When soluble lectins are purified, it is highly recommended to use Hemagglutination assay as one of the quality control procedures. In addition, the activities of purified lectins should be routinely verified by this method. This method can be used to quickly screen any inhibitors for lectins before the potential inhibitors are screened for any biological assays. Purified red blood cells (RBCs) can be stable at least several month but it is highly recommended to check the quality of cells before the usage. |
| Category | Sugar binding proteins |
| Protocol Name | |
Authors
 |
St-Pierre, Guillaume
Glycobiology and Bioimaging laboratory, Research Centre for Infectious Diseases, CHUQ, Laval University, Quebec
Milot, Valérie
Glycobiology and Bioimaging laboratory, Research Centre for Infectious Diseases, CHUQ, Laval University, Quebec
Sato, Sachiko
*
Glycobiology and Bioimaging laboratory, Research Centre for Infectious Diseases, CHUQ, Laval University, Quebec
*To whom correspondence should be addressed.
|
Reagents
 |
| ● |
Heparined tubes (BD, Franklin Lakes, NJ: Cat. #362753) |
| ● |
|
| ● |
Glutaraldehyde (Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., Waltham, MA: Cat. #O2957-1) |
| ● |
Sodium Azide (NaN3 ) (Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc.: Cat. #S227I-25) |
| ● |
96 wells round bottom plates (Corning, Corning, NY: #3799) |
| ● |
α-Lactose (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO: Cat. #L3635) |
| ● |
15 mL and 50 mL tubes (Corning: #430729 and 430829) |
|
Instruments
 |
| ● |
Centrifuge (for 50 mL tubes; ours is Beckman Allegra 6R centrifuge) |
| ● |
|
| ● |
Tube rotator (we use a Thermo Scientific Labquake Tube Rotator) |
|
| Methods |
|
1. |
Preparation of red blood cells (RBC) |
| 1) |
Collect ~10 mL of blood in heparined tubes. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 3) |
Remove the buffy coat as far as possible. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 4) |
Wash the red blood cells 3 times in PBS (spin between each wash). |
Comment 0
|

|
| 5) |
Dilute RBC at 8% in PBS-3% glutaraldehyde and rotate 1 h at RT. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 6) |
Wash 5 times in PBS-0,0025% NaN3 (spin between each wash). |
Comment 0
|

|
| 7) |
Resuspend at 3 to 4% in PBS-0,0025% NaN3. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 8) |
Store at 4ºC (good for ~3 months). |
Comment 0
|
|
|
|
2. |
Calibration of red blood cells |
| 2) |
Add RBC : 5 to 40 μL by well to the PBS. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 4) |
Incubate at 4ºC for 2 h.
Possible results: Tight button: Negative
Spread out RBC: Positive
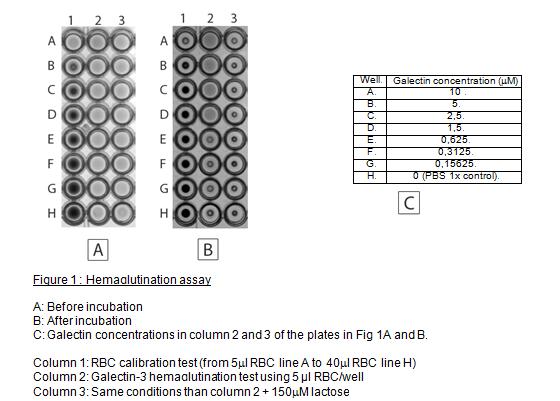
(see Fig. 1) |
Comment 0
|
|
|
|
3. |
|
| 1) |
Calculate your galectin concentration by Bradford assay. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 2) |
Put 10 μM of your galectin in 190 μL total volume (PBS) in well A. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 3) |
Put 95 μL PBS in wells B to H (line H is 95 μL PBS 1x only). |
Comment 0
|

|
| 4) |
Do a serial dilution (1:2) from well A to G. (you now have 95 μL of diluted galectin per well; line H is 95 μL PBS 1x only). |
Comment 0
|

|
| 5) |
Add 5 μL RBC per well and gently suspend RBC by using the pipette. |
Comment 0
|

|
|
|
| Notes | Calibration of red blood cells
Objective: To know how much red blood cells to put in each well; avoiding false positives
- Note 1: Fig. 1B shows that the most optimal volume of this RBC preparation is 5 μL in this preparation as we obtained a clear tight button with this amount of RBC and expected galectin-induced hemagglutination activity, which is inhibited by the antagonist, lactose.
- Note 2: Results should be clear after 30 min, but it can be clearer after 2 h at 4°C.
Assay
We usually use 5 μL of RBC in each well. The volumes in the next section are calculated for this amount of RBC. If you need to use more or less than 5 μL of RBC, adjust the others volumes to obtain 100 μL final in each well.
- Note 1: Normally galectin-3 induces hemagglutination above 1 μM.
- Note 2: The lactose is an inhibitor of the lectin activity of the galectins. It competes with others possible ligands. At the concentration of 150μM, lactose inhibit completely hemaglutination induced by the galectin-3 (Fig. 1B, column 3).
|
| Figure & Legends |
Figure & Legends 
|
| Copyrights |
 Attribution-Non-Commercial Share Alike Attribution-Non-Commercial Share Alike
This work is released underCreative Commons licenses
|
| Date of registration:2014-07-31 09:34:38 |
- Butler, W.T. (1963) Hemagglutination studies with formalinized erythrocytes. Effect of bis-diazo-benzidine and tannic acid treatment on sensitization by soluble antigen. J. Immunol. 90, 663–671 [PMID : 14053285]
|
This work is licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-Non-Commercial Share Alike. Please include the following citation
How to Cite this Work in an article:
St-Pierre, Guillaume,
Milot, Valérie,
Sato, Sachiko,
(2014). GlycoPOD https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD.
Web.24,4,2024 .
How to Cite this Work in Website:
St-Pierre, Guillaume,
Milot, Valérie,
Sato, Sachiko,
(2014).
Hemagglutination assay.
Retrieved 24,4,2024 ,
from https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD/protocolShow.action?nodeId=t135.
html source
St-Pierre, Guillaume,
Milot, Valérie,
Sato, Sachiko,
(2014).
<b>Hemagglutination assay</b>.
Retrieved 4 24,2024 ,
from <a href="https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD/protocolShow.action?nodeId=t135" target="_blank">https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD/protocolShow.action?nodeId=t135</a>.
Including references that appeared in the References tab in your work is
much appreciated.
For those who wish to reuse the figures/tables, please contact JCGGDB
management office (jcggdb-ml@aist.go.jp).
|
|