Siglec-7 (also termed p75/AIRM1) is a member of the sialic acid-binding immunoglobulin-like lectins (Siglecs) and is expressed mainly on human NK cells and monocytes. Siglec-7 preferentially binds unique sialoglycans, α2,8disialyl residue (NeuAcα2,8NeuAcα2,3Gal) and branched α2,6sialyl residue (Galβ1,3[NeuAcα2,6]GlcNAc), as potential ligands. Here, the preparation of the recombinant extracellular domain of Siglec-7 fused to human Fc and its application for cell staining are described. |
| Category | Sugar binding proteins |
| Protocol Name | Recombinant sugar binding proteins and their functional analysis: Siglec-7 |
Authors
 |
Yamaji, Toshiyuki
*
Department of Biochemistry and Cell Biology, National Institute of Infectious Diseases
Hashimoto, Yasuhiro
Department of Biochemistry, School of Medicine, Fukushima Medical University
*To whom correspondence should be addressed.
|
| KeyWords |
|
Reagents
 |
| ● |
Expression vectors that contain Siglec-7 (wild type)-Fc and Siglec-7 (R124K mutant)-Fc.: Expression plasmids, pCXN2-Siglec-7-Fc and pCXN2-R124K mutant-Fc, which lose binding ability to sialic acids, were prepared previously (Miyazaki K et al. (2004) Cancer Res., 64(13): 4498–4505). The human Fc used was derived from pEF-Fc vector constructed by Dr. Yoshihara (RIKEN BSI, Wako, Japan). |
| ● |
|
| ● |
Ham’s F-10 or F-12 10% fetal calf serum (FCS) |
| ● |
Geneticin (G418): for selection |
| ● |
HRP- and fluorescence (Alexa 488 etc.) -conjugated anti-human IgG: Alexa Fluor 488-labeled goat anti-human IgG (Invitrogen/Life Technologies, Inc., Carlsbad, CA) |
| ● |
ASF104 non-serum medium (Ajinomoto Healthy Supply, Inc., Tokyo, Japan) |
| ● |
|
| ● |
Protein G Sepharose 4 Fast Flow (GE Healthcare, Little Chalfont, UK) |
| ● |
Disposable polypropylene column |
| ● |
Millex-HV 0.45um-pore filter unit (Merck Millipore, Billerica, MA) |
| ● |
Phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) |
| ● |
|
| ● |
|
| ● |
Centricon (Merck Millipore): Ultracel YM-30 etc. |
| ● |
Bovine serum albumin (BSA) |
|
Instruments
 |
| ● |
|
| ● |
Fluorescence flow cytometer |
|
| Methods |
|
1. |
Preparation of recombinant Siglec-7-Fc and its mutant (R124K)-Fc fusion proteins (see Note 1) |
| 1) |
Transfect plasmids containing Siglec-7-Fc and R124K mutant-Fc cDNAs into CHO cells and culture for 2 days. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 2) |
Dilute the transfected cells into 96-well culture plates and add 800 μg/mL G418 to prepare stable transfectants. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 3) |
Perform dot plot analysis to select the clone that secretes the recombinant proteins at the highest level (use anti-Siglec-7 or HRP-anti human IgG). |
Comment 0
|

|
| 4) |
Adapt the cells in ASF104 non-serum medium. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 5) |
Culture the sub-confluent cells in ASF medium with 5 mM sodium butylate for 1 week. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 6) |
Collect the medium and filter with a 0.45 μm-pore filter unit to remove debris. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 7) |
Add Protein G-Sepharose beads to the filtrate and rotate overnight at 4˚C. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 8) |
Pack the beads in an empty column and wash with at least 5 column volumes of cold PBS. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 9) |
Elute the bound proteins with cold 0.1 M Glycine-HCl, pH 2.8, and immediately neutralize with 1/10 volume of 1M Tris-HCl, pH 8.0. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 10) |
Replace the buffer with PBS or an appropriate buffer by Centricon. |
Comment 0
|
|
|
|
2. |
Binding of recombinant Siglec-7-Fc to the cell surface (see Note 2) |
| 1) |
Wash cells with 1% BSA/PBS once by centrifugation (2000 rpm for 5 min at 4˚C). |
Comment 0
|

|
| 2) |
Incubate the cells with Siglec-7-Fc or R124K mutant-Fc (4–10 μg/mL in 1%BSA/PBS) for 40–60 min on ice. |
Comment 1
|

|
| 3) |
Centrifuge and wash with 1% BSA/PBS once. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 4) |
Incubate the cells with fluorescent (Alexa-488 etc.) anti-human IgG (4–10 μg/mL in 1%BSA/PBS) for 40–60 min on ice. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 5) |
Wash with 1% BSA/PBS once and re-suspend the cells in the buffer. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 6) |
Analyze with a fluorescence flow cytometer. |
Comment 0
|
|
|
| Notes |
- About 1mg recombinant Siglec-7-Fc proteins was prepared from 150 mL culture supernatant.
- As another method, the preincubated complex of recombinant Siglec-7-Fc and anti-human IgG can also be used for cell staining (Miyazaki K et al. (2004) Cancer Res., 64(13): 4498–4505). The binding amount of Siglec-7-Fc may vary with the staining protocol because the binding of Siglec-7 is affected by its multi-valency. Note that the binding of recombinant Siglec-7-Fc to the cell surface does not mean that the cells express functional Siglec-7 ligands, because the sugar-binding site of Siglec-7 on the cell surface is usually masked by endogenous sialoconjugates; therefore, as a next step, cell-cell interactions through Siglec-7 and ligand candidates should be examined.
|
| Discussion | Interpretation
Recombinant Siglec-7-Fc proteins bound to KST cells more than KV cells, suggesting that disialo-epitopes on O-glycans are more preferable ligand candidates for Siglec-7. These bindings are sialic-acid dependent because R124K mutant-Fc bound less to both cells. |
| Figure & Legends |
Figure & Legends 
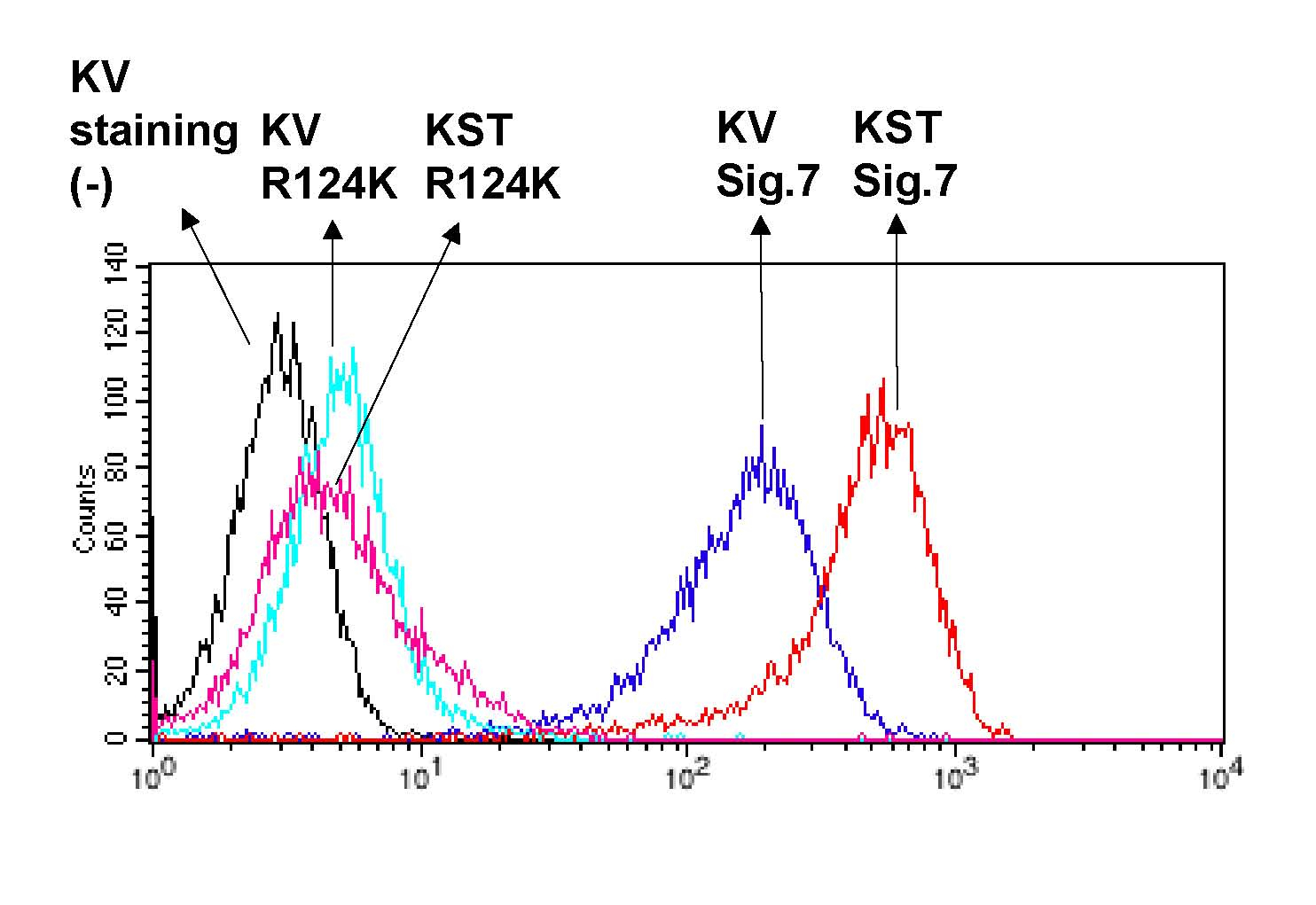
Fig. 1. Preferential binding of Siglec-7-Fc to disialo-glycans on the cell surface of K562 transfectants.
K562 transfectants that express disialo-epitopes on O-glycans by introducing ST8SiaVI sialyltransferase (named KST cells) and mock cells (KV cells) were stained with Siglec-7-Fc and R124K mutant-Fc as described above. Fluorescent intensity was measured by flow cytometry. |
| Copyrights |
 Attribution-Non-Commercial Share Alike Attribution-Non-Commercial Share Alike
This work is released underCreative Commons licenses
|
| Date of registration:2014-11-06 14:15:20 |
- Yamaji, T., Teranishi, T., Alphey, M.S., Crocker, P.R., and Hashimoto, Y. (2002) A small region of the natural killer cell receptor, Siglec-7, is responsible for its preferred binding to α2,8-disialyl and branched α2,6-sialyl residues: Comparison with Siglec-9. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 6324–6332 [PMID : 11741958]
- Miyazaki, K., Ohmori, K., Izawa, M., Koike, T., Kumamoto, K., Furukawa, K., Ando, T., Kiso, M., Yamaji, T., Hashimoto, Y., Suzuki, A., Yoshida, A., Takeuchi, M., and Kannagi, R. (2004) Loss of disialyl Lewis(a), the ligand for lymphocyte inhibitory receptor sialic acid-binding immunoglobulin-like lectin-7 (Siglec-7) associated with increased sialyl Lewis(a) expression on human colon cancers. Cancer Res. 64, 4498–4505 [PMID : 15231659]
|
This work is licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-Non-Commercial Share Alike. Please include the following citation
How to Cite this Work in an article:
Yamaji, Toshiyuki,
Hashimoto, Yasuhiro,
(2014). GlycoPOD https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD.
Web.18,4,2024 .
How to Cite this Work in Website:
Yamaji, Toshiyuki,
Hashimoto, Yasuhiro,
(2014).
Recombinant sugar binding proteins and their functional analysis: Siglec-7.
Retrieved 18,4,2024 ,
from https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD/protocolShow.action?nodeId=t107.
html source
Yamaji, Toshiyuki,
Hashimoto, Yasuhiro,
(2014).
<b>Recombinant sugar binding proteins and their functional analysis: Siglec-7</b>.
Retrieved 4 18,2024 ,
from <a href="https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD/protocolShow.action?nodeId=t107" target="_blank">https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD/protocolShow.action?nodeId=t107</a>.
Including references that appeared in the References tab in your work is
much appreciated.
For those who wish to reuse the figures/tables, please contact JCGGDB
management office (jcggdb-ml@aist.go.jp).
|
|