Efforts to make recombinant sugar binding proteins for their functional analysis and against infectious diseases as well as immunotherapies for cancer, autoimmune diseases and allergy have utilized a variety of heterologous expression systems, including viral and bacterial vectors, as well as DNA and RNA constructs. In this protocol, recombinant human mannan-binding protein (MBP) has been expressed in human hepatoma cells using a vaccinia virus expression system, and the recombinant protein has been demonstrated to be structurally and functionally similar to native human MBP. |
| Category | Sugar binding proteins |
| Protocol Name | Recombinant sugar binding proteins and their functional analysis: Mannan-binding protein |
Authors
 |
Yong Ma, Bruce
Research Center for Glycobiotechnology, Ritsumeikan University
|
| KeyWords |
|
Reagents
 |
| ● |
|
| ● |
A vaccinia virus transfer vector, pBSF-2-16. |
| ● |
Wild-type vaccinia virus strain Western Reserve (WR) and its isatin-b-thiosemicarbazone-(IBT)-dependent derivative. |
| ● |
RK13 (a rabbit kidney cell line, ATCC CCL 37), COS-7 (an African green monkey kidney cell line, ATCC CRL 1651), HLF (a human hepatoma cell line, JCRB 0405). |
| ● |
All materials for cell culture, virus proliferation, vector construction and transfection, virus purification and recombinant protein purification. |
| ● |
An affinity column of mannan-Sepharose 4B and a gel filtration chromatography with Sephacryl S-300. |
| ● |
Loading buffer: 20 mM imidazole, 1.25 M NaCl, 20 mM CaCl2, pH 7.8. |
| ● |
Elution buffer: 20 mM imidazole, 1.25 M NaCl, 4 mM EDTA, pH 7.8. |
| ● |
All chemicals for gel electrophoresis. |
| ● |
All reagents for MBP complement activation assay. |
| ● |
Gelatin-veronal buffer (GVB): 5 mM veronal buffer, pH 7.4, containing 0.145 M NaCl, 0.1% gelatin, 2 mM CaCl2, and 0.5 mM MgCl2. |
|
Instruments
 |
| ● |
Additional reagents and equipments for SDS-PAGE, immunodetection, affinity column purification, gel filtration chromatography and MBP complement activation assay. |
|
| Methods |
|
1. |
Construction of a vaccinia virus transfer vector and recombinant vaccinia virus. |
| 1) |
The human MBP cDNA is excised from the vector by digestion with SmaI and SacI and is subcloned into a vaccinia virus transfer vector, pBSF2-16. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 2) |
In the resultant transfer vector (pBSF2-16/MBP), the human MBP cDNA is located immediately downstream of the A-type inclusion body of a cowpox virus (ATI) hybrid promoter, and the human MBP cDNA flanked by the ATI hybrid promoter is interposed in the hemagglutinin (HA) gene, a selection marker for obtaining recombinant vaccinia viruses. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 3) |
5 μg of pBSF2-16/MBP and 10 mg of intact genomic DNA extracted from wild-type WR vaccinia virus are diluted in 1.5 mL of OptiMEM, and 30 μg of a cationic liposomal transfection reagent is diluted in 1.5 mL of OptiMEM. These two solutions are then mixed gently and incubated at room temperature for 45 min to yield the DNA-liposome complex. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 4) |
The cultured COS-7 cells (2.5 × 105 cells in a 10-cm dish) are infected with 2.5 × 104 PFU of IBT-dependent vaccinia virus for 1 h. The cells are exposed to the transfection solution for 8 h at 37˚C under 5% CO2. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 5) |
After 20 h incubation, the cells are harvested, and then the virus progeny is released by sonication. Monolayer culture of RK13 cells are infected with the progeny virus. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 6) |
The virus progeny obtained from HA-negative plaques inoculated onto monolayer culture of RK13 cells and further screened for the expression of human MBP by immunohistochemical staining with a monoclonal antibody specific for human MBP. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 7) |
The virus progeny obtained from MBP-positive plaqures is selected once more to purify the recombinant vaccinia virus. |
Comment 0
|
|
|
|
2. |
Expression and purification of recombinant human MBP. |
| 1) |
HLF cells at a density of 1 × 107 cells per 75 cm2 are infected with the recombinant vaccinia virus containing the human MBP cDNA at a multiplicity of infection (MOI) of 5, and then the infected cells are incubated for 48 h at 37˚C under 5% CO2. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 2) |
The culture supernatant of HLF cells is harvested and centrifuged to remove cell debris and viral particles. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 3) |
The resulting supernatant is mixed with a half volume 3 × loading buffer, filtered through a 0.45 μm filter, and then applied to a mannan-Sepharose 4B column that has been equilibrated with loading buffer. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 4) |
After washing the column with loading buffer, the bound recombinant proteins are eluted with elution buffer. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 5) |
The eluted fractions are pooled and concentrated. The purity of the recombinant MBP can be checked by SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions, and the degree of oligomerization is assessed by SDS-PAGE on a 3–10% gradient gel under nonreducing conditions. A typical yield of recombinant human MBP is 5 mg per liter of culture medium. |
Comment 0
|
|
|
|
3. |
Assay for complement activation activity of MBP by passive hemolysis. |
| 1) |
The centrifugation of sheep erythrocyte suspension is performed at 350 × g for 5 min at 4˚C, and the cell density of an erythrocyte suspension can be determined by measuring the absorbance at 541 nm after the erythrocyte suspension has been totally lysed with water. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 2) |
The sheep erythrocytes are washed with saline three times and are then resuspended in saline at 1:20. 1 mL of a 200 μg/mL mannan solution is mixed with 1 mL of a 0.5 mg/mL CrCl3 solution. The mixture is added to 2 mL of a 1 × 109 cells/mL erythrocyte suspension, followed by incubation for 5 min at room temperature with occasional mixing. The reaction is stopped by adding 3 mL of ice-cold GVB. The resulting erythrocytes coated with mannan (mannan-erythrocytes, ME) are washed with GVB three times and then resuspended at a density of 1 × 109 cells/mL. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 3) |
0.1 mL of the ME suspension prepared in the previous step and 0.4 mL of recombinant human MBP diluted with GVB are mixed and incubated with gentle shaking for sensitizing the ME with MBP. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 4) |
The ME suspension is then washed with ice-cold GVB and resuspended at a density of 1 × 109 cells/mL. Two volumes of CH50 of MBP-depleted guinea pig complement, 0.1 mL of the ME suspension sensitized with MBP, and GVB are mixed in a total volume of 1.5 mL on ice and are then incubated for 1 h at 37˚C. |
Comment 0
|

|
| 5) |
After the reaction mixture has been centrifuged, the absorbance at 541 nm of the supernatant is measured. Maximal lysis is obtained by the incubation of 0.1 mL of the ME suspension with 0.14 mL of water. The degree of specific lysis is expressed as a percentage of the maximal lysis. |
Comment 0
|
|
|
| Notes |
- Recombinant human MBPs have been produced in myeloma cells, COS cells, and CHO cells. However, these recombinant MBPs contain oligomers with fewer polypeptide chains than found in native MBP and exhibit less ability to active complement compared to native MBP. Vaccinia viruses are DNA viruses that infect almost all mammalian cells. The use of vaccinia virus as a vector to introduce cDNAs into mammalian cells has several useful advantages, including a relatively high level of protein synthesis, proper folding, disulfide bond formation, glycosylation, and other posttranslational modifications. Thus, a vaccinia virus expression system seems to be useful for the recombinant preparation of highly assembled macromolecules such as MBP.
- Recombinant human MBP produced in HLF cells with the vaccinia virus expression system exhibits several similarities to the native human MBP, as shown in Fig. 1, giving a ladder of bands of much higher molecular weights than 200,000 corresponding to higher oligomers of the structural subunit as major components on nonreducing SDS-PAGE and exhibiting an indistinguishable dose dependence of complement-activating ability from the native human MBP in the passive hemolysis test.
- The complement activation activity of MBP is assayed by passive hemolysis using mannan-coated sheep erythrocytes in the presence of complement. The binding of MBP to the surfaces of mannan-coated erythrocytes triggers the complement cascade, resulting in the formation of membrane attack complexes and cell lysis. The degree of lysis is determined by detecting the released hemoglobin colorimetrically. The complement activation activity of recombinant human MBP increases with the degree of oligomerization.
|
| Figure & Legends |
Figure & Legends 
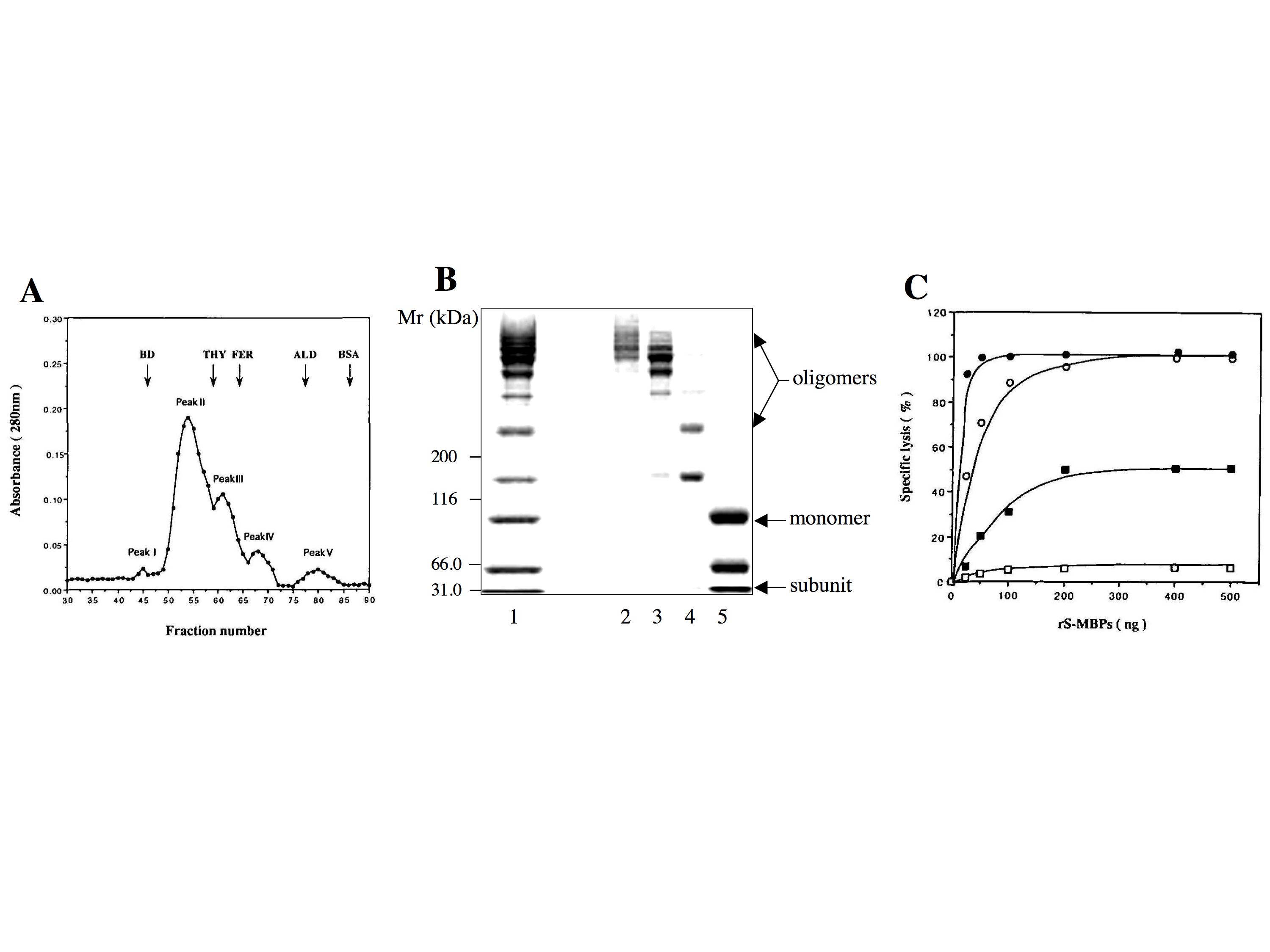
Fig. 1. Structural and functional expression of recombinant human MBP.
(A) Gel filtration chromatography of recombinant human MBP expressed in HLF hepatoma cells. Recombinant human MBP is analyzed by gel filtration chromatography on a Sephacryl S-300 HR 10/100 column. Elution positions of the marker proteins are indicated at the top, and numbers of the peaks are given above the peaks. BD, blue dextran (2000 kDa); THY, thyroglobulin (669 kDa); ferritin (440 kDa); ALD, aldolase (158 kDa); BSA, bovine serum albumin (67 kDa).
(B) SDS-PAGE of peaks II-V eluted from the Sephacryl S-300 HR 10/100 column. Samples of peaks II-V are electrophoresed on a 3-10% polyacrylamide gel under nonreducing conditions. Positions of the marker proteins are indicated at the left. Lane 1, recombinant human MBP before gel filtration; lane 2, peak II; lane 3, peak III; lane 4, peak IV; lane 5, peak V.
(C) Dose dependence of complement activation by peaks II-V eluted from the Sephacryl S-300 HR 10/100 column. Mannan-coated sheep erythrocytes are sensitized with 25-500 ng of peaks II-V and then lysed with complement (2CH50). ●, peak II; ○, peak III; ■, peak IV; □, peak V.
This figure was originally published in J Biochem. 122(4):810–8. 1997 "Functional expression of human mannan-binding proteins (MBPs) in human hepatoma cell lines infected by recombinant vaccinia virus: post-translational modification, molecular assembly, and differentiation of serum and liver MBP." Ma Y. et al. Oxford University Press. |
| Copyrights |
 Attribution-Non-Commercial Share Alike Attribution-Non-Commercial Share Alike
This work is released underCreative Commons licenses
|
| Date of registration:2015-02-03 13:44:50 |
- Ma, Y., Shida, H., and Kawasaki, T. (1997) Functional expression of human mannan-binding proteins (MBPs) in human hepatoma cell lines infected by recombinant vaccinia virus: post-translational modification, molecular assembly, and differentiation of serum and liver MBP. J. Biochem. 122, 810–818 [PMID : 9399586]
|
This work is licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-Non-Commercial Share Alike. Please include the following citation
How to Cite this Work in an article:
Yong Ma, Bruce,
(2015). GlycoPOD https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD.
Web.20,4,2024 .
How to Cite this Work in Website:
Yong Ma, Bruce,
(2015).
Recombinant sugar binding proteins and their functional analysis: Mannan-binding protein.
Retrieved 20,4,2024 ,
from https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD/protocolShow.action?nodeId=t102.
html source
Yong Ma, Bruce,
(2015).
<b>Recombinant sugar binding proteins and their functional analysis: Mannan-binding protein</b>.
Retrieved 4 20,2024 ,
from <a href="https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD/protocolShow.action?nodeId=t102" target="_blank">https://jcggdb.jp/GlycoPOD/protocolShow.action?nodeId=t102</a>.
Including references that appeared in the References tab in your work is
much appreciated.
For those who wish to reuse the figures/tables, please contact JCGGDB
management office (jcggdb-ml@aist.go.jp).
|
|