The introducing method of a fluorescent residue of small molecular weight into the reducing end came to be used worldwide as simplicity and a high sensitivity detection method of the oligosaccharides. Structural analysis of the labeled oligosaccharides is easily determined with comparison of elution positions on reversed phase, size-fractionation, and anion-exchange HPLCs. |
| Category | Isolation & structural analysis of glycans |
| Protocol Name | Fluorescent labelling of glycans and HPLC analysis |
Authors
 |
Nakakita, Shin-ichi
*
Department of Functional Glycomics, Life Science Research Center, Kagawa University
Natsuka, Shunji
Department of Biology, Faculty of Science, Niigata University
*To whom correspondence should be addressed.
|
| KeyWords |
|
Reagents
 |
| ● |
2-aminopyridine (Nacalai Tesque, Inc., Kyoto, Japan) |
| ● |
dimethylamine-borane (Wako Pure Chemical Industries Ltd., Osaka, Japan) |
| ● |
acetic acid (Wako Pure Chemical Industries Ltd.) |
| ● |
25% ammonia solution (Wako Pure Chemical Industries Ltd.) |
| ● |
1-butanol (Wako Pure Chemical Industries Ltd.) |
| ● |
acetonitrile (Wako Pure Chemical Industries Ltd.) |
| ● |
chloroform (Wako Pure Chemical Industries Ltd.) |
| ● |
phenol (Wako Pure Chemical Industries Ltd.) |
|
Instruments
 |
| ● |
C18 Sep-Pak cartridge (Waters Corp., Milford, MA) |
| ● |
HPLC connected to fluorescence detector (Waters Corp.) |
| ● |
Speed Vac Concentrator (Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., Waltham, MA) |
| ● |
Block incubator (Astec Co., Ltd., Fukuoka, Japan) |
| ● |
Mono-Q 5 × 50 mm (GE Healthcare, Little Chalfont, UK) |
| ● |
Cosmosil 5C18P 4.6 × 150 mm (Nacalai Tesque, Inc.) |
| ● |
Shodex Asahipak NH2P-50 4.6 × 50 mm (Showa Denko K.K., Tokyo, Japan) |
|
| Methods |
|
1. |
Fluorescent labelling of glycan and HPLC analysis |
| 1) |
Infuse saccharide solution in conical micro tube. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 3) |
Add 0.02 mL of the coupling reagent solution (552 mg of 2-aminopyridine dissolved in 0.2 mL acetic acid). |
Comment 0
|

|
| 4) |
Mix coupling reagent solution and sample. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 6) |
Add 0.07 mL of the reducing reagent solution (200 mg of borane-dimethylamine complex dissolved in 0.08 mL of acetic acid and 0.05 mL of water). |
Comment 0
|

|
| 7) |
Mix reducing reagent solution and sample. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 9) |
Mix 0.09 mL water and 0.09 mL phenol/chloroform solution. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 14) |
Analyze by HPLCs(Reversed-phase, size-fractionation, anion-exchange). |
Comment 1
|
|
|
| Figure & Legends |
Figure & Legends 
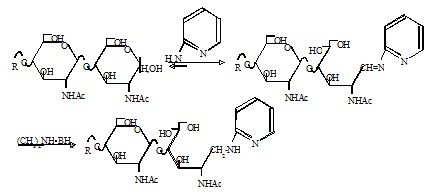
Fig. 1. Scheme of pyridylamination
This figure was originally published in "Mirai wo Hiraku Tousa Kagaku" edited by Nagai K, Kawasaki T. Kinpodo. 2005, pp.10–11 (Section 1.6, Nakakita S.).

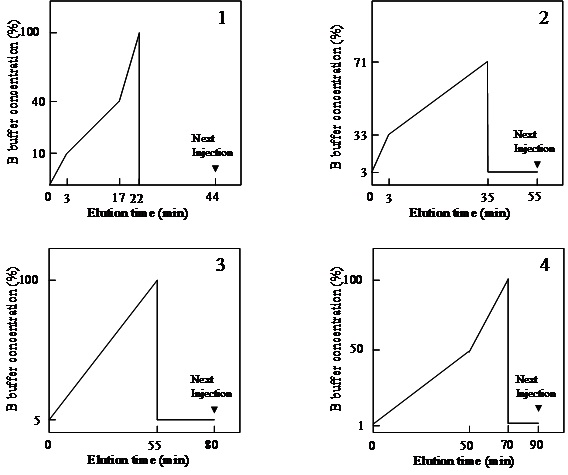
Fig. 2. Gradient programs of HPLC using of PA-oligosaccharide analysis
1. Anion exchange HPLC (MonoQ), A buffer: ammonia solution (pH 9.0); B buffer: 500 mM ammonium-acetate buffer (pH 9.0), flow rate 1 mL/min, 25˚C.
2. Size-fractionation HPLC (Shodex Asahipak NH2P-50), 50 mM ammonium-acetate buffer (pH 7.0) in 93% acetonitrile; B buffer: 50 mM ammonium-acetate buffer (pH 7.0) in 20% acetonitrile, , flow rate 0.6 mL/min, 25˚C.
3. Reversed-phase HPLC of N-glycan mode (Cosmosil 5C18P,), 100 mM ammonium-acetate buffer (pH 4.0); B buffer: 100 mM ammonium-acetate buffer (pH 4.0) in 0.5% 1-butanol, flow rate 1.5 mL/min, 25˚C.
4. Reversed-phase HPLC of O-glycan mode (Cosmosil 5C18P), 100 mM ammonium-acetate buffer (pH 6.0); B buffer: 100 mM ammonium-acetate buffer (pH 6.0) in 1% 1-butanol, flow rate 1.5 mL/min, 25˚C. |
| Copyrights |
 Attribution-Non-Commercial Share Alike Attribution-Non-Commercial Share Alike
This work is released underCreative Commons licenses
|
| Date of registration:2015-05-08 15:03:27 |
- Hase, S., Ikenaka, T., and Matsushima, Y. (1978) Structure analyses of oligosaccharides by tagging of the reducing end sugars with a fluorescent compound. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 85, 257–263 [PMID : 743278]
- Yanagida, K., Natsuka, S., and Hase, S. (1999) A pyridylamination method aimed at automatic oligosaccharide analysis of N-linked sugar chains. Anal Biochem 274, 229–234 [PMID : 10527520]
- Natsuka, S., Adachi, J., and Kawaguchi, M., et al. (2002) Method for purification of fluorescence-labeled oligosaccharides by pyridylamination. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 66, 1174–1175 [PMID : 12092840]
|
This work is licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-Non-Commercial Share Alike. Please include the following citation
How to Cite this Work in an article:
Nakakita, Shin-ichi,
Natsuka, Shunji,
(2015). GlycoPOD https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD.
Web.26,4,2024 .
How to Cite this Work in Website:
Nakakita, Shin-ichi,
Natsuka, Shunji,
(2015).
Fluorescent labelling of glycans and HPLC analysis.
Retrieved 26,4,2024 ,
from https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD/protocolShow.action?nodeId=t12.
html source
Nakakita, Shin-ichi,
Natsuka, Shunji,
(2015).
<b>Fluorescent labelling of glycans and HPLC analysis</b>.
Retrieved 4 26,2024 ,
from <a href="https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD/protocolShow.action?nodeId=t12" target="_blank">https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD/protocolShow.action?nodeId=t12</a>.
Including references that appeared in the References tab in your work is
much appreciated.
For those who wish to reuse the figures/tables, please contact JCGGDB
management office (jcggdb-ml@aist.go.jp).
|
|