Hyaluronan is a polysaccharide composed of repeating GlcNAcβ(1→4)-GlcAβ(1→3) disaccharide units and has a molecular mass ranging from 103 to 107 Da, depending on the tissue source and physiological conditions. Despite its apparently simple structure, hyaluronan exhibits multiple properties depending on its molecular size and its binding molecules. This polysaccharide regulates a variety of cell behaviors, such as cell adhesion, motility, growth, and differentiation as an extracellular matrix molecule. Its production in vertebrates is tightly regulated by three hyaluronan synthases, HAS1, HAS2 and HAS3. Sequence analysis has shown that all HAS proteins are composed of multiple membrane-spanning regions and large cytoplasmic loops possessing catalytic motifs. Each HAS isoform differs in such enzymatic properties as stability, substrate kinetics, and rate of sugar chain elongation, and may thus synthesize distinct forms of hyaluronan. |
| Category | Glycosyltransferases & related proteins |
| Protocol Name | Enzyme assay of hyaluronan synthase |
Authors
 |
Itano, Naoki
Department of Molecular Biosciences, Faculty of Life Sciences, Kyoto Sangyo University
|
| KeyWords |
|
Reagents
 |
| ● |
HAS reaction buffer: 25 mM Hepes-NaOH buffer, pH 7.1, 5 mM dithiothreitol, 15 mM MgCl2, 0.1 mM UDP-GlcNAc, 2 μM UDP-GlcA, and 2 μCi of UDP-[14C]GlcA (NEN/PerkinELmer, Waltham, MA) |
| ● |
Lysis buffer: 10 mM Hepes-NaOH buffer, pH 7.1, 0.5 mM dithiothreitol, 0.25 M sucrose |
| ● |
|
| ● |
Streptomyces hyaluronidase (Seikagaku Corp., Tokyo, Japan) |
| ● |
|
| ● |
TAE buffer: 40 mM Tris-HCl buffer, pH 7.9, 5 mM sodium acetate, 0.8 mM sodium EDTA |
| ● |
Staining solution: 0.005% Stains-All in 50% ethanol |
|
Instruments
 |
| ● |
Paper chromatography chamber |
| ● |
|
| ● |
Centrifuge and ultracentrifuge |
| ● |
Horizontal electrophoresis apparatus |
|
| Methods |
|
1. |
Preparation of membrane fraction |
| 1) |
Wash cultured cells three times with PBS (−) and harvest them by scraping. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 2) |
Centrifuge at 1,200 rpm for 5 min at 4˚C. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 3) |
Suspend the cell pellets in 1 mL of ice-chilled lysis buffer. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 4) |
Disrupt the cells by sonication for 1 min with a sonicator. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 5) |
Ultracentrifuge the cell lysate at 105,000 × g at 4˚C for 1 h to give high-speed pellets. |
Comment 0
|
|
|
|
2. |
|
| 1) |
Suspend the high-speed pellets with 0.2 mL of HAS reaction buffer. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 3) |
Further incubate aliquot (0.1 mL) of the sample with 1 TRU of Streptomyces hyaluronidase. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 4) |
Stop the reaction by addition of SDS to 2% (w/v). |
Comment 0
|

|
| 5) |
Spot the mixtures onto Whatman no. 3MM paper. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 6) |
Transfer the paper to a paper chromatography chamber. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 7) |
Perform descending paper chromatography in the solvent containing 1 M ammonium acetate (pH 5.5) and ethanol (65:35 v/v) for three days. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 8) |
Cut the origin containing the synthesized polymers from the paper. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 9) |
Determine the amount of radioactivity in the high molecular mass hyaluronan by liquid scintillation counting. |
Comment 0
|
|
|
|
3. |
Determination of hyaluronan size |
| 1) |
Incubate the synthesized hyaluronan at 37˚C for 1 h with or without 1 TRU of Streptomyces hyaluronidase. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 2) |
Mix 14 μL of the hyaluronan sample with 2 μL of 2 M sucrose/TAE buffer. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 3) |
Prepare a 0.5% (w/v) agarose gel (20 × 20 cm) by melting 0.6 g agarose in 108 mL of TAE buffer. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 4) |
Transfer the gel plate to the horizontal electrophoresis apparatus. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 5) |
Apply the sample to each lane of the agarose gel. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 6) |
Electrophorese at 2V/cm for 10 h in TAE buffer at room temperature. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 7) |
Stain the gel for 4 h under light-protective cover at room temperature in a staining solution. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 8) |
Destain the gel in water and then dry. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 9) |
Photograph and detect the radioactive HA on x-ray film. |
Comment 0
|
|
|
| Notes | Hyaluronan with average mass (21.3, 14.1, 9.9, 6.4, 4.6, and 1.0 × 105 Da) were used to estimate molecular sizes of the products. |
| Figure & Legends |
Figure & Legends 
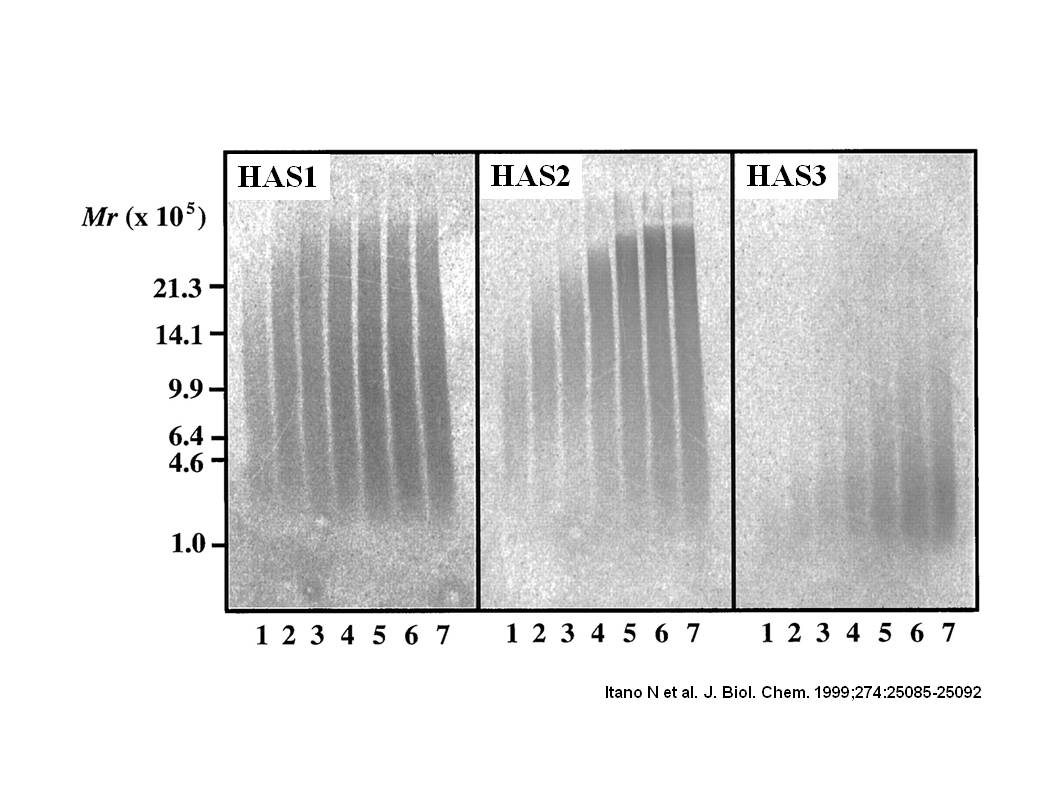
Fig. 1. Size distribution of hyaluronan synthesized by mammalian HAS proteins.
The membrane fractions isolated from HAS transfectants were incubated for the indicated times with UDP-sugar precursors at saturating concentrations in the presence of UDP-[14C]GlcA. Radioactive hyaluronan samples were separated on one gel by 0.5% agarose gel electrophoresis. The incubation times were 10 min (lane 1), 20 min (lane 2), 30 min (lane 3), 1 h (lane 4), 2 h (lane 5), 4 h (lane 6), and 8 h (lane 7).
This figure was originally published in J Biol Chem. Itano N. et al. "Three isoforms of mammalian hyaluronan synthases have distinct enzymatic properties." 1999, 274(35):25085–92. © the American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology. |
| Copyrights |
 Attribution-Non-Commercial Share Alike Attribution-Non-Commercial Share Alike
This work is released underCreative Commons licenses
|
| Date of registration:2017-02-16 16:34:15 |
- Itano, N. (2008) Hyaluronan synthase assay. Experimental Glycoscience (Eds. N. Taniguchi, A., Suzuki, Y. Ito, H. Narimatsu, T. Kawasaki, S. Hase) Springer pp.70–71.
- Itano, N., Sawai, T., Yoshida, M., Lenas, P., Yamada, Y., Imagawa, M., Shinomura, T., Hamaguchi, M., Yoshida, Y., Ohnuki, Y., Miyauchi, S., Spicer, AP., McDonald, JA., and Kimata K. (1999) Three isoforms of mammalian hyaluronan synthases have distinct enzymatic properties. J Biol Chem. 274, 25085–25092 [PMID : 10455188]
- Lee, HG., and Cowman, MK. (1994) An agarose gel electrophoretic method for analysis of hyaluronan molecular weight distribution. Anal Biochem. 219, 278–287 [PMID : 8080084]
|
This work is licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-Non-Commercial Share Alike. Please include the following citation
How to Cite this Work in an article:
Itano, Naoki,
(2017). GlycoPOD https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD.
Web.19,4,2024 .
How to Cite this Work in Website:
Itano, Naoki,
(2017).
Enzyme assay of hyaluronan synthase.
Retrieved 19,4,2024 ,
from https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD/protocolShow.action?nodeId=t126.
html source
Itano, Naoki,
(2017).
<b>Enzyme assay of hyaluronan synthase</b>.
Retrieved 4 19,2024 ,
from <a href="https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD/protocolShow.action?nodeId=t126" target="_blank">https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD/protocolShow.action?nodeId=t126</a>.
Including references that appeared in the References tab in your work is
much appreciated.
For those who wish to reuse the figures/tables, please contact JCGGDB
management office (jcggdb-ml@aist.go.jp).
|
|