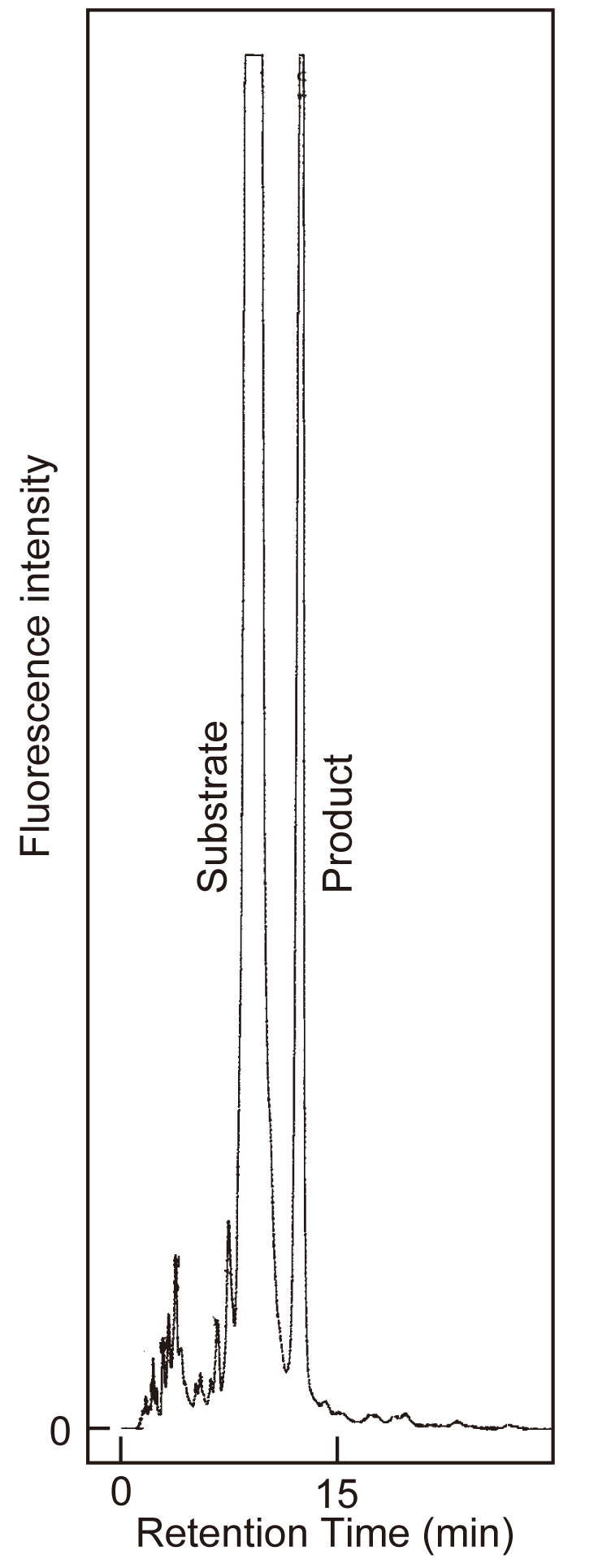
Fig. 2. GnT-IV assay: HPLC separation of substrate and product.
A recombinant human GnT-IVa was incubated in the 10 μL of reaction mixtures for 2 h at 37˚C. After the addition of 30 μL of 10mM EDTA and boiling, an aliquot (10 μL) of the supernatant was subjected to HPLC as described. The retention times for substrate and product were 9.02 min and 12.33 min, respectively. Column: ODS-80Tm (4.6 mm × 150 mm), eluent: 50 mM ammonium acetate (pH 4.0) containing 0.15% n-butanol, flow-rate: 1.2 mL/min, column temperature: 50˚C; detection: Ex = 320nm and Em = 400 nm. |
| Copyrights |
 Attribution-Non-Commercial Share Alike Attribution-Non-Commercial Share Alike
This work is released underCreative Commons licenses
|
| Date of registration:2014-07-30 11:37:31 |
- Oguri, S., Minowa, M. T., Ihara, Y., Taniguchi, N., Ikenaga, H. and Takeuchi, M. (1997) Purification and characterization of UDP-N-acetylglucosamine: α1,3-D-mannoside β1,4-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase (N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase-IV) from bovine small intestine. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 22721–22727 [PMID : 9278430]
- Yoshida, A., Minowa, M. T., Takamatsu, S., Hara, T., Ikenaga, H. and Takeuchi, M. (1998) A novel second isoenzyme of the human UDP-N-acetylglucosamine:alpha1,3-D-mannoside beta1,4-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase family: cDNA cloning, expression, and chromosomal assignment. Glycoconj J. 15, 1115–1123 [PMID : 10372966]
- Takamatsu, S., Inoue, N., Katsumata, T., Nakamura, K., Fujibayashi, Y. and Takeuchi, M. (2005) The relationship between the branch-forming glycosyltransferases and cell surface sugar chain structures. Biochemistry 44, 6343–6349 [PMID : 15835923]
- Oguri, S., Yoshida, A., Minowa, M. T., and Takeuchi, M. (2006) Kinetic properties and substrate specificities of two recombinant human N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase-IV isozymes. Glycoconj J. 23, 473–480 [PMID : 17006639]
- Nishikawa, A., Gu, J., Fujii, S. and Taniguchi, N. (1990) Determination of N-acetylglucosaminyltransferases III, IV and V in normal and hepatoma tissues of rats. Biochim Biophys Acta 1035, 313–318 [PMID : 2145037]
- Tokugawa, K., Oguri, S. and Takeuchi, M. (1996) Large scale preparation of PA-oligosaccharides from glycoproteins using an improved extraction method. Glycoconj J. 13, 53–56 [PMID : 8709573]
|
This work is licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-Non-Commercial Share Alike. Please include the following citation
How to Cite this Work in an article:
Oguri, Suguru,
(2014). GlycoPOD https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD.
Web.24,4,2024 .
How to Cite this Work in Website:
Oguri, Suguru,
(2014).
Enzyme assay of beta-1,4-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase-IV (GnT-IV).
Retrieved 24,4,2024 ,
from https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD/protocolShow.action?nodeId=t152.
html source
Oguri, Suguru,
(2014).
<b>Enzyme assay of beta-1,4-<em>N</em>-acetylglucosaminyltransferase-IV (GnT-IV)</b>.
Retrieved 4 24,2024 ,
from <a href="https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD/protocolShow.action?nodeId=t152" target="_blank">https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD/protocolShow.action?nodeId=t152</a>.
Including references that appeared in the References tab in your work is
much appreciated.
For those who wish to reuse the figures/tables, please contact JCGGDB
management office (jcggdb-ml@aist.go.jp).
|
|