ENGase (endo-β-N-acetylglucosaminidase (EC 3.2.1.96)) is an endoglycosidase that hydrolyzes the β1,4-glycosidic bond in the N,N’-diacetylchitobiose core of N-glycans. The activity of cytoplasmic ENGase activity was described in various animal cells, and the gene encoding this enzyme was identified [Kato, et al., Glycobiology 2002; Suzuki, et al., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2002]. This enzyme activity was known to be involved in the catabolism of free oligosaccharides accumulated in the cytosol [Katoh, et al., Trends Glycosci. Glycotechnol. 2009; Suzuki, Trends Glycosci. Glycotechnol., 2009]. |
| Category | Biosynthesis & Metabolism |
| Protocol Name | Assay for cytoplasmic ENGase |
Authors
 |
Suzuki, Tadashi
Glycometabolome Team, RIKEN Global Research Cluster
|
| KeyWords |
|
Reagents
 |
| ● |
|
| ● |
|
| ● |
1 M Tris-HCl buffer (pH 7.5/8.0) |
| ● |
|
| ● |
0.5 M EDTA (pH adjusted with 1 N NaOH to 8.0) |
| ● |
AESMF (Pefabloc SC: Roche Applied Science, Penzberg, Germany) |
| ● |
CompleteTM protease inhibitor cocktails (Roche Applied Science) |
| ● |
200 mM Mes-NaOH buffer (pH 6.0) |
| ● |
|
| ● |
Man9GlcNAc2-PA (from Takara Bio Inc., Otsu, Japan: 4120) |
| ● |
0.1 M Ammonium acetate buffer (pH 4.0) (buffer A) |
| ● |
0.1 M Ammonium acetate buffer (pH 4.0)/0.5% n-butanol (buffer B) |
|
Instruments
 |
| ● |
|
| ● |
|
| ● |
|
| ● |
|
| ● |
HPLC with a fluorescence detector |
|
| Methods |
|
1. |
Preparation of Cytoplasmic fraction for enzyme source |
| 1) |
Culture cells of your interest. Collect cells. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 2) |
Perform all the subsequent procedures either on ice or at 4°C. Suspend cells at a density of 5 × 107 cells/mL in 10 mM Tris-HCl buffer (pH 7.5)/1 mM EDTA/250 mM sucrose/1 mM DTT with various protease inhibitors (1 × completeTM protease inhibitor cocktail/1 mM AEBSF (Pefabloc SC)). |
Comment 0
|

|
| 3) |
Homogenize cells using Potter-Elvehjem homogenizer or equivalent. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 4) |
Clear the solution first with regular centrifuge at 14,000 rpm for 10 min |
Comment 0
|

|
| 6) |
Centrifuge the sup further using ultracentrifuge at 100,000 × g for 1 h. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 7) |
Soluble (cytosol) fraction thus obtained can be used for ENGase assay. For later use, the sample can be aliquoted, stored at −80°C. Avoid repeated freeze-thawing. |
Comment 0
|
|
|
|
2. |
Assay for ENGase assay [Li et al, Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2008] |
| 1) |
Mix 1 mL of the cytosol fraction with 3 μL of 200 mM Mes-NaOH buffer (pH 6.0) and start the reaction by adding 1 μL of the substrate (Man9GlcNAc2-PA; 2 pmol) to the solution. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 2) |
Incubate at 37°C for 6 h (incubation time has to be optimized for your enzyme source). |
Comment 0
|

|
| 3) |
Stop the reaction by heating sample at 95°C for 5 min. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 4) |
Add 1.5 volume of ethanol (final concentration; 60%) to the sample, and centrifuge at 14,000 rpm for 15 min at 4°C. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 6) |
Evaporate the sup to dryness using centrifugal evaporator. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 7) |
Dissolve the sample with 5 mL of distilled water for HPLC analysis. |
Comment 0
|
|
|
|
3. |
|
| 1) |
Prepare buffer A (0.1 M ammonium acetate buffer, pH 4.0) and buffer B (0.1 M ammonium acetate buffer, pH 4.0/0.5 % n-butanol). |
Comment 0
|

|
| 2) |
Elution conditions are as follows:
Column: ODS column (TSK gel ODS-80-TM; 7.5 × 75 mm; Tosoh Corp., Tokyo, Japan)
Column temperature: 30°C
Flow rate: 1.0 mL/min
Elution condition: linear gradient of 5% (0.025% n-butanol) to 100% (0.5% n-butanol) buffer B for 55 min. Wash the column with the starting buffer (5% B solution) between the analyses.
Fluorescence detection: λex=320 nm; λex=400 nm. |
Comment 0
|
|
|
| Notes | Precaution has to be taken if samples with high a-mannosidase activity are applied. It won’t be a concern for most of the mammalian-derived tissues/cells. |
| Figure & Legends |
Figure & Legends 
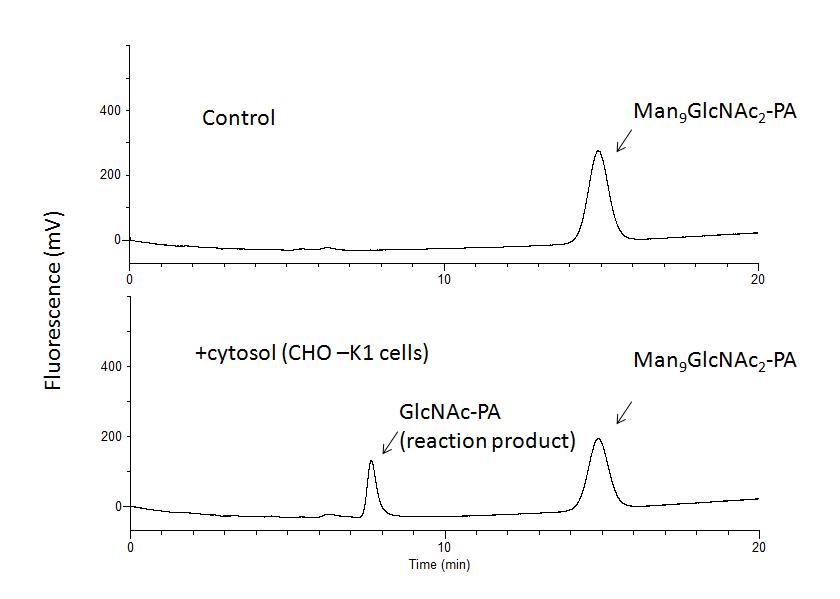
Fig. 1.
For enzyme source, CHO-K1 cells were used and incubation was carried out at 30°C for 6 h. Similar results can be obtained for other mammalian-derived culture cells. GL Sciences HPLC system (PU611 double pumps/CO630 column over) with a fluorescence detector (LaChrom, Hitachi High-Technologies, Tokyo, Japan) was used. |
| Copyrights |
 Attribution-Non-Commercial Share Alike Attribution-Non-Commercial Share Alike
This work is released underCreative Commons licenses
|
| Date of registration:2014-12-16 09:32:34 |
- Kato, T., Fujita, K., Takeuchi, M., Kobayashi, K., Natsuka, S., Ikura, K., Kumagai, H., and Yamamoto, K. (2002) Identification of an endo-β-N-acetylglucosaminidase gene in Caenorhabditis elegans and its expression in Escherichia coli. Glycobiology 12, 581–587 [PMID : 12244070]
- Katoh, T., Ashida, H., and Yamamoto, K. (2009) Generation and Metabolism of Cytosolic Free Oligosaccharides in Caenorhabditis elegans. Trends Glycosci. Glycotechnol. 21, 163–177 [PMID : not available]
- Suzuki,T., Yano, K., Sugimoto, S., Kitajima, K., Lennarz, W.J., Inoue, S., Inoue, Y., and Emori, Y. (2002) Endo-β-N-acetylglucosaminidase, an enzyme involved in processing of free oligosaccharides in the cytosol. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 99, 9691–9696 [PMID : 12114544]
- Suzuki, T. (2009) Introduction to "Glycometabolome". Trends Glycosci. Glycotechnol. 21, 219–227 [PMID : not available]
- Li, B., Takegawa, K., Suzuki, T., Yamamoto, K., and Wang, L.X. (2008) Synthesis and inhibitory activity of oligosaccharide thiazolines as a class of mechanism-based inhibitors for endo-β-N-acetylglucosaminidase. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 16, 4670–4675 [PMID : 18304822]
|
This work is licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-Non-Commercial Share Alike. Please include the following citation
How to Cite this Work in an article:
Suzuki, Tadashi,
(2014). GlycoPOD https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD.
Web.23,4,2024 .
How to Cite this Work in Website:
Suzuki, Tadashi,
(2014).
Assay for cytoplasmic ENGase.
Retrieved 23,4,2024 ,
from https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD/protocolShow.action?nodeId=t125.
html source
Suzuki, Tadashi,
(2014).
<b>Assay for cytoplasmic ENGase</b>.
Retrieved 4 23,2024 ,
from <a href="https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD/protocolShow.action?nodeId=t125" target="_blank">https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD/protocolShow.action?nodeId=t125</a>.
Including references that appeared in the References tab in your work is
much appreciated.
For those who wish to reuse the figures/tables, please contact JCGGDB
management office (jcggdb-ml@aist.go.jp).
|
|