Fast, reproducible and non-radioisotope methods of determining the activity of glucosylceramide synthase (GlcT) and lactosylceramide synthase (GalT) are described. The methods utilize fluorescent acceptor substrates, C6-NBD-ceramide (C6-NBD-Cer) for the GlcT assay and C6-NBD-glucosylceramide (C6-NBD-GlcCer) for the GalT assay, and normal-phase high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). The reaction products, C6-NBD-GlcCer for GlcT and C6-NBD-lactosylceramide (C6-NBD-LacCer) for GalT, could be separated from the corresponding acceptor substrates within 6 min under the conditions used. |
| Category | Glycolipids and related compounds |
| Protocol Name | Assay of glycosphingolipid synthases using HPLC and fluorescent substrates |
Authors
 |
Hayashi, Yasuhiro
*
Faculty of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Teikyo University
Ito, Makoto
Department of Bioscience and Biotechnology, Graduate School of Bioresource and Bioenvironmental Sciences, Kyushu University
*To whom correspondence should be addressed.
|
| KeyWords |
|
Reagents
 |
| ● |
C6-NBD-Cer (#N1154: Invitrogen/Life Technologies, Carlsbad, CA) |
| ● |
C6-NBD-GlcCer (#N6783: Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO) |
| ● |
C6-NBD-LacCer (#N8908: Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO) |
| ● |
|
| ● |
|
| ● |
|
| ● |
Normal-phase column (Intersil SIL 15A-5: GL-Sciences, Tokyo, Japan) |
| ● |
|
| ● |
|
| ● |
|
|
Instruments
 |
| ● |
HPLC (Hitachi L-7100: Hitachi, Ltd. Tokyo, Japan) |
| ● |
Fluorescent detector (L-7480: Hitachi, Ltd. Tokyo, Japan) |
| ● |
Autosampler (L-7200: Hitachi, Ltd. Tokyo, Japan) |
| ● |
Speed Vac concentrator (Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., Waltmam, MA) |
|
| Methods |
|
1. |
Assay of glycosphingolipid synthases using HPLC and fluorescent substrates |
| 1) |
Mix 50 pmol of C6-NBD-Cer or C6-NBD-GlcCer with 5 mg (6.5 nmol) of lecithin in 100 μL of ethanol and then evaporate the solvent. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 2) |
Add 10 μL of water and sonicate to form liposomes. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 3) |
For the GlcT assay, 50 μL of reaction mixture should contain 500 μM UDP-Glc, 1 mM EDTA, 10 μL of C6-NBD-Cer liposome, and 20 μL of an appropriate concentration of enzyme. For the GalT assay, 50 μL of mixture should contain 100 μM UDP-Gal, 5 mM MgCl2, 5 mM MnCl2, 10 μL of C6-NBD-GlcCer liposome, and 20 μL of an appropriate concentration of enzyme. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 4) |
Stop the reaction by adding 200 μL of chloroform/methanol (2:1, v/v). After a few seconds of vortexing, 5 μL of 500 μM KCl was added and then centrifuged. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 5) |
Dry the organic phase, dissolve the lipids in 200 μL of isopropyl alcohol/n-hexane/H2O (55:44:1, v/v/v), and transferr to a glass vial in an auto-sampler. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 6) |
An aliquot of sample is automatically loaded onto a normal-phase column and eluted with isopropyl alcohol/n-hexane/H2O (55:44:1, v/v/v) for the GlcT assay or isopropyl alcohol/n-hexane/H2O/phosphoric acid (110:84:5.9:0.1, v/v/v/v) for the GalT assay, at a flow rate of 2.0 mL/min. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 7) |
Determine fluorescence using a detector set to excitation and emission wavelengths of 470 and 530 nm, respectively. Peaks of fluorescence peaks can be identified by comparing retention times with those of standards. |
Comment 0
|
|
|
| Notes | With this procedure, 50 fmol – 50 pmol of GlcCer and LacCer can be determined within 5 min. |
| Figure & Legends |
Figure & Legends 
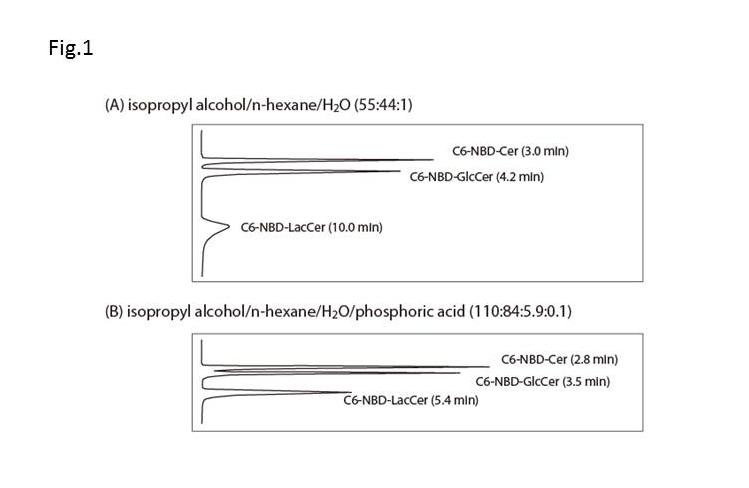
Reprinted from Anal Biochem., 345(2), Hayashi Y, Ito M. et al., A sensitive and reproducible assay to measure the activity of glucosylceramide synthase and lactosylceramide synthase using HPLC and fluorescent substrates, 181-6, 2005, with permission from Elsevier. doi:10.1016/j.ab.2005.05.029. |
| Copyrights |
 Attribution-Non-Commercial Share Alike Attribution-Non-Commercial Share Alike
This work is released underCreative Commons licenses
|
| Date of registration:2013-11-27 15:02:59 |
- Hayashi, Y., Horibata, Y., Sakaguchi, K., Okino, N., and Ito, M. (2005) A sensitive and reproducible assay to measure the activity of glucosylceramide synthase and lactosylceramide synthase using HPLC and fluorescent substrates. Anal. Biochem. 345, 181-186 [PMID : 16140251]
|
This work is licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-Non-Commercial Share Alike. Please include the following citation
How to Cite this Work in an article:
Hayashi, Yasuhiro,
Ito, Makoto,
(2013). GlycoPOD https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD.
Web.20,4,2024 .
How to Cite this Work in Website:
Hayashi, Yasuhiro,
Ito, Makoto,
(2013).
Assay of glycosphingolipid synthases using HPLC and fluorescent substrates.
Retrieved 20,4,2024 ,
from https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD/protocolShow.action?nodeId=t137.
html source
Hayashi, Yasuhiro,
Ito, Makoto,
(2013).
<b>Assay of glycosphingolipid synthases using HPLC and fluorescent substrates</b>.
Retrieved 4 20,2024 ,
from <a href="https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD/protocolShow.action?nodeId=t137" target="_blank">https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD/protocolShow.action?nodeId=t137</a>.
Including references that appeared in the References tab in your work is
much appreciated.
For those who wish to reuse the figures/tables, please contact JCGGDB
management office (jcggdb-ml@aist.go.jp).
|
|